How Does Radiocarbon Dating Work? - Instant Egghead #28
Summary
TLDRThe script from Scientific American Instant Egghead explains how scientists determine the age of fossils using carbon dating. It details the presence of two carbon isotopes, Carbon 12 and unstable Carbon 14, in living organisms. After an organism's death, Carbon 14 decays into nitrogen at a known rate, with a half-life of 5,730 years. By measuring the ratio of Carbon 14 to Carbon 12 remaining in a fossil, scientists can estimate its age up to approximately 60,000 years. For older specimens, elements with longer half-lives are used.
Takeaways
- 🕰️ Fossils contain an internal clock that helps determine their age.
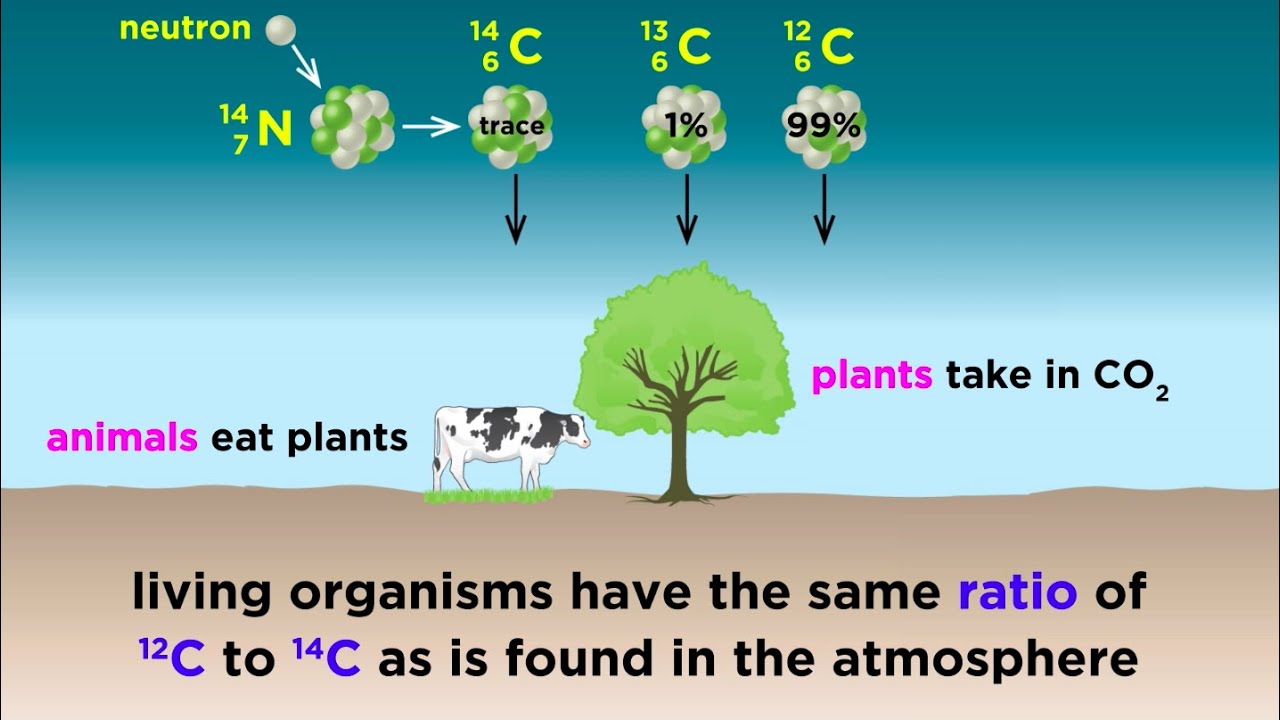
- 🌳 For dating fossils, scientists use the ratio of Carbon-14 to Carbon-12 isotopes.
- 🌿 Plants absorb carbon from the atmosphere, including both Carbon-12 and Carbon-14.
- 🐘 Animals obtain carbon, including isotopes, by consuming plants.
- ⚛️ Carbon-12 has six protons and six neutrons, while Carbon-14 has six protons and eight neutrons.
- ☢️ Carbon-14 is radioactive and decays into nitrogen at a predictable rate.
- 📉 The half-life of Carbon-14 is 5,730 years, during which half of the Carbon-14 atoms decay.
- 🔍 By measuring the Carbon-14 to Carbon-12 ratio, scientists can estimate the time elapsed since an organism's death.
- 🦴 Carbon dating is effective for fossils up to approximately 60,000 years old.
- 🔬 For older fossils, scientists use other radioactive elements with longer half-lives for dating.
Q & A
How do scientists determine the age of fossils?
-Scientists determine the age of fossils by measuring the ratio of Carbon 14 to Carbon 12 isotopes within the fossil.
What is the difference between Carbon 12 and Carbon 14?
-Carbon 12 has six protons and six neutrons, while Carbon 14 has six protons and eight neutrons. Carbon 14 is unstable and decays over time.
How is Carbon 14 formed?
-Carbon 14 is formed in the atmosphere when cosmic rays hit nitrogen atoms, causing a transformation into carbon with an unstable number of neutrons.
What is the half-life of Carbon 14?
-The half-life of Carbon 14 is 5,730 years, which means that after this period, about half of the Carbon 14 atoms will have decayed into nitrogen.
How does the decay of Carbon 14 help in dating fossils?
-The decay of Carbon 14 allows scientists to measure the time elapsed since the death of an organism by comparing the remaining Carbon 14 to the stable Carbon 12.
What is the maximum age limit for Carbon 14 dating?
-Carbon 14 dating is effective for dating fossils up to approximately 60,000 years old.
Why can't Carbon 14 dating be used for very old fossils?
-For very old fossils, the amount of Carbon 14 left is too small to measure accurately, so scientists use other dating methods with longer half-lives.
How do plants incorporate Carbon into their system?
-Plants incorporate Carbon by taking in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and using it to form complex organic molecules.
How do animals get their carbon?
-Animals obtain carbon by consuming plants that have already incorporated carbon dioxide into their organic molecules.
What happens to the Carbon 12 in a fossil over time?
-Unlike Carbon 14, the amount of Carbon 12 in a fossil remains constant over time and does not decay.
What alternative methods are used for dating fossils older than 60,000 years?
-For dating older fossils, scientists use other unstable elements with longer half-lives, such as Potassium-Argon or Uranium-Lead dating.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)