Endocrinologia 4 - Hormônios Tireodianos
Summary
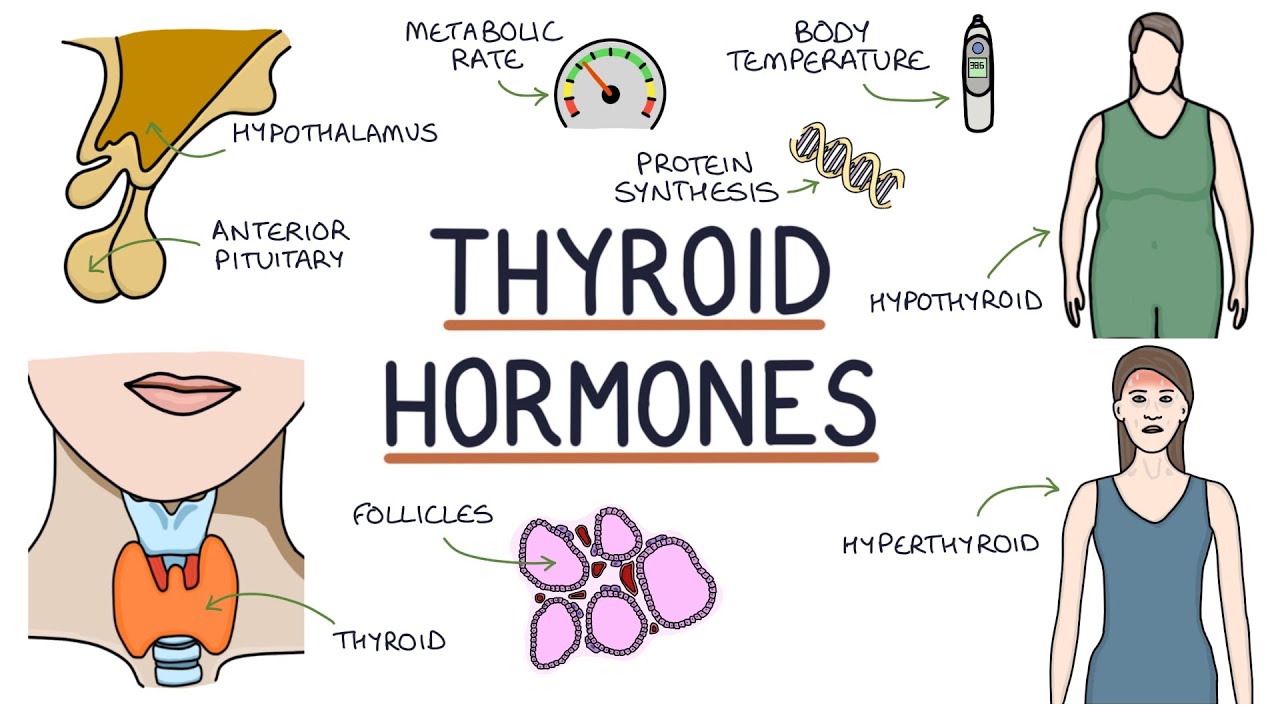
TLDRThis video explains the complex process of thyroid hormone synthesis and regulation. It covers how the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 are produced and their role in metabolism and growth. The video also discusses conditions like goiter and Graves' disease, highlighting the impact of iodine deficiency and autoimmune responses on thyroid function. It emphasizes the feedback mechanisms between the hypothalamus, pituitary, and thyroid gland, and how disruptions in this system can lead to disorders such as hyperthyroidism. This overview offers valuable insights into thyroid physiology and its impact on overall health.
Takeaways
- 😀 Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) are essential for regulating metabolism and various bodily functions.
- 😀 The production of thyroid hormones is controlled through a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- 😀 Low levels of thyroid hormones trigger the release of TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone), which stimulates the release of TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone).
- 😀 High levels of T3 and T4 inhibit the release of TRH and TSH to maintain balance in thyroid hormone production.
- 😀 A goiter (bócio) can develop due to iodine deficiency, which prevents the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- 😀 When thyroid hormones are not produced due to iodine deficiency, the pituitary gland compensates by releasing more TSH, which stimulates thyroid gland growth.
- 😀 Autoimmune diseases like Graves' disease can result in the production of antibodies that stimulate the thyroid, leading to excessive hormone production.
- 😀 The uncontrolled release of thyroid hormones in autoimmune diseases can lead to symptoms such as goiter and hyperthyroidism.
- 😀 The absence of iodine in the diet disrupts the negative feedback loop, resulting in continuous stimulation of the thyroid gland by TSH.
- 😀 In autoimmune conditions, immunoglobulins (antibodies) act on the thyroid gland, mimicking TSH and causing overstimulation and hormone overproduction.
- 😀 Thyroid hormone levels impact the regulation of other hormones, including reducing the release of LH (Luteinizing Hormone) in some cases.
Q & A
What are the main functions of thyroid hormones T3 and T4?
-Thyroid hormones T3 and T4 increase the size and number of thyroid cells and enhance their secretory activity. These hormones regulate metabolic processes and influence target tissues throughout the body.
How does the thyroid gland regulate the release of thyroid hormones?
-The thyroid gland regulates thyroid hormone release through a feedback loop. When T3 and T4 levels are sufficient, they provide negative feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, reducing the release of TRH and TSH, which in turn reduces the stimulation of the thyroid gland.
What happens when there is a deficiency of iodine in the diet?
-In the absence of iodine, the thyroid gland cannot synthesize T3 and T4. This leads to a lack of feedback inhibition on the pituitary gland, which increases the release of TSH, causing the thyroid to enlarge and potentially lead to goiter.
What is goiter and what causes it?
-Goiter is the enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is caused by excessive stimulation from TSH due to iodine deficiency or other factors that impair the synthesis of thyroid hormones, such as autoimmune disorders.
How does autoimmune thyroid disease affect the thyroid gland?
-Autoimmune thyroid diseases, such as Graves' disease, can cause excessive stimulation of the thyroid, leading to overproduction of thyroid hormones. This can disturb the negative feedback system, resulting in hyperthyroidism and potentially causing goiter.
What role does TSH play in the feedback mechanism of thyroid hormone regulation?
-TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) plays a critical role in stimulating the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. When these hormones are deficient, TSH levels rise in an attempt to stimulate thyroid hormone production. Once adequate levels of T3 and T4 are reached, they inhibit further TSH release.
What is the relationship between TRH and TSH in regulating thyroid hormone production?
-TRH (Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone) is released from the hypothalamus to stimulate the pituitary gland to produce TSH. TSH then stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4. As T3 and T4 levels rise, they provide negative feedback to reduce both TRH and TSH production, maintaining balance.
Why does the thyroid continue to enlarge in the absence of iodine?
-In the absence of iodine, the thyroid cannot produce adequate levels of T3 and T4. As a result, the pituitary gland releases more TSH to try to stimulate the thyroid. This prolonged stimulation causes the thyroid gland to enlarge, leading to goiter.
What is the impact of autoimmune diseases like Graves' disease on thyroid hormone regulation?
-Autoimmune diseases like Graves' disease cause the immune system to produce antibodies that stimulate the thyroid gland, leading to excessive production of T3 and T4. This disrupts the negative feedback mechanism and can lead to hyperthyroidism and goiter.
How does the release of TSH affect the growth of the thyroid gland?
-The release of TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to grow and produce thyroid hormones. Continuous stimulation of the thyroid by high levels of TSH, especially in the absence of iodine or due to autoimmune conditions, leads to the enlargement of the thyroid, resulting in goiter.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)