video1935403234 Trim
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the speaker introduces the importance of measurement in science, emphasizing its role in ensuring accuracy and repeatability. The video covers basic and derived quantities, explaining fundamental units like length, mass, time, and electric current, as well as derived units like speed, force, and energy. The speaker also highlights the international system of units and the tools used for measuring various quantities, such as rulers, vernier calipers, thermometers, and voltmeters. The session concludes with a reminder to study measurement tools for an upcoming lesson.
Takeaways
- 😀 Measurement is crucial in science to ensure accuracy and repeatability in experiments and findings.
- 😀 There are two types of quantities: basic quantities and derived quantities.
- 😀 Basic quantities include length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, light intensity, and amount of substance.
- 😀 Derived quantities are formed from basic quantities, such as speed, volume, force, and energy.
- 😀 The International System of Units (SI) standardizes measurements globally, using units like meter (m), kilogram (kg), and second (s).
- 😀 Seven basic quantities are defined internationally: length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, light intensity, and amount of substance.
- 😀 Derived quantities like speed, area, and energy can be expressed through combinations of the basic units.
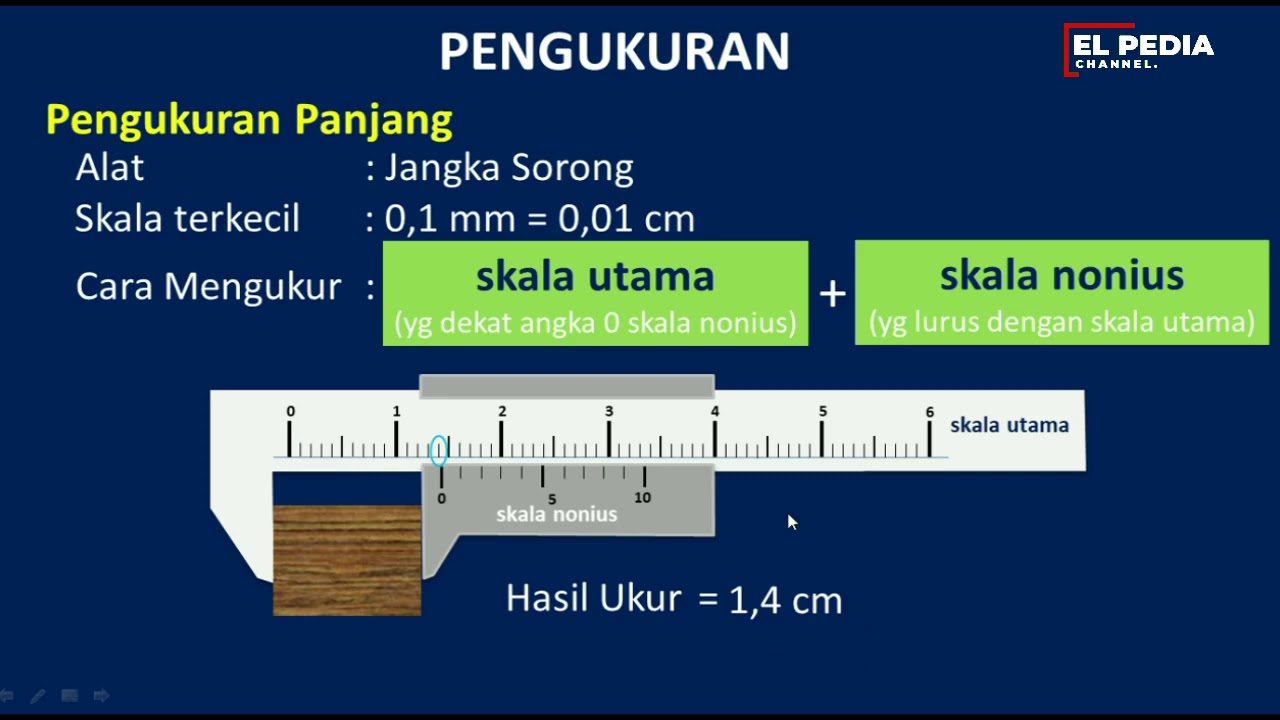
- 😀 Precision in measurement is determined by the tool used, with smaller values indicating greater precision (e.g., micrometers are more precise than rulers).
- 😀 Measurement tools for different quantities include rulers for length, balances for mass, and stopwatches for time.
- 😀 Understanding derived quantities and their respective units, like force (Newton) or energy (Joule), is key for scientific calculations.
- 😀 Various instruments, like ammeters, voltmeters, and pressure sensors, are essential for measuring electrical properties and other physical quantities.
Q & A
What are the two types of quantities discussed in the lesson?
-The two types of quantities discussed are basic quantities and derived quantities. Basic quantities include length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, amount of substance, and light intensity. Derived quantities are combinations of these basic quantities, such as speed, volume, and force.
What is the importance of measurement in science?
-Measurement is crucial in science because precise measurements ensure that results are accurate, repeatable, and understandable. Without precise measurements, scientific experiments would lack clarity and consistency.
Why are international units important in scientific measurements?
-International units are important because they allow scientists worldwide to use the same standards, ensuring consistency and preventing confusion or mistakes in scientific work. Examples include the meter for length, kilogram for mass, and second for time.
What are some examples of derived quantities?
-Examples of derived quantities include speed (m/s), area (m²), volume (m³), force (N), energy (J), and power (W). These quantities are derived from basic quantities like length, mass, and time.
What is the symbol for electric current and what is its SI unit?
-The symbol for electric current is 'I', and its SI unit is the ampere (A).
How are derived quantities formed from basic quantities?
-Derived quantities are formed by combining basic quantities through mathematical operations. For example, speed is derived from length divided by time (m/s), and force is derived from mass multiplied by acceleration (N).
What are the seven basic quantities in the International System of Units (SI)?
-The seven basic quantities in SI are length (L), mass (M), time (T), temperature (K), electric current (A), amount of substance (mol), and light intensity (cd).
What is the formula for calculating speed, and what is its unit?
-Speed is calculated as distance divided by time. The unit for speed is meters per second (m/s).
What is the most accurate tool for measuring length, based on the script?
-The most accurate tool for measuring length is the screw micrometer, which has an accuracy of 0.01 mm.
Which tool is used to measure the electric current and voltage, and what is its unit?
-The ammeter and multimeter are used to measure electric current, while the voltmeter and multimeter are used for measuring voltage. The units for electric current and voltage are amperes (A) and volts (V), respectively.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)