Anatomía - Pulmón (Segmentación, Caras, Vértice, Vasos y Nervios)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video provides an in-depth overview of the pulmonary system, covering key structures such as the pulmonary and bronchial arteries, veins, and innervation. It explains the two circulations in the lungs, functional (pulmonary arteries) and nutritional (bronchial arteries). The video also details the pressures in the pulmonary arteries, the branching of bronchial arteries, and the venous systems of the lungs. Lastly, it discusses the innervation of the lungs by the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, highlighting their roles in bronchoconstriction, bronchodilation, and secretion. The video concludes with a teaser for an upcoming lesson on the perineum.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lungs have two circulations: functional (pulmonary arteries) and nutritive (bronchial arteries).
- 😀 Pulmonary arteries originate from the right ventricle and follow the bronchial tree's path.
- 😀 The diastolic pressure of pulmonary arteries is 8 mm Hg, and systolic pressure is 25 mm Hg, with an average pressure of 15–17 mm Hg.
- 😀 There are three bronchial arteries: one on the right and two on the left, providing blood to the bronchi and lungs.
- 😀 Bronchial arteries arise from the aorta or the first posterior intercostal artery in some cases.
- 😀 Bronchial arteries anastomose below the tracheal carina, forming the subcarinal arcade.
- 😀 Pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium, with four veins total (two right, two left).
- 😀 Bronchial veins drain blood from the bronchi and terminate in the azygos and hemiazygos veins.
- 😀 Broncopulmonary veins drain blood from segmental and terminal bronchi, as well as alveoli, and drain into pulmonary veins.
- 😀 The innervation of the lungs is controlled by the pulmonary plexus, with parasympathetic fibers causing broncho-constriction and sympathetic fibers causing broncho-dilation.
Q & A
What is the function of the pulmonary arteries?
-The pulmonary arteries are responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for gas exchange (hematosis).
What is the difference between the functional and nutritional circulation of the lungs?
-The functional circulation refers to the pulmonary arteries that are involved in gas exchange, while the nutritional circulation refers to the bronchial arteries, which supply oxygenated blood to the lung tissues.
Where do the pulmonary arteries originate from, and how are they distributed to the lungs?
-The pulmonary arteries originate from the pulmonary trunk, which emerges from the right ventricle of the heart. They follow the bronchial tree’s path and branch out into the lungs.
What is the role of the ligamentum arteriosum?
-The ligamentum arteriosum is a remnant of the ductus arteriosus from fetal development, connecting the left pulmonary artery to the aorta.
What are the normal pressure values in the pulmonary arteries?
-The normal diastolic pressure in the pulmonary arteries is 8 mmHg, the systolic pressure is 25 mmHg, and the average pressure is between 15 and 17 mmHg.
How many bronchial arteries are there, and where do they originate from?
-There are three bronchial arteries: one on the right, originating from the first intercostal artery, and two on the left, originating from the thoracic aorta.
What is the function of the bronchial arteries?
-The bronchial arteries supply blood to the bronchial tree and lung tissues, ensuring the oxygenation and nourishment of the lungs.
What is the significance of the subcarinal arcade?
-The subcarinal arcade is the network formed by the anastomosis of the bronchial arteries beneath the tracheal carina, providing collateral blood flow to the lungs.
What is the role of the pulmonary veins?
-The pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium of the heart. There are four pulmonary veins, two from each lung.
How do the bronchial veins differ from the pulmonary veins?
-Bronchial veins drain deoxygenated blood from the bronchial tree into the azygos vein (right) or hemiazygos vein (left), while pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
What is the role of the pulmonary plexus in lung function?
-The pulmonary plexus provides both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation to the lungs and bronchial tree. The parasympathetic fibers cause bronchoconstriction and vasodilation, while the sympathetic fibers promote bronchodilation and vasoconstriction.
How do sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers affect the lungs differently?
-Parasympathetic fibers cause bronchoconstriction, vasodilation, and stimulate gland secretion, while sympathetic fibers cause bronchodilation, vasoconstriction, and inhibit gland secretion.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
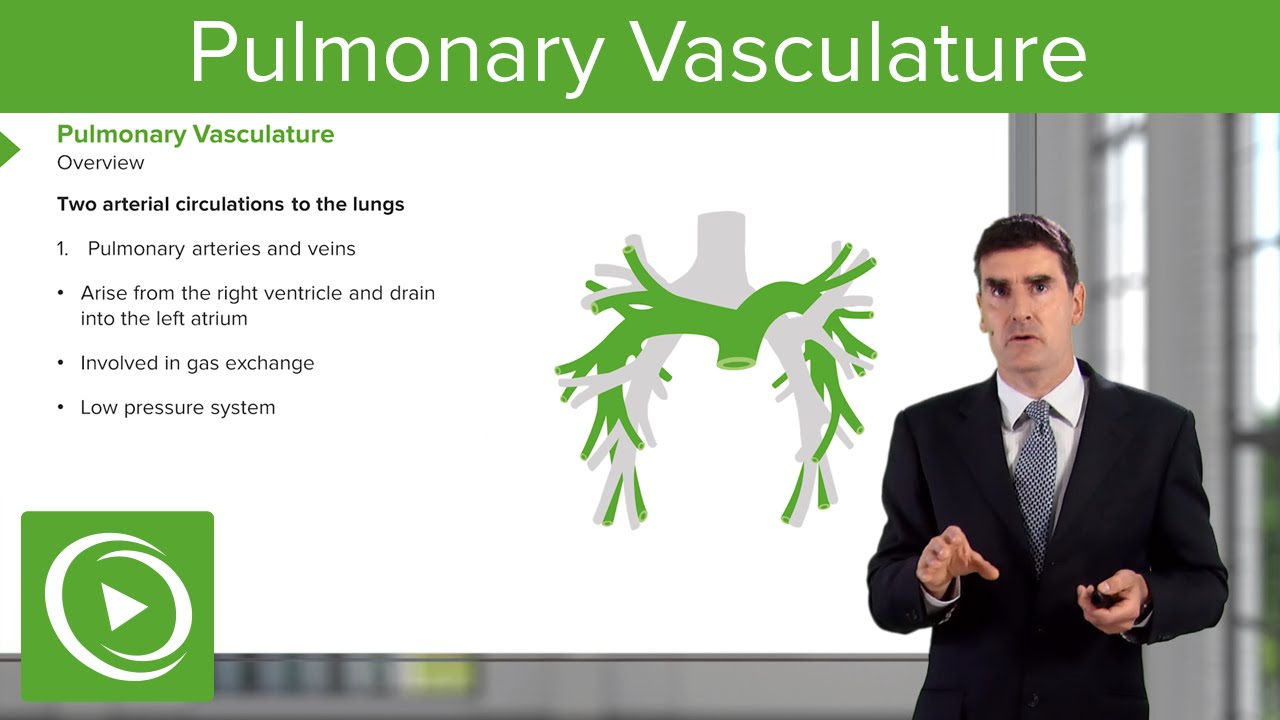
Pulmonary Vasculature – Respiratory Medicine | Medical Education Videos

CAVIDADES CARDIACAS

BL DISTUM - Iacoviello - Lezione 1 - Principi di anatomia

Sistema Circulatório - CORAÇÃO - Pequena e grande circulação

I vasi sanguigni e la circolazione
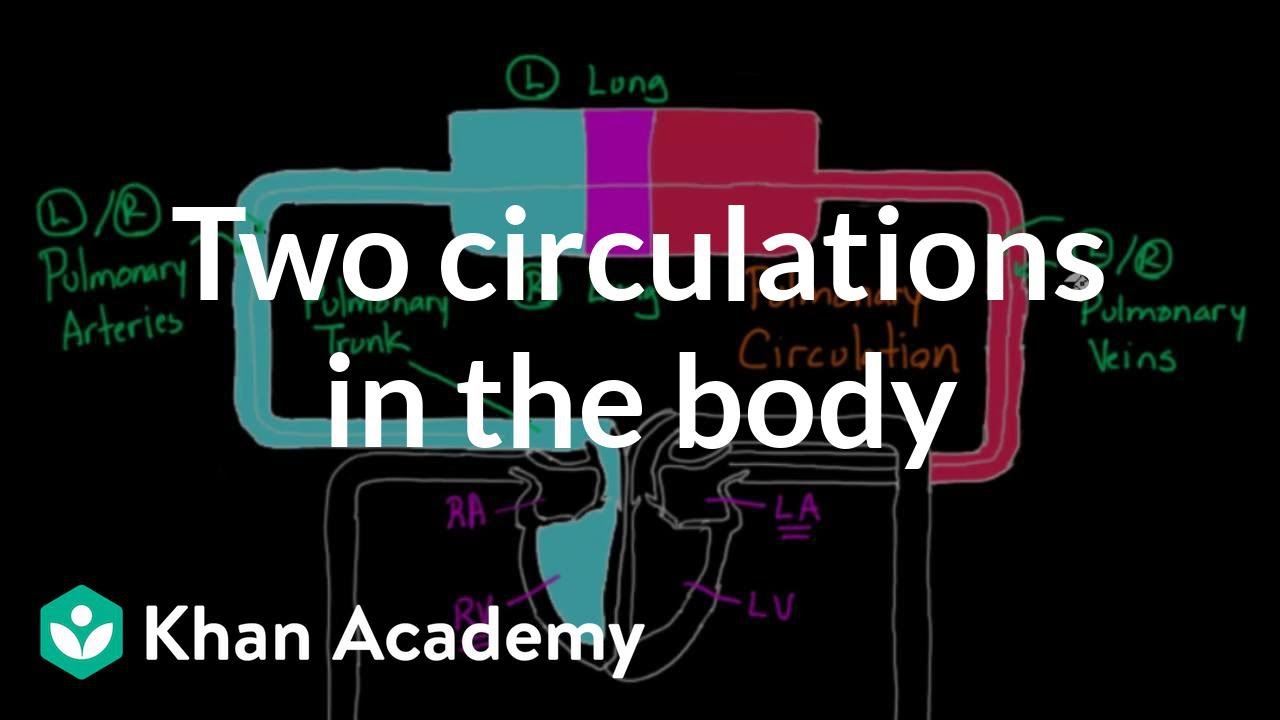
Two Circulations in the Body | Circulatory system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
