Contração Muscular - Resumo Professor Gustavo Schmidt
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of muscle contraction in skeletal muscles, highlighting the structure of muscle fibers (myocytes) and the role of sarcomeres, which are made of actin and myosin filaments. The contraction is triggered by a nerve impulse that releases acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction, followed by calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcium enables myosin to bind to actin, and ATP provides the energy for the movement. As myosin pulls actin, the sarcomere shortens, resulting in muscle contraction. Key factors for contraction include nerve stimulation, calcium, and ATP.
Takeaways
- 😀 Skeletal muscles are made of myocytes (muscle fibers), which are composed of myofibrils.
- 😀 Myofibrils are divided into sarcomeres, the fundamental contractile units of muscle.
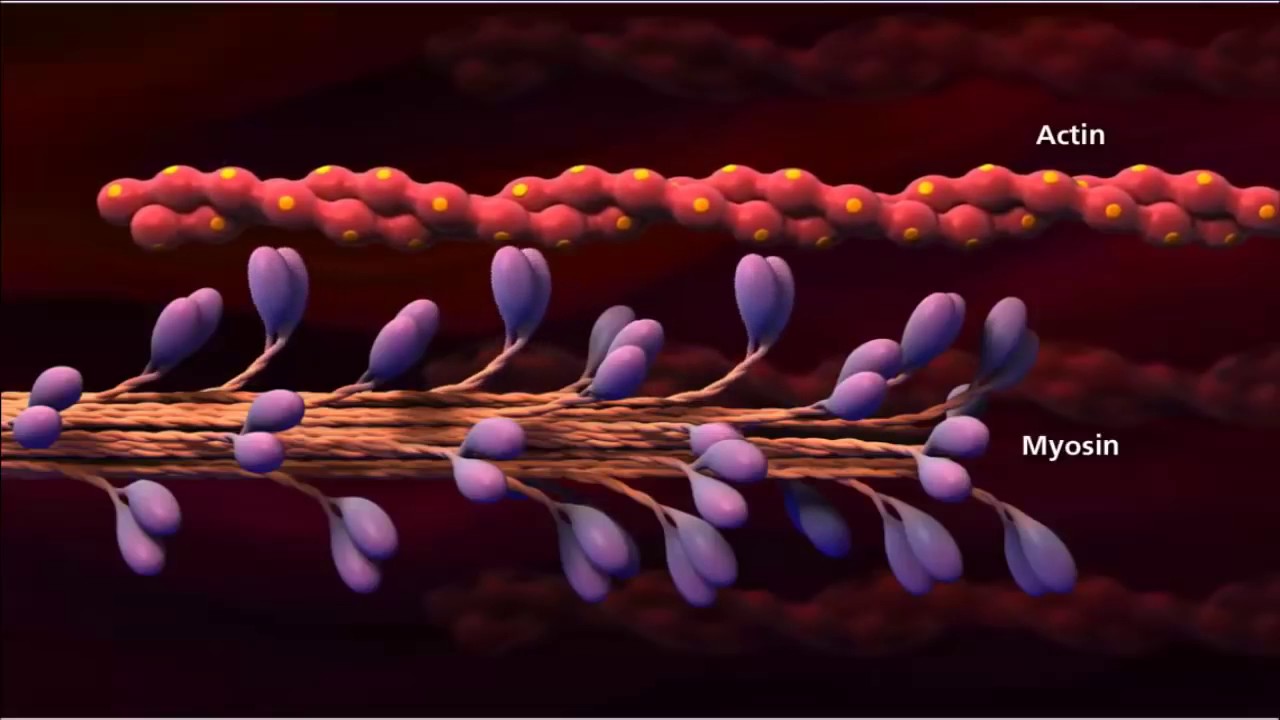
- 😀 Sarcomeres contain thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments, which interact during muscle contraction.
- 😀 Muscle contraction occurs when myosin binds to exposed binding sites on actin, pulling the actin filaments.
- 😀 The binding sites on actin are blocked by tropomyosin until calcium is released into the cytoplasm.
- 😀 Calcium ions bind to troponin, which causes tropomyosin to shift, exposing the binding sites on actin.
- 😀 ATP is required for the myosin heads to attach to actin and perform the power stroke, causing muscle contraction.
- 😀 A nerve stimulus is essential to initiate muscle contraction by transmitting a signal from the motor neuron.
- 😀 The neuromuscular junction is where the motor neuron communicates with the muscle, using the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
- 😀 The stimulus travels through T-tubules to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which releases calcium into the muscle fibers.
- 😀 The essential steps for muscle contraction are: 1) Nerve stimulus, 2) Calcium release, and 3) ATP utilization.
Q & A
What is the structure of skeletal muscle?
-Skeletal muscle is attached to bones by tendons and is made up of muscle fibers (myocytes). These fibers contain myofibrils, which are further composed of repeating contractile units called sarcomeres.
What is the role of myofibrils in muscle contraction?
-Myofibrils are the key components of muscle fibers responsible for contraction. They contain the contractile units, sarcomeres, which consist of actin and myosin filaments, crucial for the muscle's ability to contract.
What are sarcomeres and how do they contribute to muscle contraction?
-Sarcomeres are the repeating contractile units within myofibrils. They contain actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments), whose interaction leads to the contraction of the muscle.
What is the function of acetylcholine in muscle contraction?
-Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used by the nervous system to transmit the nerve impulse from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction, initiating muscle contraction.
How does a nerve impulse travel to stimulate muscle contraction?
-The nerve impulse travels from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber at the neuromuscular junction. From there, it is conducted through the T-tubules to the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which releases calcium ions to trigger contraction.
Why is calcium important for muscle contraction?
-Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm. Calcium binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to shift, which exposes binding sites on actin, allowing myosin to attach and begin muscle contraction.
What role does ATP play in muscle contraction?
-ATP provides the energy needed for the myosin heads to bind to actin and perform the power stroke, pulling the actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere, leading to muscle contraction.
What happens at the neuromuscular junction?
-At the neuromuscular junction, a motor neuron releases acetylcholine, which stimulates the muscle fiber to generate an action potential. This leads to the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, initiating muscle contraction.
What is the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
-Tropomyosin blocks the binding sites on actin, preventing myosin from attaching during muscle relaxation. When calcium binds to troponin, it causes a conformational change that moves tropomyosin, allowing myosin to bind and contract the muscle.
How does the sarcomere shorten during muscle contraction?
-The myosin heads bind to exposed sites on actin, pulling the actin filaments toward the center of the sarcomere. This sliding action of actin over myosin shortens the sarcomere and leads to muscle contraction.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)