11 - Relações entre C, T, d, M Concentração comum, título, densidade e molaridade.
Summary
TLDRThis educational video focuses on explaining different units of concentration in chemistry, specifically common concentration and molarity. The instructor highlights key formulas for calculating these concentrations and their conversions, using examples like sodium chloride and acetic acid. The video emphasizes the relationships between concentration units and provides step-by-step instructions for calculating molarity from given data. Additionally, viewers are encouraged to engage with the content, like, and subscribe for more lessons on concentration and other chemistry topics. It’s a valuable resource for understanding concentration concepts and applying them in practical situations.
Takeaways
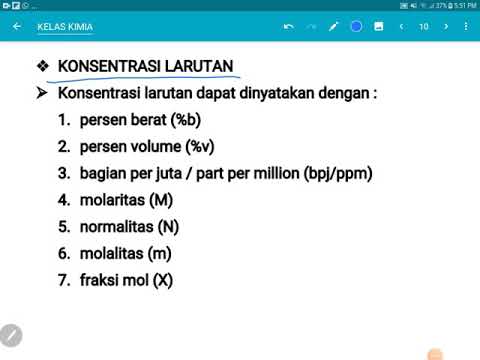
- 😀 The video explains different concentration units in chemistry, focusing on molarity and common concentration.
- 😀 Molarity is calculated by dividing the moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
- 😀 Common concentration (C_com) is calculated by dividing the mass of the solute by the volume of the solution.
- 😀 The formula to convert between molarity and common concentration involves using the molar mass of the solute.
- 😀 To calculate molarity from common concentration, the formula is M = C_com / molar mass.
- 😀 Similarly, to calculate common concentration from molarity, the formula is C_com = M * molar mass.
- 😀 Density can be used in concentration calculations, especially when converting from percentage to molarity.
- 😀 To convert a solution's percentage to molarity, one must first calculate the common concentration and then apply the appropriate formula.
- 😀 Practical examples, such as calculating the molarity of a NaCl solution, help demonstrate these concentration conversions.
- 😀 The video stresses the importance of understanding how to handle density in concentration calculations, especially in different unit systems like g/mL.
- 😀 The presenter encourages students to practice these concepts with exercises involving real-world chemical solutions.
Q & A
What is molarity and how is it calculated?
-Molarity (M) is the amount of solute in moles per liter of solution. It is calculated using the formula M = mol of solute / volume of solution (in liters).
What is the formula for common concentration?
-The formula for common concentration is C = mass of solute / volume of solution (in liters).
How can you convert common concentration to molarity?
-To convert common concentration to molarity, you divide the concentration by the molar mass of the solute, using the formula Molarity = Common concentration / molar mass of the solute.
What is the relationship between molarity and common concentration?
-Molarity and common concentration are related through the molar mass of the solute. Molarity is calculated by dividing the common concentration by the molar mass of the solute.
How do you calculate the molarity of NaCl from a given common concentration?
-To calculate the molarity of NaCl, divide the common concentration (in g/L) by the molar mass of NaCl (58.5 g/mol). For example, if the common concentration is 2.95 g/L, the molarity would be 2.95 / 58.5 = 0.05 mol/L.
What is the molar mass of NaCl and how is it used in calculations?
-The molar mass of NaCl is 58.5 g/mol. It is used to convert between grams of NaCl and moles when calculating molarity or making other concentration-related conversions.
How is the concentration of acetic acid in vinegar calculated?
-To calculate the concentration of acetic acid, first determine the concentration common by dividing the mass of acetic acid by the volume of vinegar. Then, calculate the molarity by dividing the concentration common by the molar mass of acetic acid (60 g/mol).
What is the formula for converting percentage concentration to molar concentration?
-To convert percentage concentration to molar concentration, you must first convert the percentage to common concentration (g/L), and then divide by the molar mass of the solute to get the molarity.
How is density used to calculate concentration in certain problems?
-Density is used to convert between mass and volume. If the density is given in g/mL or g/L, you can use it to calculate the mass of solute in a given volume, which can then be used to find the concentration.
What should be considered when working with units of concentration?
-When working with units of concentration, it’s important to ensure that the units of mass, volume, and molar mass are consistent. For example, ensure that the volume is in liters and that the molar mass is in g/mol to maintain correct unit conversions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)