NÚMEROS NATURAIS COMPARAÇÃO DE NÚMEROS NATURAIS | O QUE É NÚMERO NATURAL? | RETA NUMÉRICA
Summary
TLDRThis educational transcript provides an in-depth exploration of natural numbers, their sequences, and how we use them in everyday life. It begins with simple examples like counting pens or chairs and progresses to explaining natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, and real numbers. The focus is primarily on natural numbers, covering their sequence, odd and even numbers, and their representation on a number line. The transcript also delves into concepts like comparison, successors, and predecessors, using engaging metaphors like the 'hungry crocodile' for comparing numbers. The lesson is rich in examples and exercises to help students understand the concepts better.
Takeaways
- 😀 Numbers are used in everyday life for counting and measuring various items, like pens, money, and distance.
- 😀 There are different types of numbers, including natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and imaginary numbers.
- 😀 Natural numbers are whole numbers used for counting, starting from zero and continuing infinitely.
- 😀 A sequence of natural numbers is formed by adding one unit to the previous number, making it an infinite sequence.
- 😀 Even numbers are those that can be grouped into pairs, while odd numbers cannot form complete pairs.
- 😀 The concept of comparing natural numbers involves determining which number is greater or smaller, often represented with symbols like '>' and '<'.
- 😀 In comparison, a 'hungry alligator' metaphor is used where the alligator's mouth opens towards the greater number.
- 😀 A number’s predecessor is the number before it, while its successor is the number after it.
- 😀 The numbers in a sequence can be ordered either in ascending (smaller to larger) or descending (larger to smaller) order.
- 😀 When teaching number comparison, it's crucial to ensure the sequence on the number line is maintained and numbers are in correct order.
- 😀 Exercises often involve identifying the predecessor and successor of numbers, as well as arranging numbers in ascending or descending order.
Q & A
What are natural numbers?
-Natural numbers are the set of whole numbers used for counting, starting from 0, and continuing infinitely (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...). They are numbers that do not have fractions or decimals.
Can natural numbers be negative or include fractions?
-No, natural numbers are always positive whole numbers, including zero, and they do not include negative numbers or fractions.
What is the difference between even and odd natural numbers?
-Even numbers are those that can be divided by 2 without leaving a remainder (e.g., 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, ...). Odd numbers, on the other hand, cannot be divided by 2 evenly (e.g., 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, ...).
What is the significance of the number 0 in natural numbers?
-Zero is the starting point of the natural number sequence. It represents the absence of quantity, and it is a part of the natural numbers but has no predecessor in the natural number system.
How do we represent natural numbers on a number line?
-Natural numbers are represented on a number line starting from 0, and each number is placed at equal intervals. The sequence continues infinitely to the right.
What does the symbol '>' and '<' represent when comparing natural numbers?
-'>' means 'greater than,' and '<' means 'less than.' When comparing two natural numbers, the symbol points to the smaller number, and the larger number is represented by the open side of the symbol (like a mouth of a hungry alligator).
What is a successor and a predecessor in relation to natural numbers?
-The successor of a natural number is the number that comes immediately after it (for example, the successor of 5 is 6), and the predecessor is the number that comes immediately before it (for example, the predecessor of 5 is 4).
What are even and odd numbers examples based on counting pairs?
-Even numbers can be paired up without any leftovers, such as 2 socks making 1 pair. Odd numbers cannot be fully paired, for example, 7 socks form 3 full pairs with 1 leftover.
What is the difference between finite and infinite sequences of numbers?
-A finite sequence has a definite end, while an infinite sequence continues without an end. For example, a sequence like 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5... is infinite, while a sequence like 1, 4, 7, 10 (with a clear stopping point) is finite.
How do you find the next number in a sequence of natural numbers?
-To find the next number in a sequence of natural numbers, simply add 1 to the current number (for example, after 4, the next number is 5).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Usos de "USED TO" en inglés: cómo usar "used to" en inglés

pola bilangan kelas 8 part 1 (mudah)

BELAJAR KONSEP HIMPUNAN BILANGAN RIIL DALAM 3 MENIT !
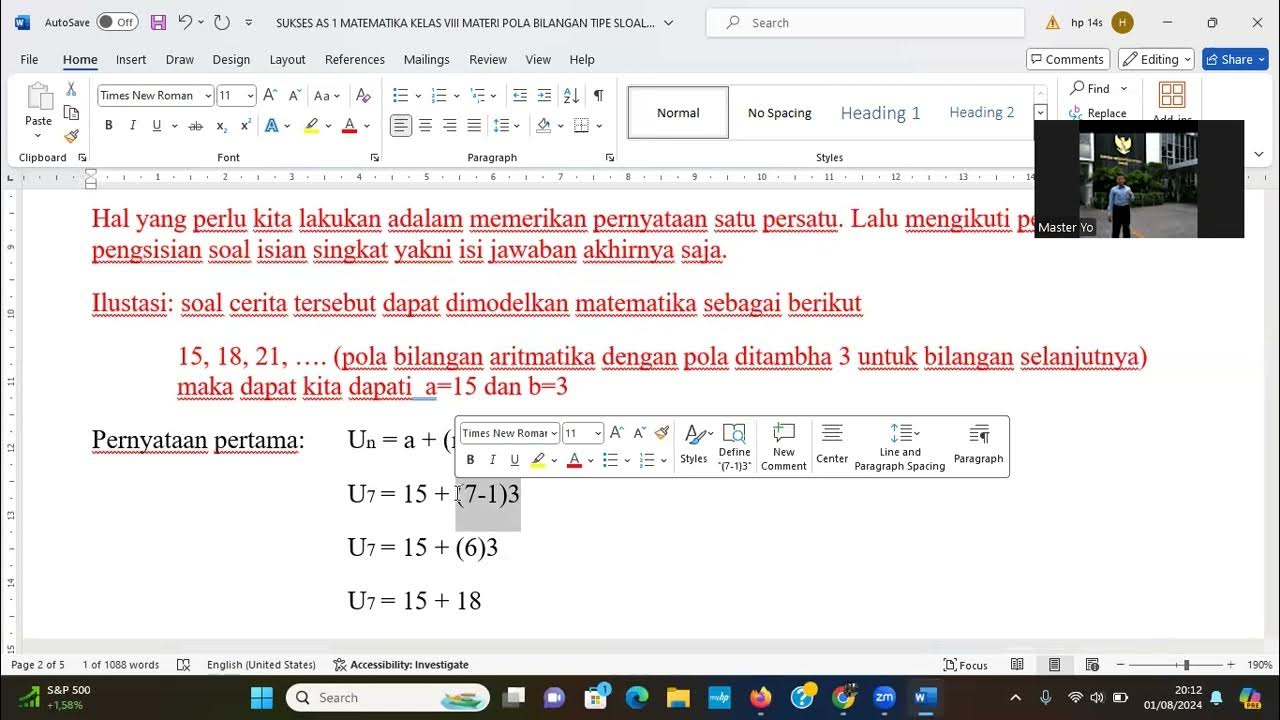
Latihan Soal Pola Bilangan

[Video Edukasi] Tematik Kelas 1 : Pola Bilangan

Kalkulus | Barisan dan Deret Tak Hingga (Part 1) - Definisi dan Penulisan Barisan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
