MedPhys - Kerma, Collision Kerma and Absorbed Dose Part 1
Summary
TLDRIn this comprehensive lecture, key concepts related to kerma, collision kerma, and absorbed dose are discussed through a series of twelve problems. The definitions of dose, exposure, and kerma are clearly articulated, alongside relevant formulas for calculating kerma and its components. Visual aids and plots enhance understanding of how these measures interact with depth and attenuation in photon beams. The lecture concludes with practical calculations, demonstrating the application of theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios in radiation physics, making it essential for students and professionals alike.
Takeaways
- 😀 Kerma stands for Kinetic Energy Released per unit Mass and is crucial in understanding radiation interactions.
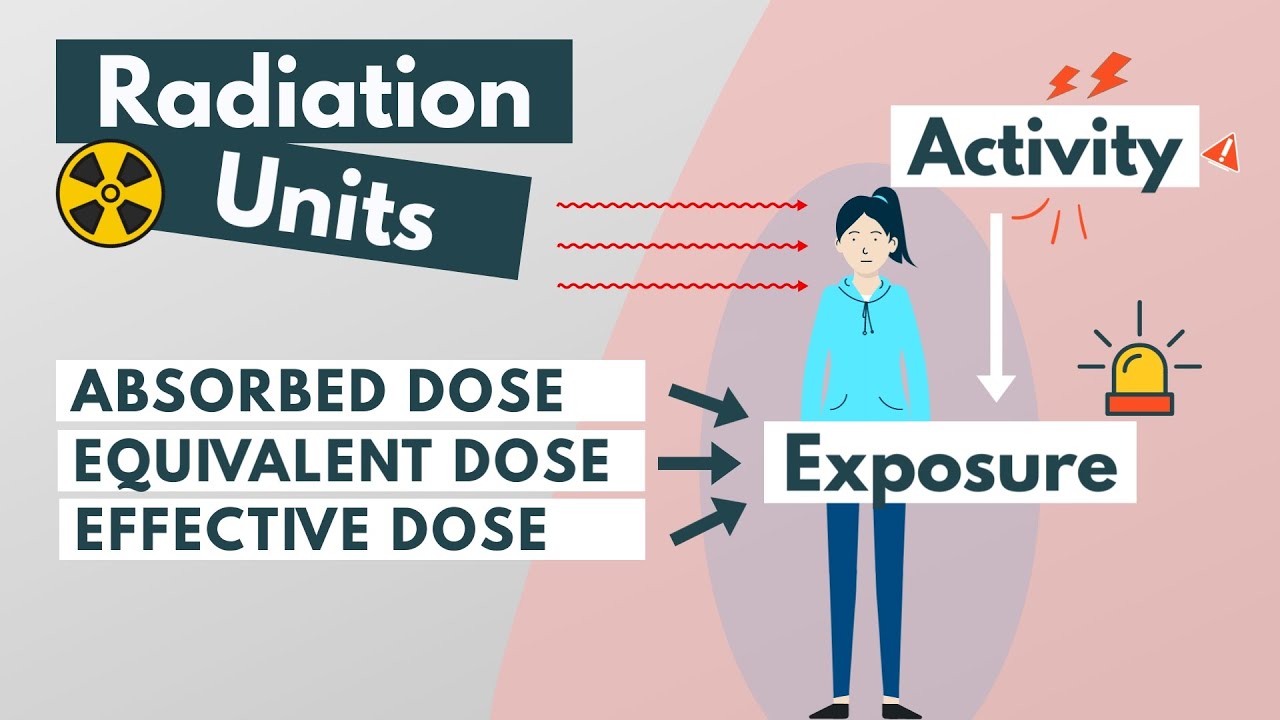
- 📏 Dose is defined as the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to a given material per unit mass.
- 🌬️ Exposure is the total charge of ions produced in air when all liberated electrons are completely stopped.
- ⚡ Collision kerma refers to the energy transferred to electrons primarily through ionization interactions.
- 🌟 Radiative kerma describes energy dissipation via radiative interactions, such as bremsstrahlung.
- 📊 Understanding the relationship between kerma, dose, and collision kerma is essential for radiation dose calculations.
- 📈 In scenarios without photon attenuation, kerma and dose are equivalent beyond the buildup region.
- 📉 With photon beam attenuation, the largest to smallest measurement order is dose, kerma, then collision kerma.
- 🔍 Formulas relating different mass attenuation coefficients are crucial for calculating energy transfer and absorption.
- 🔬 The average kerma in water for a 6 MeV photon was calculated to be 1.56 joules per kilogram.
Q & A
What is the definition of dose in the context of ionizing radiation?
-Dose is the mean energy imparted by ionizing radiation to a given material per unit mass.
How is exposure defined according to the transcript?
-Exposure is the total charge of ions produced in air when all electrons liberated by photons in a volume of air are completely stopped.
What does the term 'kerma' stand for?
-Kerma stands for Kinetic Energy Released per unit Mass, representing the energy transferred from photons to charged particles per unit mass.
What is the formula to calculate kerma?
-The formula to calculate kerma is K = Φ * μ_tr/ρ, where Φ is the energy fluence.
What distinguishes collision kerma from radiative kerma?
-Collision kerma refers to energy dissipated by collisional interactions (like ionizations), while radiative kerma refers to energy dissipated by radiative interactions, such as bremsstrahlung.
What is the relationship between dose and collision kerma with increasing depth?
-When there is attenuation of the photon beam, the relationship is described as Dose = Collision Kerma * e^(-μ_eff * x), indicating a transient equilibrium rather than charged particle equilibrium.
How are the units for kerma expressed?
-The units for kerma are expressed in joules per kilogram, which is equivalent to gray.
What are the steps to calculate the average energy transfer to kinetic energy of electrons?
-The average energy transfer to kinetic energy of electrons is calculated using the formula E_tr = (μ_tr/μ) * E_photon, where E_photon is the initial photon energy.
In the context of the lecture, what factors are crucial for calculating kerma in water for a photon beam?
-Factors crucial for calculating kerma include the photon energy, the mass attenuation coefficient, and the energy fluence.
What is the average kerma in water for a 6 MeV photon with a specific fluence?
-The average kerma in water for a 6 MeV photon with a fluence of 1 × 10^11 cm^-2 is calculated to be 1.56 joules per kilogram.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)