[#1] OVÁRIOS: OVOGÊNESE E FOLICULOGÊNESE | MK Fisiologia
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Miriam Caut introduces ovarian physiology, detailing the structure and functions of the ovaries as key endocrine and reproductive glands. She explains the processes of oogenesis, where oocytes develop from primordial to mature stages, and folliculogenesis, the growth of ovarian follicles, regulated by hormones like FSH and LH. The video emphasizes the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle and the interplay between these processes, inviting viewers to deepen their understanding of human physiology. Stay tuned for the next video focusing on hormonal regulation.
Takeaways
- 😀 The ovaries are endocrine glands part of the female reproductive system located in the peritoneal cavity.
- 🌸 Oogenesis is the process of generating the female gamete (oocyte) that begins before birth and ends with ovulation during the menstrual cycle.
- 🔍 Folliculogenesis accompanies oogenesis and involves the development of ovarian follicles, starting from primordial follicles to mature follicles.
- 🩸 Hormones like estrogen and progesterone are primarily produced and secreted by ovarian follicles before and after ovulation.
- 📅 A woman's ovaries contain approximately 300,000 to 400,000 primordial follicles by puberty, but only a few will mature and be ovulated throughout her reproductive life.
- ⏳ The development of follicles includes both a slow phase (lasting around 85 days) and a rapid phase that coincides with the menstrual cycle.
- ⚖️ Follicular development is regulated by hormones from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, primarily follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH).
- 🔄 The luteal phase involves the transformation of the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum, which produces hormones if fertilization occurs.
- ❌ If the oocyte is not fertilized, the corpus luteum regresses into a scar-like structure called the corpus albicans, marking the end of one cycle and the start of another.
- 📖 The video serves as an introduction to the ovarian functions, emphasizing the importance of understanding both oogenesis and folliculogenesis in female reproductive health.
Q & A
What are the primary functions of the ovaries?
-The primary functions of the ovaries are oogénesis (the generation of the ovum), foliculogénesis (the development of ovarian follicles), and the production of ovarian hormones, mainly estrogen and progesterone.
How do the ovaries relate to the female reproductive system?
-The ovaries are endocrine glands that are part of the female reproductive system, located in the peritoneal cavity alongside other reproductive organs such as the uterine tubes and uterus.
What is the role of the corpus luteum?
-The corpus luteum is formed from the remnants of the mature follicle after ovulation and is primarily responsible for the synthesis and secretion of hormones like progesterone and estrogen following ovulation.
What happens to the corpus luteum if fertilization occurs?
-If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum continues to produce hormones to support the early stages of pregnancy. If fertilization does not occur, it regresses and forms a scar known as the corpus albicans.
How does the ovarian follicle develop through the menstrual cycle?
-Ovarian follicles undergo a slow development phase before the menstrual cycle and a rapid development phase during the cycle. The rapid phase is triggered by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), resulting in the maturation of one dominant follicle.
What is the difference between oogenesis and spermatogenesis?
-Oogenesis occurs in the ovaries and begins before birth, producing a limited number of ova, whereas spermatogenesis occurs in the testes, starting at puberty and continuing throughout life, resulting in a continuous supply of sperm.
What hormonal changes occur during the menstrual cycle related to folliculogenesis?
-During the menstrual cycle, FSH stimulates the rapid development of antral follicles, while luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers ovulation and supports the transformation of the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum.
At what stage does a primary oocyte complete its meiosis?
-A primary oocyte completes its meiosis only if it is fertilized by a sperm cell. Otherwise, it remains in the metaphase of meiosis II until fertilization occurs.
What is atresia in relation to ovarian follicles?
-Atresia refers to the degeneration of ovarian follicles that do not mature. This process occurs during fetal development and childhood, resulting in the loss of many primordial and primary follicles.
What role do granulosa cells play in follicular development?
-Granulosa cells nourish the oocytes and form protective layers around them, contributing to the structure of the ovarian follicles and producing hormones that aid in follicular development.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Macam macam Kelenjar endokrin pada manusia - Biologi bab. sistem hormonal/sistem endokrin kls 11

Histology of the Ovary and Ovarian Follicles [Female Reproductive Histology Part 1 of 2]

GCSE Biology - Endocrine System & Hormones #59
Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology | 3D Glands & Hormones Animation

tugas Ilmu Biomedik Dasar, tentang sistem endokrim. Kelompok 2
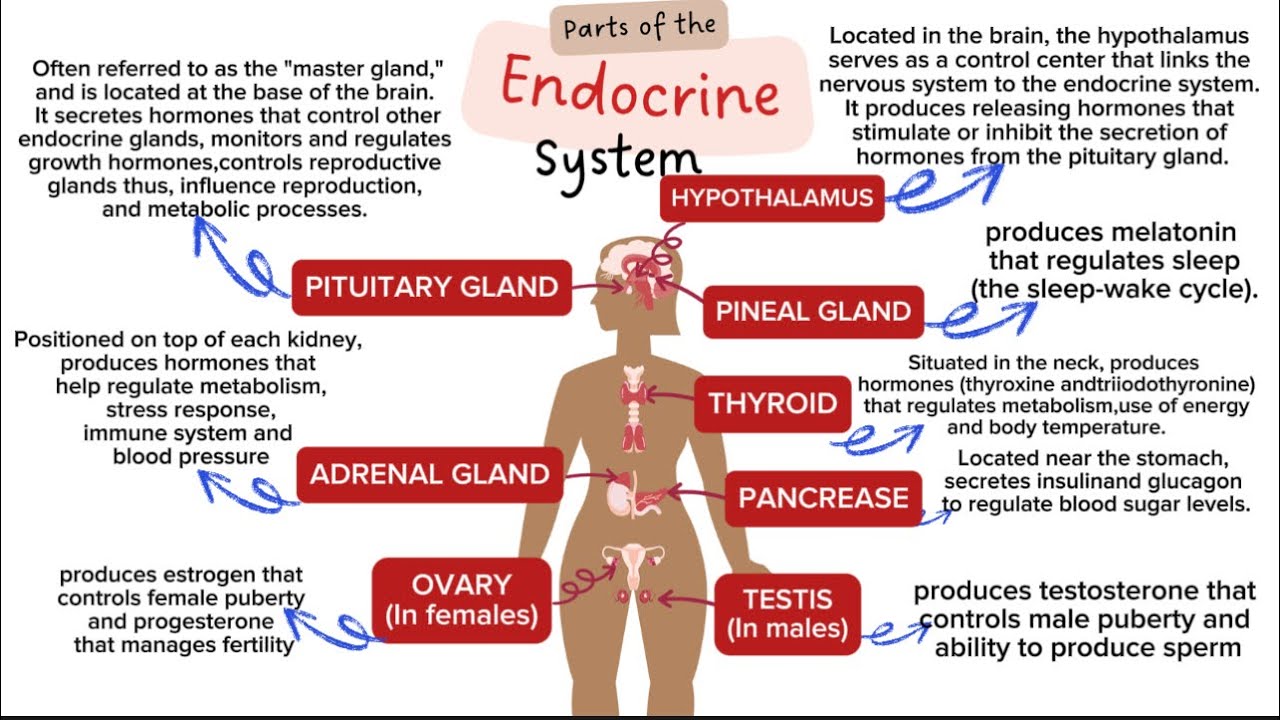
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM : What It Is, Parts and Functions of the Endocrine System.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
