Explaining Economic Integration
Summary
TLDREconomic integration involves reducing or eliminating trade barriers and coordinating policies between nations to lower costs and boost trade. It can take various forms, from preferential trade agreements to free trade areas, customs unions, and economic or monetary unions. While integration promotes economic growth and reduces expenses for member countries, it can also limit individual governments' flexibility to adjust policies. Moreover, economic challenges in one member nation can negatively impact the entire bloc, making the balance between cooperation and national autonomy crucial.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Economic integration reduces or eliminates trade barriers among nations and coordinates monetary and fiscal policies.
- 💰 The goal of economic integration is to lower costs for consumers and producers while increasing trade between member countries.
- 🔗 The more integrated economies become, the fewer trade barriers exist, and the more politically coordinated they are.
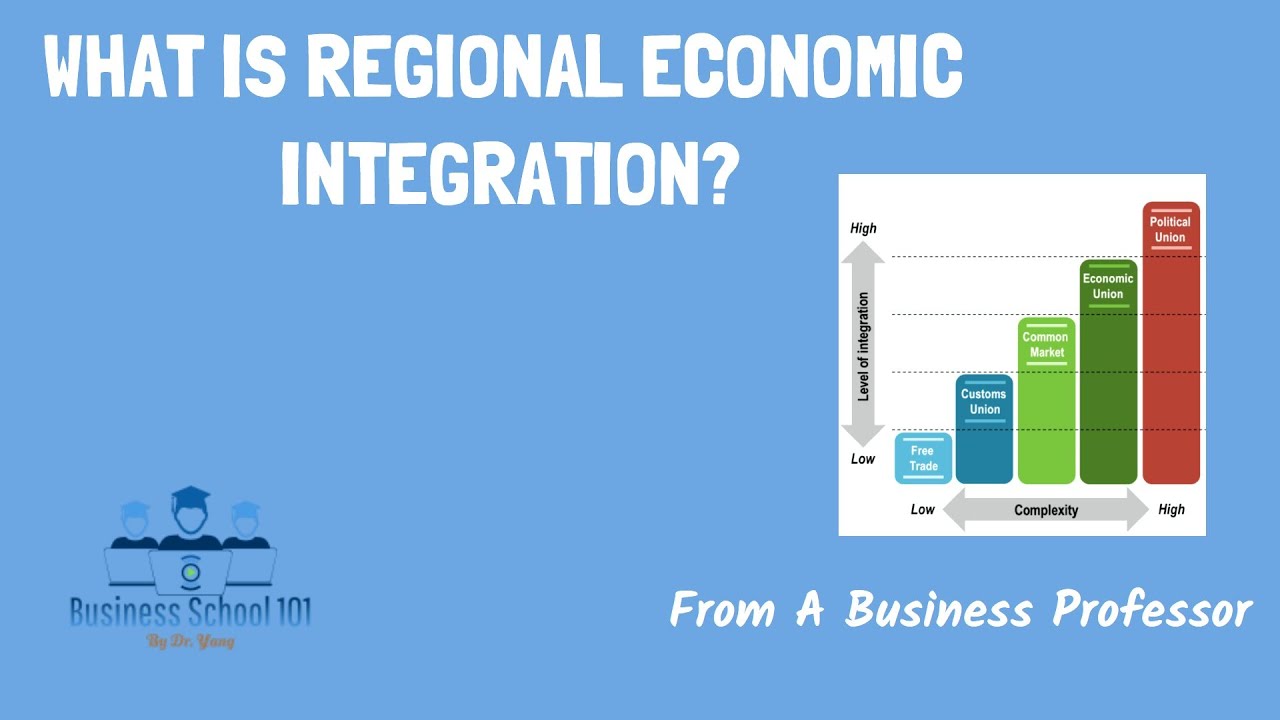
- 📉 Countries can agree to different levels of economic integration, from preferential trade agreements to full monetary unions.
- 📦 A preferential trade agreement involves reducing or removing tariffs on certain goods within a trading block.
- 🌐 A free trade area eliminates tariffs on all goods traded among member nations, like the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
- 🛃 In a customs union, countries reduce or remove tariffs among themselves and impose a common tariff on non-member countries.
- 🛠️ Common markets allow free exchange of goods, services, labor, and capital among member nations.
- 💶 An economic union involves members sharing trade policies with non-members, and a monetary union includes a shared currency, such as the Euro.
- 📉 While economic integration can boost growth, it can also limit governments' flexibility to make adjustments that benefit individual economies.
Q & A
What is economic integration?
-Economic integration is the process of reducing or eliminating trade barriers among nations and coordinating monetary and fiscal policies to reduce costs for consumers and producers and to increase trade between participating countries.
What are the aims of economic integration?
-The aims of economic integration are to reduce costs for consumers and producers, increase trade between countries, and potentially spur economic growth through easier and cheaper trade.
What are the different levels of economic integration?
-Different levels of economic integration include a preferential trade agreement, a free trade area, a customs union, a common market, and an economic union.
What is a preferential trade agreement?
-A preferential trade agreement is a trading block where members reduce or remove tariffs on certain goods imported and exported throughout their region.
Can you provide an example of a free trade area?
-An example of a free trade area is the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), where member countries reduce or remove tariffs on all goods among member nations.
How does a customs union differ from a free trade area?
-In a customs union, member countries not only reduce or remove tariffs among themselves but also impose a common tariff against non-member countries.
What is a common market?
-A common market is a trading block where member countries freely exchange all goods, services, labor, and capital.
What is an economic union?
-An economic union is a common market among members that also share one trade policy with non-members.
What is a monetary union?
-A monetary union is the highest level of economic integration where nations share a single currency, such as the Euro.
What are the potential benefits of economic integration?
-The potential benefits of economic integration include smaller expenses for trade, which can spur economic growth and increase efficiency through the specialization of production.
What are the potential risks associated with economic integration?
-One potential risk of economic integration is that if one member's economy slows down, it can bring down the other members of the block. Additionally, more integrated economies have less flexibility for individual governments to make adjustments that would benefit their own economies.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Regional Economic Integration | International Business | From A Business Professor

Manfaat dan Hambatan Perdagangan Internasional || Materi IPS || Kelas 9 || SMP

PASAR BEBAS - Materi IPS SMP Kelas 9

Globalisasi Ekonomi dan Liberalisasi Perdagangan

Episode 38: Trade Blocs

CPCS / 19-223 / Animation fine-cut (EN) (v11)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
