POLARIDADE DAS MOLÉCULAS
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Marcos Enes dives into the concept of molecular polarity, explaining how to determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar. The tutorial covers essential steps, such as understanding molecular geometry and applying vector analysis. Enes provides practical examples like HCl, H2O, and CO2, offering tips on analyzing electronegativity and bond interactions. The video emphasizes the importance of three-dimensional molecular structures and includes insightful explanations of dipole moments. The session wraps up with useful tips for students to grasp these concepts more easily and stay engaged in chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video introduces Monster Chemistry, a platform offering a variety of learning materials including exercises, podcasts, and tutoring services by Professor Marcos Enes.
- 😀 To determine the polarity of molecules, it's essential to consider the three-dimensional geometry of the molecule, not just the flat structural formula.
- 😀 The central atom of a molecule is crucial for determining its geometry. It's usually the atom that is present in the smallest quantity and forms the most bonds.
- 😀 The VSBR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) model is used to determine the geometry of a molecule by considering the electron pairs around the central atom.
- 😀 The polarity of a molecule is determined through vector analysis, where the presence or absence of a resulting dipole moment helps classify it as polar or nonpolar.
- 😀 If the resulting dipole moment of a molecule equals zero, the molecule is nonpolar; if not, the molecule is polar.
- 😀 A polar molecule is one where the electronegative atoms create an unequal distribution of electrons, leading to a dipole moment.
- 😀 In molecules with polar covalent bonds, the vectors (representing electron pulls) may cancel each other out or combine to produce a net dipole moment.
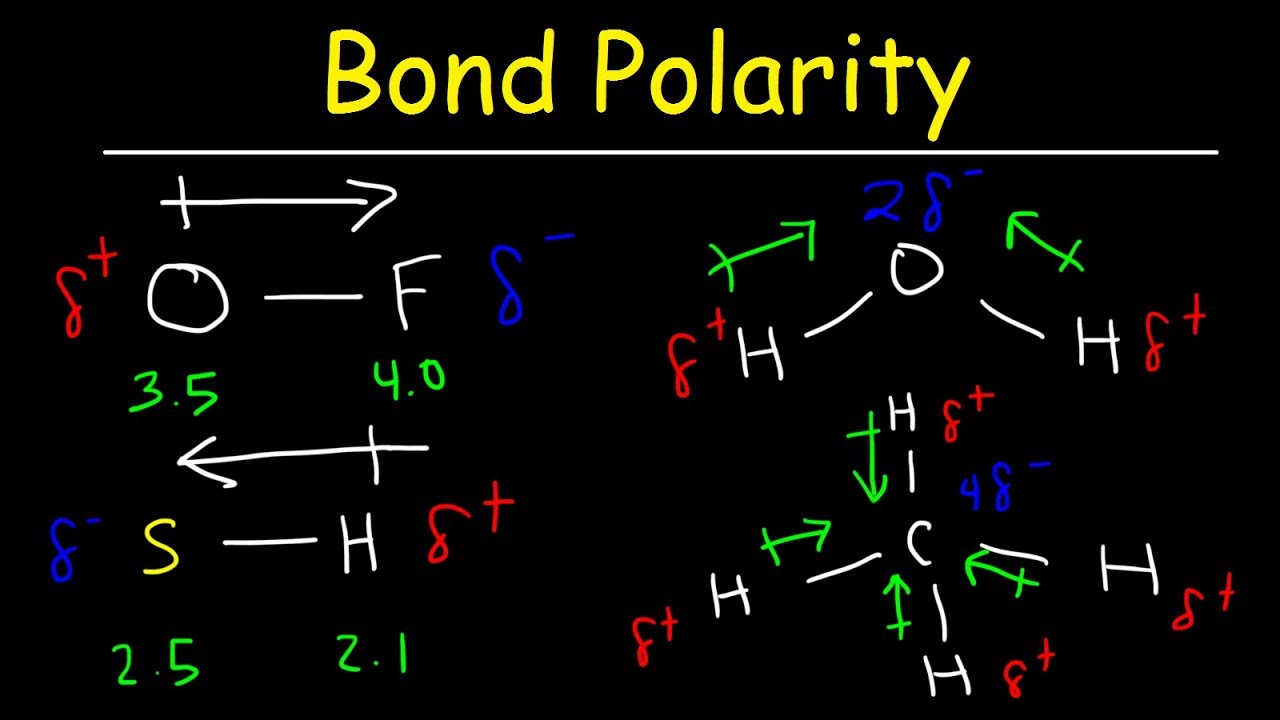
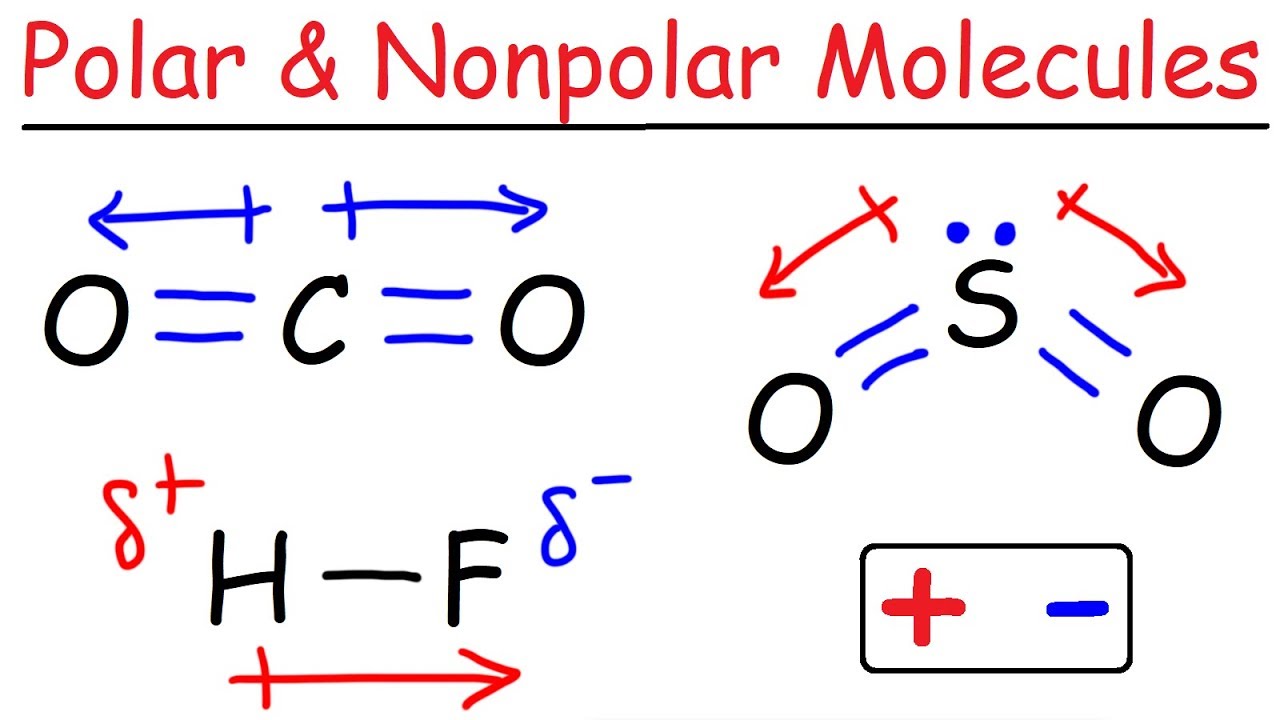
- 😀 Example molecules like HCl (hydrochloric acid) demonstrate how vector analysis helps determine polarity—HCl is polar due to its bond structure.
- 😀 Molecules with symmetrical geometries, such as BF3, may have polar bonds but be nonpolar overall due to the cancellation of vectors.
- 😀 The video highlights that ammonia (NH3) is polar because of the directional pull of electrons towards nitrogen, while methane (CH4) is nonpolar because of its symmetrical tetrahedral structure.
Q & A
What is the first step in determining the polarity of a molecule?
-The first step is to determine the geometry of the molecule. This requires using the three-dimensional structure of the molecule, not just the flat structural formula.
Why is the central atom important when determining molecular geometry?
-The central atom is important because it is typically the atom with the largest number of bonds and is usually present in the smallest quantity in the molecular formula. This atom helps determine the overall geometry of the molecule.
How do you apply the VSBR model in molecular geometry?
-You apply the VSBR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) model by determining the number of electron pairs around the central atom. This model helps predict the shape of the molecule based on electron pair repulsion.
What is vector analysis, and how is it used to determine the polarity of a molecule?
-Vector analysis is used to assess the direction and magnitude of bond dipoles in a molecule. By summing the vectors, we can determine if there is a resultant dipole moment. If the resultant is zero, the molecule is nonpolar; if the resultant is different from zero, the molecule is polar.
Can a molecule be nonpolar if it contains polar covalent bonds?
-Yes, a molecule can still be nonpolar if the polar bonds cancel each other out. For example, in carbon dioxide (CO2), the polar bonds are arranged symmetrically, resulting in no net dipole moment, making the molecule nonpolar.
What is the significance of electronegativity in determining the polarity of a molecule?
-Electronegativity determines how strongly atoms attract electrons in a bond. The more electronegative atom pulls the electrons toward itself, creating a dipole. The direction of these dipoles contributes to whether the molecule is polar or nonpolar.
What happens if a molecule has a central atom with leftover electron pairs?
-If the central atom has leftover electron pairs, the molecule is typically polar. The presence of these lone pairs affects the molecule's symmetry, causing an imbalance in the distribution of charge.
How does the shape of the ammonia (NH3) molecule influence its polarity?
-Ammonia (NH3) has a pyramidal shape due to the lone electron pair on nitrogen. This asymmetry results in a nonzero dipole moment, making ammonia a polar molecule.
What is the polarity of methane (CH4), and why?
-Methane (CH4) is nonpolar because it has a tetrahedral geometry with four identical hydrogen atoms around the central carbon. The symmetry of the molecule causes the dipole moments to cancel each other out.
Why is water (H2O) a polar molecule?
-Water is polar because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, creating two dipole moments that don't cancel out. The bent shape of the molecule ensures that the dipoles add up to a nonzero resultant dipole moment.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Polar, Non-Polar, and Ionic Compounds: Explanation, Examples, and Practice
Bond Polarity, Electronegativity and Dipole Moment - Chemistry Practice Problems
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
POLARITY OF MOLECULES - Part II | MOLECULAR GEOMETRY | VSEPR THEORY | Physical Science

Polarity

POLARITY OF MOLECULES - Part I | ELECTRONEGATIVITY DIFFERENCE | Physical Science
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
