Simple Harmonic Motion & Damped Motion | lect.-01 | Classical Mechanics #physics #bsc
Summary
TLDRThe lecture focuses on simple harmonic motion and oscillatory motion in mechanics, which is the third unit of the course. It emphasizes the importance of understanding basic terms like periodic motion, oscillatory motion, and restoring forces. The lecture explains the concept of simple harmonic motion as oscillatory, periodic motion under a restoring force that is directly proportional to displacement. It also covers the damping forces that cause a decrease in the amplitude of oscillation over time, leading to a stop. The instructor discusses the derivation of differential equations for oscillatory motion and the calculation of relaxation time, which is crucial for understanding the behavior of oscillators in a medium.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lecture introduces the concept of simple harmonic motion and harmonic motion in the context of mechanics.
- 🎓 The course is structured with a focus on central forces, which are completely uploaded to the channel for students to access.
- 📚 The third unit of mechanics, part two, is being discussed, which includes limited topics and questions that appear in exams.
- 🔍 Basic terms such as periodic motion, oscillatory motion, and the difference between them are explained.
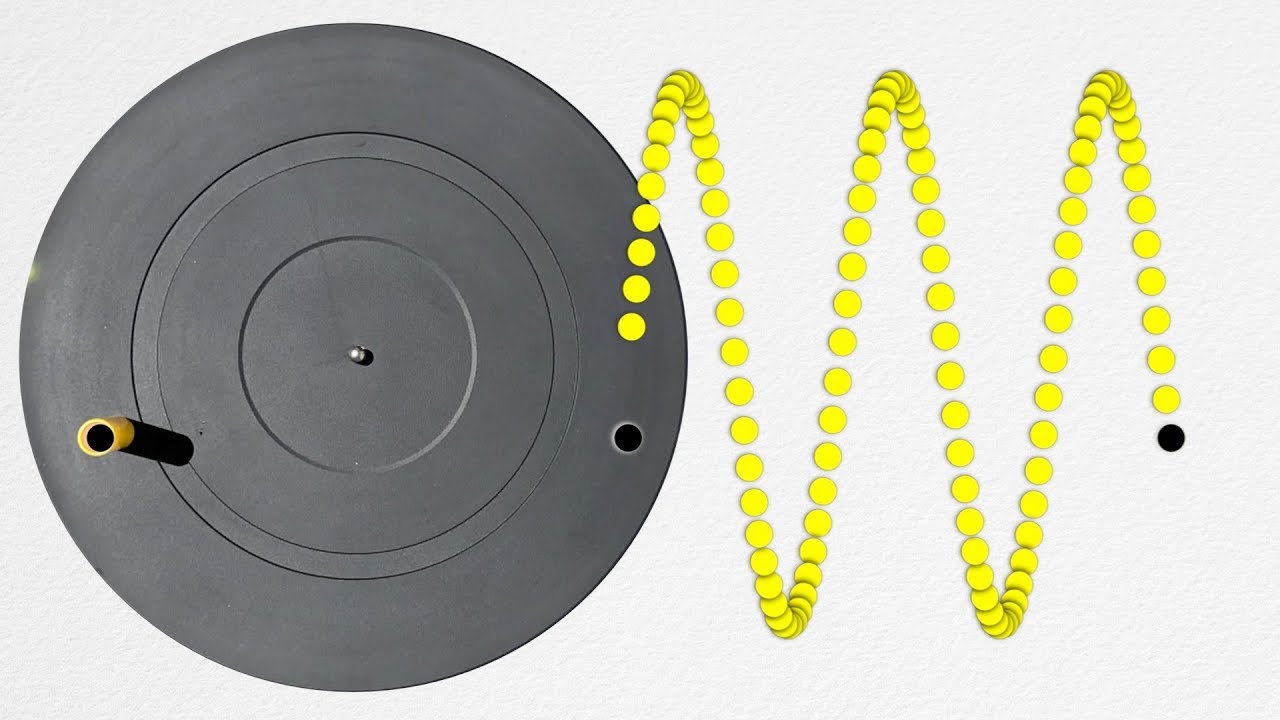
- 🌐 Periodic motion is defined as motion that repeats itself in a fixed time interval, while oscillatory motion involves a body or particle moving to and fro about a fixed point.
- 📈 The lecture emphasizes the importance of understanding the difference between periodic and oscillatory motion, especially for exam preparation.
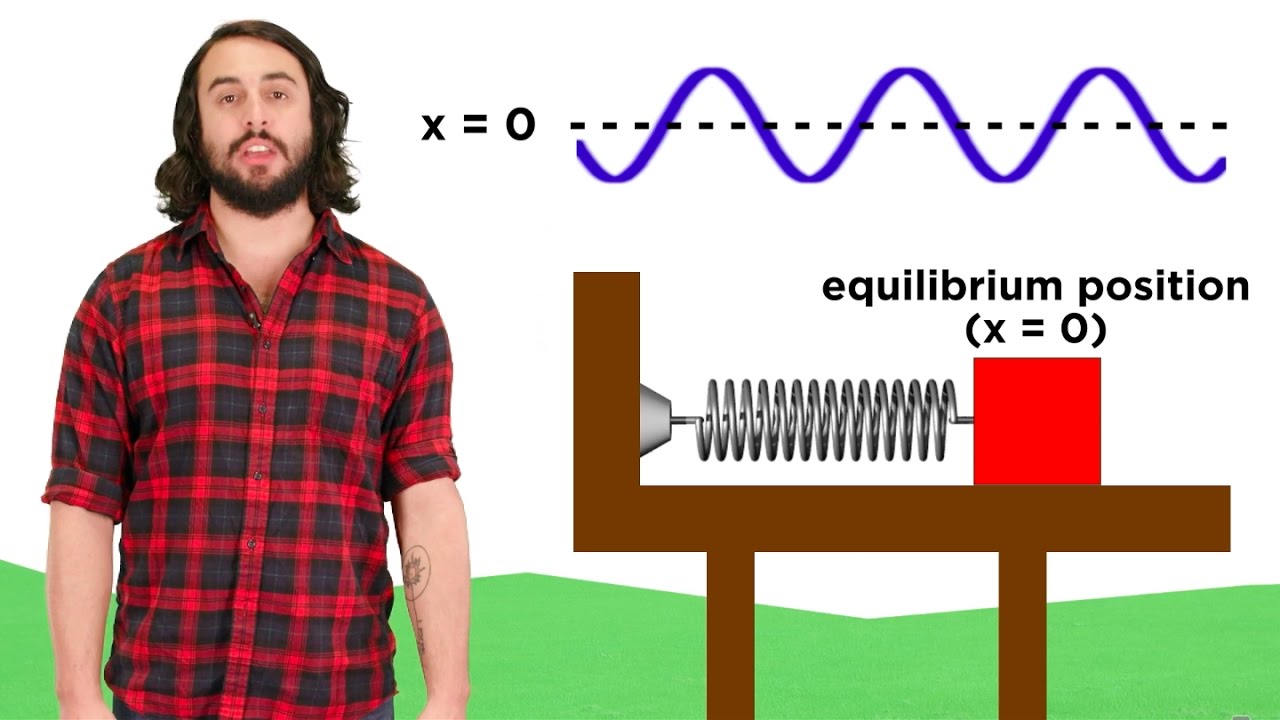
- 📊 Simple harmonic motion is a type of oscillatory motion where the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement and in the opposite direction.
- 📐 The formula for the restoring force in simple harmonic motion is discussed, involving the spring constant and displacement.
- 📖 The lecture covers the derivation of the differential equation for simple harmonic motion and how to calculate the period of the motion.
- 🔬 Damped forces and damped harmonic motion are introduced, explaining how the amplitude of an oscillator decreases over time due to frictional forces.
- ⏱️ The concept of relaxation time is introduced, which is the time it takes for the velocity of the oscillator to decrease to a certain fraction of its initial value.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is 'Simple Harmonic Motion', which is a part of the third unit in Mechanics.
What is the significance of the term 'Central Force' in the context of the lecture?
-In the context of the lecture, 'Central Force' refers to a force that acts along the line connecting the particle to the center of force, and it is completely applied on the channel.
What is the definition of 'Periodic Motion' as discussed in the lecture?
-Periodic Motion is defined as motion that repeats itself in a fixed time interval. This type of motion is important for understanding the behavior of particles and bodies in various physical systems.
What is an example of periodic motion mentioned in the lecture?
-An example of periodic motion mentioned in the lecture is the motion of electrons in the outer shells of atoms, which revolve in a periodic manner.
What is the difference between 'Oscillatory Motion' and 'Periodic Motion' as explained in the lecture?
-Oscillatory Motion refers to the back and forth movement of a body or particle around a fixed point, while Periodic Motion is a type of oscillatory motion that repeats itself in equal intervals of time.
What is 'Damped Motion' and how is it different from 'Simple Harmonic Motion'?
-Damped Motion is a type of oscillatory motion where the amplitude of the oscillator gradually decreases due to the resistive forces, eventually coming to a stop. It is different from Simple Harmonic Motion, where the oscillator moves with a constant amplitude under the influence of restoring forces.
What is the role of 'Restoring Force' in Simple Harmonic Motion?
-In Simple Harmonic Motion, the Restoring Force is the force that acts in the direction opposite to the displacement and is directly proportional to the displacement, causing the oscillator to return to its equilibrium position.
What is the formula for the restoring force in the context of Simple Harmonic Motion?
-The formula for the restoring force in Simple Harmonic Motion is F = -kx, where 'k' is the spring constant and 'x' is the displacement from the equilibrium position.
How is the differential equation for Simple Harmonic Motion derived in the lecture?
-The differential equation for Simple Harmonic Motion is derived by considering the restoring force (F = -kx) and applying Newton's second law (F = ma), which leads to the equation m(d^2x/dt^2) + kx = 0.
What is the significance of 'Damping Forces' in the context of oscillatory motion?
-Damping Forces are resistive forces that oppose the motion of an oscillator, causing the amplitude of oscillation to decrease over time. They are significant in understanding how oscillatory systems lose energy and eventually come to rest.
What is the 'Relaxation Time' in the context of damped motion, and how is it calculated?
-Relaxation Time is the time it takes for the velocity of the oscillator to decrease to a fraction of its initial value, typically to 1/e (approximately 36.8%) of its initial velocity. It is calculated using the formula t = m / (b * sqrt(m/k)), where 'm' is the mass, 'b' is the damping coefficient, and 'k' is the spring constant.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Movimento Harmônico Simples - Aula 02 (Força no MHS)
Simple Harmonic Motion: Hooke's Law

Simple Harmonic Motion | Formulae and Concept REVISION in 25 min | JEE Physics by Mohit Sir (IITKGP)

Dao động điều hòa: Chu kì. Tần số. Tần số góc. Vận tốc và gia tốc của vật dao động điều hòa

Periodic Motion | Definition/Examples

Comparing Simple Harmonic Motion(SHM) to Circular Motion - Demonstration
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
