Mitosis: How One Cell Becomes Two
Summary
TLDRProfessor Dave's script delves into the intricate process of mitosis, a fundamental aspect of cell division. It outlines the five phases—prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase—culminating in cytokinesis, resulting in two genetically identical cells. The script explains the role of centrosomes, microtubules, and kinetochores in organizing and separating chromosomes, highlighting the cell cycle's G2 phase and the M checkpoint. This educational narrative offers a clear insight into the continuous cellular renewal in the human body.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical cells.
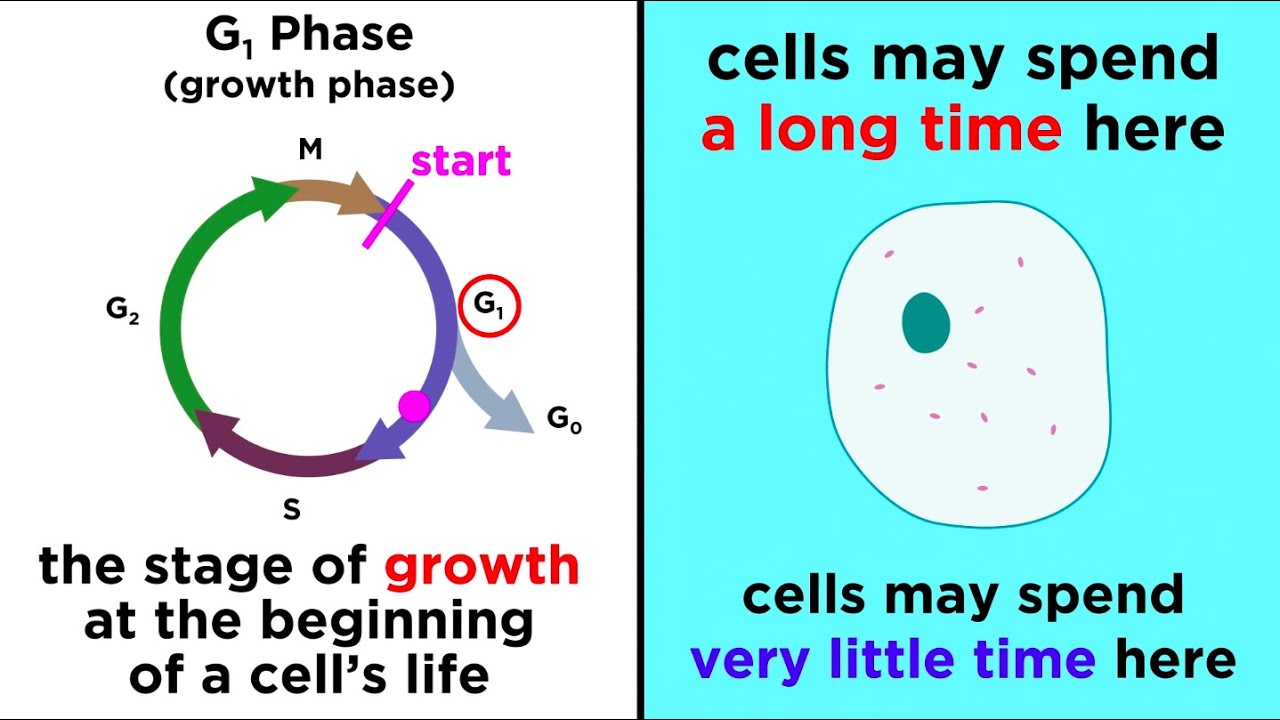
- 📚 The cell cycle includes preparation for cell division and the actual process of mitosis.
- 🌀 Mitosis is divided into five phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, followed by cytokinesis.
- 🧬 Before mitosis, the cell has two copies of all chromosomes in a loose state, and the centrosome has duplicated.
- 🧵 During prophase, chromatin coils to form chromosomes, and the mitotic spindle begins to form from the centrosomes and microtubules.
- 🌌 In prometaphase, the nucleus breaks apart, and microtubules from the spindle attach to kinetochores on the chromosomes.
- 🧲 Metaphase sees chromosomes align at the metaphase plate with centrosomes at cell poles, ensuring attachment to the spindle.
- 🛑 There is a checkpoint in metaphase to confirm that sister chromatids are attached to opposite spindle ends.
- 💔 Anaphase is the shortest phase, where separase cleaves cohesins, and sister chromatids are pulled apart by kinetochores.
- 🌈 Telophase involves the formation of two new nuclei from the original nucleus fragments, with chromosomes loosening and spindle fibers disassembling.
- 💥 Cytokinesis completes the cell division by dividing the cytoplasm and physically separating the two new cells.
- 👶 Mitosis is essential for growth, healing, and the production of new somatic cells, except for the first fertilized egg cell.
Q & A
What is mitosis and why is it important?
-Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in multicellular organisms.
What are the five phases of mitosis mentioned in the script?
-The five phases of mitosis are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What happens during the prophase of mitosis?
-During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, sister chromatids are formed, and the mitotic spindle begins to form from the centrosomes.
What is the function of the mitotic spindle?
-The mitotic spindle is a structure composed of microtubules that helps in the separation and movement of chromosomes to opposite ends of the cell during cell division.
What occurs in the prometaphase of mitosis?
-In prometaphase, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and microtubules attach to kinetochores on the chromosomes, preparing for the separation of sister chromatids.
Why is the metaphase plate significant during metaphase?
-The metaphase plate is an imaginary plane where all chromosomes align at the center of the cell, ensuring equal distribution of genetic material during cell division.
What is the role of the enzyme separase in anaphase?
-Separase cleaves the cohesin proteins that hold sister chromatids together, allowing them to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
What changes occur during telophase?
-In telophase, two new nuclei form, chromosomes decondense, and the mitotic spindle disassembles, marking the end of mitosis.
What is cytokinesis and how does it relate to mitosis?
-Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm and cellular contents into two daughter cells following mitosis, resulting in two separate and distinct cells.
How does the process of mitosis contribute to the body's ability to heal and grow?
-Mitosis allows for the production of new cells, which is essential for healing wounds, replacing damaged cells, and supporting growth during development.
What is the difference between mitosis and the process that produces gametes?
-Mitosis produces genetically identical somatic cells, while gametes are produced through a different process called meiosis, which results in cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)