Chapter 9
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the basics of DNA, focusing on its structure, function, and role in genetics. It covers the nucleotide composition of DNA, the process of complementary base pairing, and how genetic sequences differ across species. The script delves into the concept of genotype vs. phenotype and how mutations can impact protein function, exemplified by sickle cell anemia. The lecture also touches on DNA replication, the proofreading mechanism of DNA polymerase, and the types of mutations that can occur. Overall, it provides a clear and engaging explanation of foundational genetic concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic blueprint for all life, containing all the information that makes up organisms.
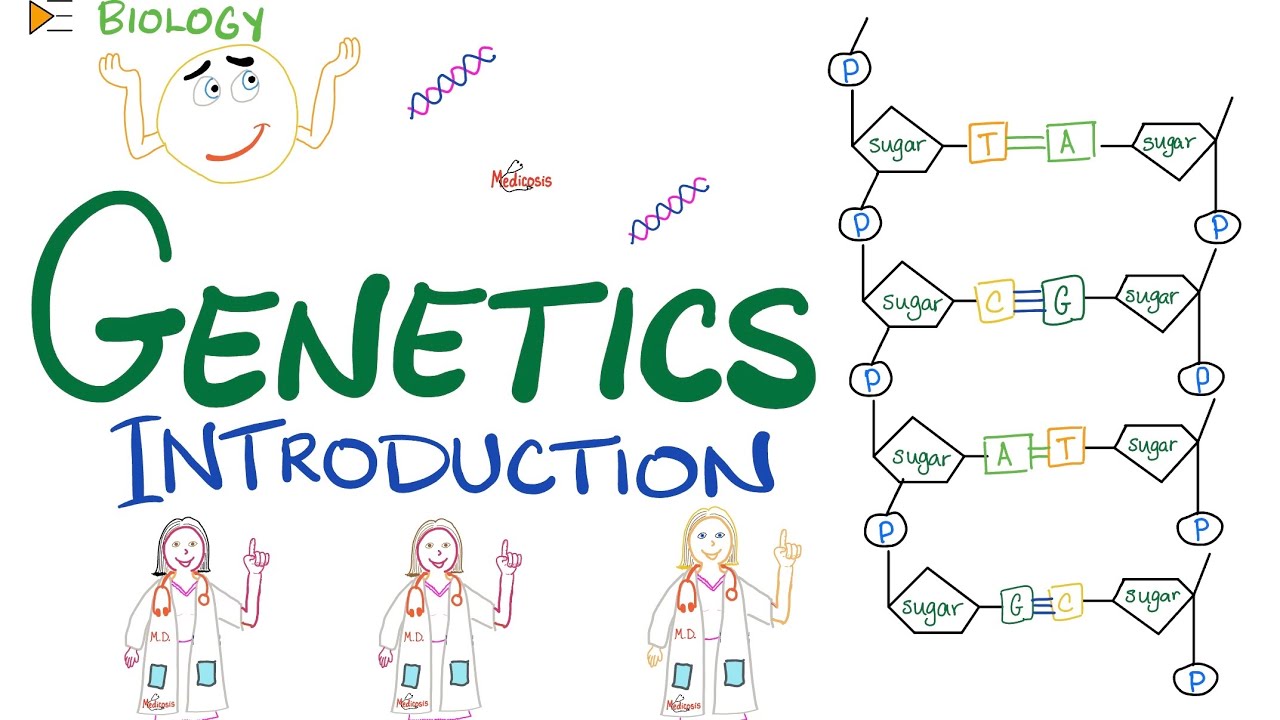
- 😀 DNA is a double-stranded molecule made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar group, phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
- 😀 There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Guanine (G).
- 😀 In DNA, complementary base pairing occurs: A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, forming the structure of the double helix.
- 😀 The sequence of bases on one DNA strand determines the sequence on the opposite strand, allowing for accurate replication and genetic information transfer.
- 😀 The genetic sequence of DNA can vary across different species, subtypes, and individuals, with more similarities seen in closely related organisms.
- 😀 Genotype refers to an organism's genetic composition, while phenotype refers to the observable traits or characteristics resulting from the genotype.
- 😀 Small variations in DNA sequences can lead to differences in protein production, affecting an organism's traits, such as feather color.
- 😀 DNA is condensed into chromosomes to fit within a cell. This condensation is necessary for proper DNA distribution during cell division, such as mitosis and meiosis.
- 😀 DNA replication occurs during the S phase of interphase, where enzymes like DNA polymerase help copy the DNA by adding complementary bases.
- 😀 Mutations are errors in DNA sequences, and DNA polymerase includes proofreading mechanisms to correct most errors, ensuring minimal mutation rates.
- 😀 Point mutations, which involve changes to a single nucleotide, can lead to significant health issues, such as sickle cell anemia, caused by a single nucleotide mutation in hemoglobin.
Q & A
What is the basic structure of DNA?
-DNA is a large, double-stranded molecule made up of nucleotides. It consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone with nitrogenous bases sticking out in the middle, which form the 'rungs' of the ladder-like structure.
What are the components of a nucleotide?
-A nucleotide is composed of a sugar group, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The sugar is a five-carbon sugar, and the nitrogenous bases include adenine (A), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and guanine (G).
How do the nitrogenous bases in DNA pair up?
-Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), forming two hydrogen bonds, while cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G), forming three hydrogen bonds. This complementary base pairing ensures accurate replication of DNA.
What is the significance of complementary base pairing in DNA?
-Complementary base pairing allows one strand of DNA to serve as a template for the other strand. This ensures that the genetic code is accurately replicated and passed on during cell division.
What is the double helix structure of DNA?
-The double helix refers to the twisted shape of the DNA molecule. The two strands of DNA are coiled around each other, with the nitrogenous base pairs forming the 'rungs' of the ladder-like structure.
What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the genetic makeup or sequence of genes in an organism, while phenotype refers to the physical traits or characteristics that are expressed. The genotype influences the phenotype.
How does a mutation in the DNA sequence affect protein production?
-A mutation in the DNA sequence can cause changes in the protein that is produced. Even a small mutation, such as a substitution, insertion, or deletion of a nucleotide, can lead to a dysfunctional protein, potentially causing disorders.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase is an enzyme that moves along a single-stranded DNA template during replication. It adds nucleotides that are complementary to the template strand, building a new DNA strand.
What is the proofreading mechanism in DNA replication?
-DNA polymerase has a proofreading mechanism that allows it to check and correct errors as it adds nucleotides during replication. This reduces the likelihood of mutations, ensuring high fidelity in the replication process.
What is sickle cell anemia and how is it related to DNA mutations?
-Sickle cell anemia is a blood disorder caused by a single nucleotide mutation in the gene that codes for hemoglobin. This mutation leads to the production of an abnormal hemoglobin protein, which changes the shape of red blood cells, resulting in impaired oxygen transport.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

GENETIKA MIKROORGANISME. OH JADI INI BEDA ANTARA DNA DAN RNA YA?

Bioquímica - Aula 09 - Ácidos Nucleicos
Introduction to Genetics - DNA, RNA, Genes, Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Transcription, Translation

LESSON ON CHROMOSOMES, DNA AND GENES | IN FILIPINO

Genética e Biologia Molecular – Aula 02 – Estrutura e Função do DNA e RNA

BIOLOGI SMA Kelas 12 - Materi Genetik | GIA Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
