[[ 𝙈𝙀𝙆𝘼𝙉𝙄𝙎𝙈𝙀 𝙋𝙀𝙉𝙂𝙃𝘼𝙉𝙏𝘼𝙍𝘼𝙉 𝙄𝙈𝙋𝙐𝙇𝙎 𝙈𝙀𝙇𝘼𝙇𝙐𝙄 𝙎𝙀𝙇 𝙎𝘼𝙍𝘼𝙁 (𝘼𝙧𝙪𝙨 𝙇𝙞𝙨𝙩𝙧𝙞𝙠) & 𝙈𝙀𝙇𝘼𝙇𝙐𝙄 𝙎𝙄𝙉𝘼𝙋𝙎𝙄𝙎 ]]
Summary
TLDRThis video script provides a detailed explanation of the mechanism behind nerve impulse transmission. It covers the structure of neurons, including dendrites, axons, and myelin sheaths, and describes how impulses travel through nerve cells via electrical signals and synapses. The script outlines the stages of impulse transmission—polarization, depolarization, repolarization, and undershoot—along with the role of neurotransmitters in synaptic transmission. It also explores reflex actions, where sensory neurons detect stimuli and trigger a quick motor response. Overall, the script offers a clear and comprehensive overview of how the nervous system processes and transmits impulses.
Takeaways
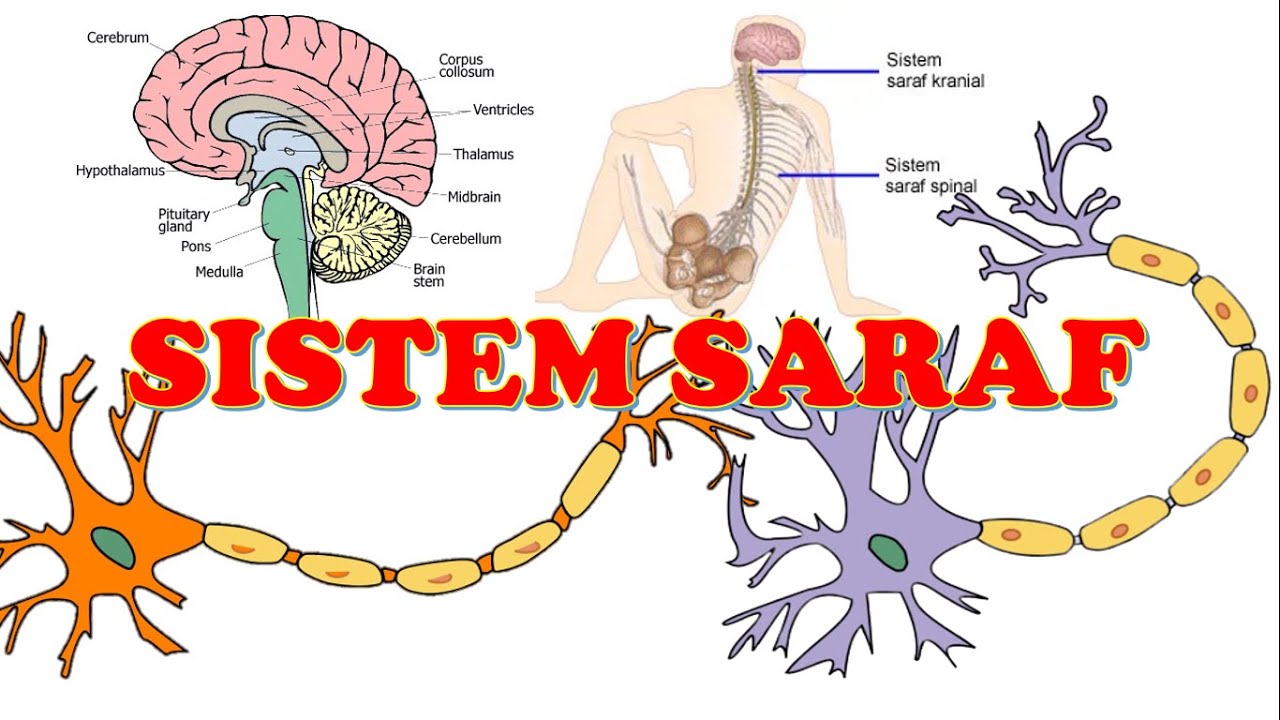
- 😀 Impulses are signals received by the body and carried by neurons, which are the building blocks of the nervous system.
- 😀 The neuron has several important components: dendrites, nucleus, cell body, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, nodes of Ranvier, and axon terminals.
- 😀 Dendrites receive impulses and transmit them to the cell body, while the axon transmits signals to other neurons or tissues.
- 😀 The nucleus controls the activities of the neuron, including responding to signals.
- 😀 The myelin sheath protects the axon and provides nutrients, allowing for faster signal transmission.
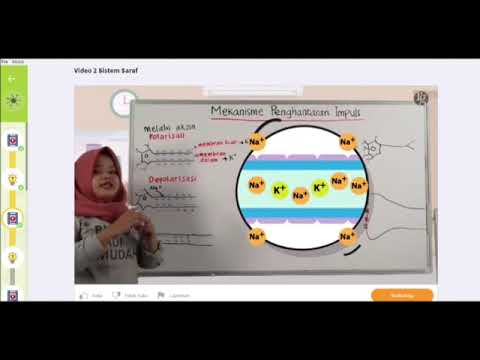
- 😀 Neurons communicate through electrical impulses, with the process involving several phases: polarization, depolarization, repolarization, and undershoot.
- 😀 Polarization is the resting state of the neuron where there is a difference in charge inside and outside the cell membrane.
- 😀 Depolarization occurs when sodium ions enter the neuron, reversing the charge inside the cell and leading to an electrical impulse.
- 😀 Repolarization restores the negative charge inside the neuron and the positive charge outside by allowing potassium ions to exit.
- 😀 The synapse is the gap between two neurons, where neurotransmitters are released to transmit impulses from one neuron to another.
- 😀 Reflex actions are involuntary and rapid responses to stimuli, where sensory neurons carry signals to the spinal cord, which then sends responses through motor neurons.
Q & A
What is an impulse in the context of the nervous system?
-An impulse, or stimulus, is a message received by the body and transmitted by neurons, which carry it to the necessary parts of the body for response.
What are the main components of a neuron?
-A neuron consists of dendrites, a nucleus, a cell body, an axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, Ranvier nodes, and axon terminals.
What is the role of dendrites in the nervous system?
-Dendrites are the parts of a neuron that receive impulses and transmit them to the cell body.
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
-The myelin sheath protects the axon and helps in the transmission of nerve impulses by increasing the speed of conduction.
How does the impulse travel through a neuron?
-Impulses travel through a neuron via electrical signals that pass through the dendrites to the cell body, then through the axon, and are transmitted via synapses to other neurons.
Can you explain the process of depolarization in neurons?
-Depolarization occurs when the inside of a neuron becomes positively charged due to sodium ions entering the cell, which reverses the normal polarity of the neuron.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in synaptic transmission?
-Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that carry nerve impulses across the synapse from one neuron to another, facilitating communication between neurons.
What happens during the repolarization phase in a neuron?
-During repolarization, the inside of the neuron returns to a negative charge as potassium ions flow out of the cell, restoring the original resting potential.
What is a reflex action and how is it related to nerve impulses?
-A reflex action is an automatic, rapid response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought. It involves the transmission of nerve impulses through sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons.
How do synapses function in the transmission of nerve impulses?
-In synaptic transmission, impulses reach the axon terminal of a neuron, causing neurotransmitters to be released into the synaptic gap. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the next neuron, allowing the impulse to continue its journey.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)