Introduction to Cells: The Grand Cell Tour
Summary
TLDRThe Amoeba Sisters take viewers on an engaging journey inside a cell, exploring the modern cell theory and the fascinating world of cellular biology. From the single-celled amoeba to the complex structures of multicellular organisms, they explain the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting the roles of various organelles like the nucleus, ribosomes, and mitochondria. The video script is a lively introduction to the cell's inner workings, emphasizing the importance of each component in maintaining life.
Takeaways
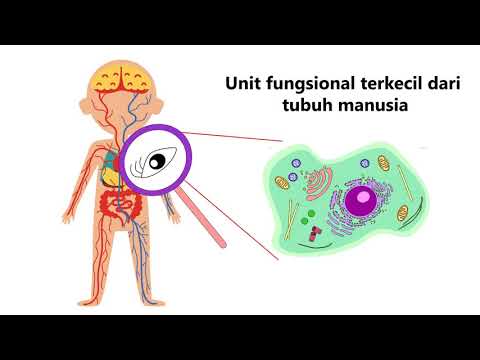
- 🔬 The modern cell theory states that all living things are composed of one or more cells, which are the smallest living units in organisms.
- 🌿 Amoebas are single-celled organisms that can perform all life functions within one cell, highlighting the complexity of cellular life.
- 🧬 Cells can be categorized as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic, with the main difference being the presence of a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes.
- 🌐 The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is selectively permeable, maintaining homeostasis by controlling the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
- 🌀 The cytoskeleton provides support and can facilitate movement within the cell, playing a crucial role in the organization of cellular components.
- 🏭 Ribosomes are non-membrane-bound organelles found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, responsible for protein synthesis based on DNA codes.
- 🧠 The nucleus is the control center of eukaryotic cells, containing genetic material and regulating cell activities, with the nucleolus being the site of ribosome production.
- 🛣️ The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in protein folding and transportation, with the rough ER being associated with ribosomes for protein synthesis and the smooth ER having additional roles like detoxification.
- 📦 The Golgi apparatus functions as the cell's packaging center, modifying and sorting molecules for various destinations, including secretion outside the cell.
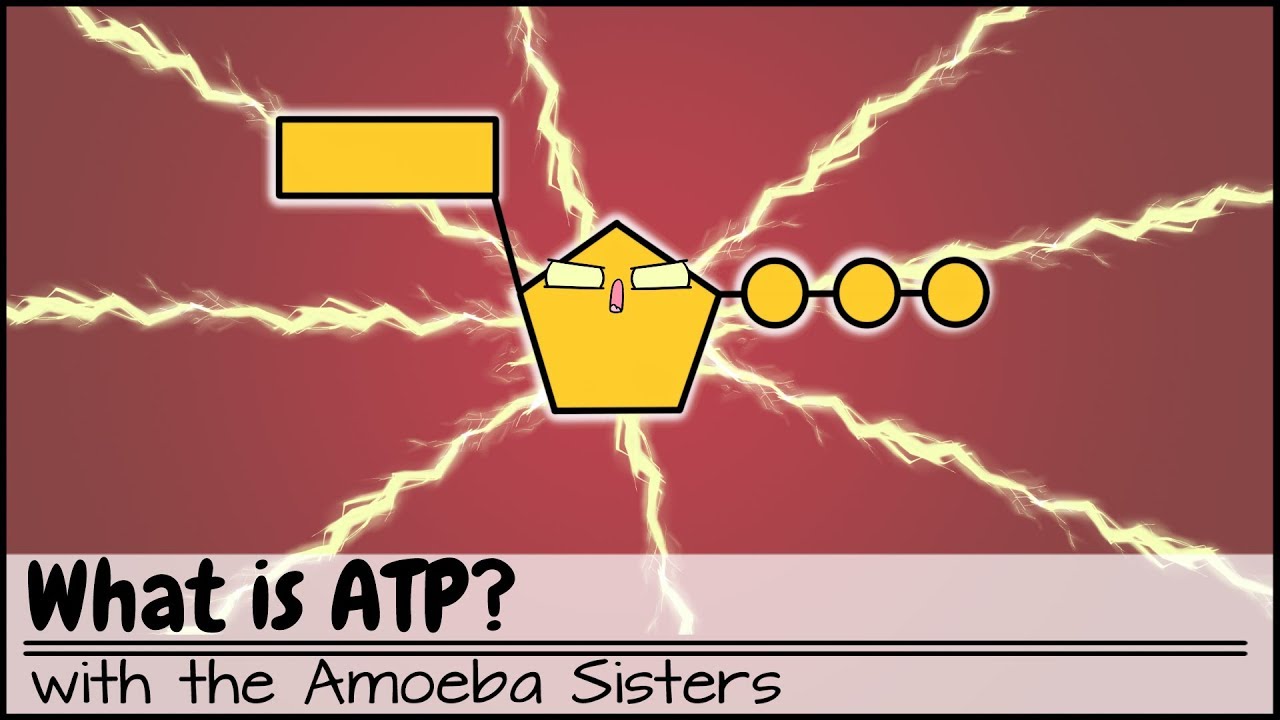
- 💪 Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, generating ATP through cellular respiration, and are essential for energy production in eukaryotic cells.
- 🌱 Plant cells have unique organelles like chloroplasts, which produce glucose through photosynthesis, and often contain a large central vacuole for storage, in addition to the cell wall for structural support.
Q & A
What was the most memorable day in the narrator's 9th grade science class?
-The most memorable day was when the teacher brought in pond water, and the narrator saw an amoeba under the microscope, which sparked a lifelong interest in science.
What are the three main points of the modern cell theory?
-The three main points are: 1) The cell is the smallest living unit in all organisms. 2) All living things are made of one or more cells. 3) All cells come from pre-existing cells.
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms?
-Unicellular organisms, like amoebas, are composed of a single cell. Multicellular organisms, like humans, are made up of many cells.
What are the two major groups of cells on our planet?
-The two major groups are prokaryotes, which include bacteria and archaea, and eukaryotes, which include plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
What are the similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have genetic material, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and cell membranes.
What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-The primary difference is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both.
What is the function of the cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane?
-The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing only certain materials to pass in and out, thus maintaining the stability and homeostasis of the cell.
What is the role of ribosomes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Ribosomes are responsible for making proteins, which are coded by genetic material such as DNA.
What is the nucleus and what does it contain?
-In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is the membrane-bound organelle that holds the genetic material, such as DNA, and controls cell activities. It also contains the nucleolus, where ribosomes are produced.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
-The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the processing of molecules, such as protein folding, and in the transportation of these molecules throughout the cell.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus acts as the cell's packaging center, modifying and sorting molecules it receives from the ER, and determining their final destinations, including secretion outside the cell.
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
-Mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP energy through the process of cellular respiration, using glucose and oxygen.
How do plant cells differ from animal cells in terms of energy production?
-Plant cells contain chloroplasts, which produce glucose using light energy through photosynthesis, in addition to mitochondria for cellular respiration.
What is the function of vacuoles in cells?
-Vacuoles serve various functions, including storage of materials. In plant cells, there is often one large central vacuole, while animal cells may have several smaller vacuoles.
What is the additional structure that plant cells have compared to animal cells?
-Plant cells have a cell wall, which provides additional protection and helps maintain the cell's shape, a feature not present in animal cells.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)