Types of Pumps | All in One Guide to Industrial Pump Types
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the critical role of pumps in various industries, highlighting their importance in hydraulic systems. It defines pumps as devices that move and energize fluids, distinguishing between positive displacement pumps, which use volume changes to move fluid, and rotodynamic pumps, which convert velocity to pressure. The video explores different pump types, such as reciprocating, membrane, radial plunger, sliding vane, screw, lobe, gear, and centrifugal pumps, each with unique mechanisms and applications. It emphasizes the prevalence of centrifugal pumps in petroleum plants due to their simplicity and efficiency.
Takeaways
- 💧 Pumps are essential in various industries, including water management, automotive, and energy sectors.
- 🔧 A pump is a mechanical device that moves fluids by converting mechanical energy into pressure energy.
- 🔄 There are two main types of pumps: positive displacement pumps and rotodynamic pumps.
- 🌀 Positive displacement pumps move fluid by expanding or contracting a closed volume, like the human heart.
- 🏗️ Rotodynamic pumps, such as centrifugal and axial flow pumps, use rotating blades called impellers to transfer energy to the fluid.
- 🔩 Reciprocating or piston pumps operate on a crank and connecting rod mechanism, moving fluid through suction and discharge actions.
- 🛑 Membrane pumps use a flexible membrane to create suction and discharge, making them leak-proof and suitable for hazardous liquids.
- 🔄 Radial plunger pumps have plungers that move radially, creating high RPMs and pressures.
- 🔄 Sliding vane pumps use centrifugal force to push vanes against the casing, creating chambers for fluid movement.
- 🔄 Screw pumps use counter-rotating screw rotors to trap and compress fluid, moving it axially.
- 🔄 Low pumps, similar to gear pumps, are designed for self-priming and handling contaminated or solid-laden liquids.
- 🔄 Gear pumps are used for high-viscosity liquids, with gears rotating in the housing to move fluid.
- 🔄 Internal gear pumps have improved efficiency and quieter operation compared to classic gear pumps.
- 🌐 Centrifugal pumps are widely used due to their simplicity, high efficiency, and ease of maintenance.
- 🌐 Axial flow pumps are known for their high flow rates at low head, suitable for large-scale fluid circulation.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a pump?
-A pump's primary function is to move fluids from one place to another by means of mechanical action and to add energy to the fluid, thereby increasing its pressure.
What are the two main types of pumps mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of pumps mentioned are positive displacement pumps and rotodynamic pumps.
How does a positive displacement pump operate?
-In a positive displacement pump, fluid is directed into a closed volume and energy transfer to the liquid is accomplished by the movement of the boundary of the closed volume, causing it to expand or contract, which sucks in and squeezes out the liquid.
What is an example of a positive displacement pump?
-The human heart is an excellent example of a positive displacement pump.
How do rotodynamic pumps convert energy in the fluid?
-Rotodynamic pumps convert energy by using rotating blades, called impellers, which supply energy to the fluid and mostly convert velocity to pressure's energy.
What is the working principle of a reciprocating or piston pump?
-A reciprocating or piston pump works on the principle of a classic crank, connecting rod mechanism, creating a suction and discharge action as the piston moves back and forth within the cylinder.
Why are membrane pumps considered hermetic?
-Membrane pumps are considered hermetic because they do not leak, as the liquid cannot penetrate the seal, making them suitable for handling explosive, radioactive, or corrosive substances.
What is unique about the operation of a screw pump?
-Screw pumps operate using two counter-rotating screw rotors that are engineered to rotate towards each other, trapping and compressing the liquid, and moving it towards the exhaust in an axial direction.
How does a gear pump handle high viscosity liquids?
-A gear pump is used for high viscosity liquids as it fills tooth cavities on the suction side and presses the liquid away by repression on the discharge side, making it suitable for such applications.
What is the typical application of a mono pump?
-A mono pump is typically used for self-priming properties and is suitable for handling contaminated liquids or liquids with solid parts, such as yogurt from fruits.
Why are centrifugal pumps so prevalent in petroleum plants?
-Centrifugal pumps are prevalent in petroleum plants because of their design simplicity, high efficiencies, and ease of operation and maintenance.
What is the main advantage of axial flow pumps in terms of flow rate and head?
-Axial flow pumps provide a high flow rate at a low head, making them suitable for circulating fluids in power plants, sewage digesters, and evaporators.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
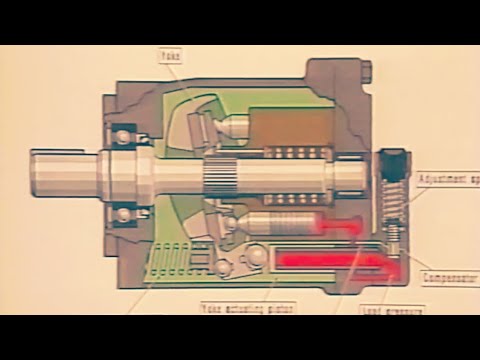
Hydraulic Training Series - Chapter 2 - Hydraulic Pumps
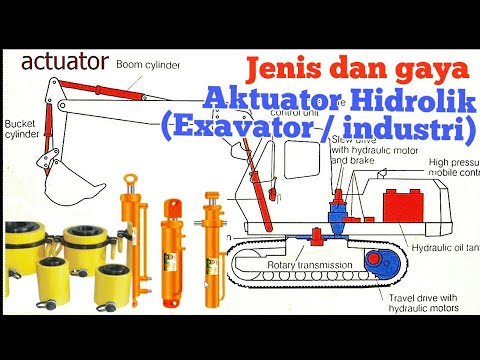
HLP10⚛Hidrolik Actuator merubah energi hidrolik jadi Mekanik sesuai gaya kerjanya

Hydraulic Pumps - Hydraulics - Airframes & Aircraft Systems #7

Hydraulic Training Series - Chapter 3 - Actuators
Video Presentasi Dasar Mekanika dan Hidrolika pada alat berat Kelompok 2

Hydraulic fluids: Types Properties & Applications
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
