Video Animasi – Perkembangan penyakit hati NASH dari hati yang sehat kepada sirosis
Summary
TLDRThe liver plays a vital role in nutrient metabolism, particularly through specialized cells called hepatocytes, which regulate lipid metabolism and transform excess glucose into fatty acids. Unhealthy lifestyle habits can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and if left unchecked, it can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), causing liver damage, inflammation, and fibrosis. NASH increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and can evolve into cirrhosis or liver cancer. The rising global prevalence of obesity and diabetes makes NASH a growing concern, highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatments to address this silent epidemic.
Takeaways
- 😀 The liver plays a critical role in nutrient metabolism, carried out by specialized cells called hepatocytes.
- 😀 Hepatocytes can convert excess glucose into fatty acids through a process known as de novo synthesis.
- 😀 Hepatocytes also regulate lipid metabolism by taking up fatty acids from the blood and combining them with glycerol to form triglycerides.
- 😀 An unhealthy diet and lack of physical activity can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) with isolated steatosis, which involves abnormal fat accumulation in hepatocytes.
- 😀 Individuals with metabolic disorders like insulin resistance, type-2 diabetes, and obesity are at higher risk of developing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
- 😀 In NASH, liver homeostasis is disrupted by the accumulation of toxic lipids, causing inflammation and hepatocyte damage.
- 😀 Certain gut bacteria-derived products penetrate the liver and activate immune responses, leading to local inflammation and tissue damage.
- 😀 Ballooning, steatosis, and inflammation are the three main lesions defining NASH histologically.
- 😀 Hepatocyte apoptosis and inflammation trigger the activation of hepatic stellate cells, which release collagen fibers, leading to hepatic fibrosis.
- 😀 NASH can progress to cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma and is also associated with increased cardiovascular risks due to a pro-atherogenic lipid profile.
- 😀 NASH is a growing global concern, especially with rising rates of diabetes and obesity, and is predicted to become the leading cause of liver transplantation by 2020.
- 😀 There is an urgent need to develop innovative treatments targeting the various aspects of NASH pathology to combat this silent epidemic.
Q & A
What are the main functions of the liver, as discussed in the script?
-The liver is responsible for vital functions such as nutrient metabolism, including glucose transformation and lipid metabolism. It also regulates fat storage and produces important molecules like triglycerides.
How do hepatocytes contribute to nutrient metabolism?
-Hepatocytes are specialized liver cells that play a crucial role in nutrient metabolism. They can convert excess glucose into fatty acids (de novo synthesis) and regulate lipid metabolism by taking up fatty acids from the blood and forming triglycerides.
What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and how does it develop?
-NAFLD is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver without alcohol consumption. It can develop due to unhealthy lifestyle habits, including poor diet and lack of physical activity, leading to isolated steatosis, which is abnormal fat accumulation in hepatocytes.
What is the difference between NAFLD and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)?
-While NAFLD involves fat accumulation in the liver, NASH is a more severe condition where the fat accumulation leads to liver inflammation, hepatocyte ballooning, and cellular damage. NASH can progress to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer.
What role do gut bacteria play in the development of NASH?
-Certain gut bacteria-derived products can penetrate the liver, triggering immune responses that contribute to local inflammation in hepatic tissue. This inflammation worsens liver damage and accelerates the progression to NASH.
What are the three lesions that define NASH histologically?
-The three histological lesions that define NASH are steatosis (fat accumulation), inflammation, and hepatocyte ballooning.
What are hepatic stellate cells, and what is their role in liver fibrosis?
-Hepatic stellate cells are involved in liver fibrosis. When activated by liver damage, they secrete collagen fibers that form scar tissue, which leads to the progression of fibrosis and potential cirrhosis.
How does NASH affect cardiovascular health?
-NASH increases the risk of cardiovascular events due to a pro-atherogenic lipid profile in affected patients, which promotes the development of arterial plaque and other cardiovascular issues.
What factors contribute to the rising global prevalence of NASH?
-The rising global prevalence of NASH is primarily linked to the increasing rates of obesity and type-2 diabetes, both of which are major risk factors for the development and progression of NASH.
Why is there an urgent need for innovative treatments for NASH?
-As NASH is rapidly becoming a leading cause of liver transplantation and significantly contributes to liver-related mortality and cardiovascular diseases, there is an urgent need for treatments that address the multiple aspects of NASH pathology.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Liver Function 3, Carbohydrate storage and metabolism

Fatty Acid Synthesis - Part I

122-Summary of Lipid Metabolism

Destino del esqueleto de carbonos | Catabolismo de aminoácidos - Parte 2

Insulin Resistance Explained! What Is Insulin Resistance & How It Leads To Type II Diabetes?
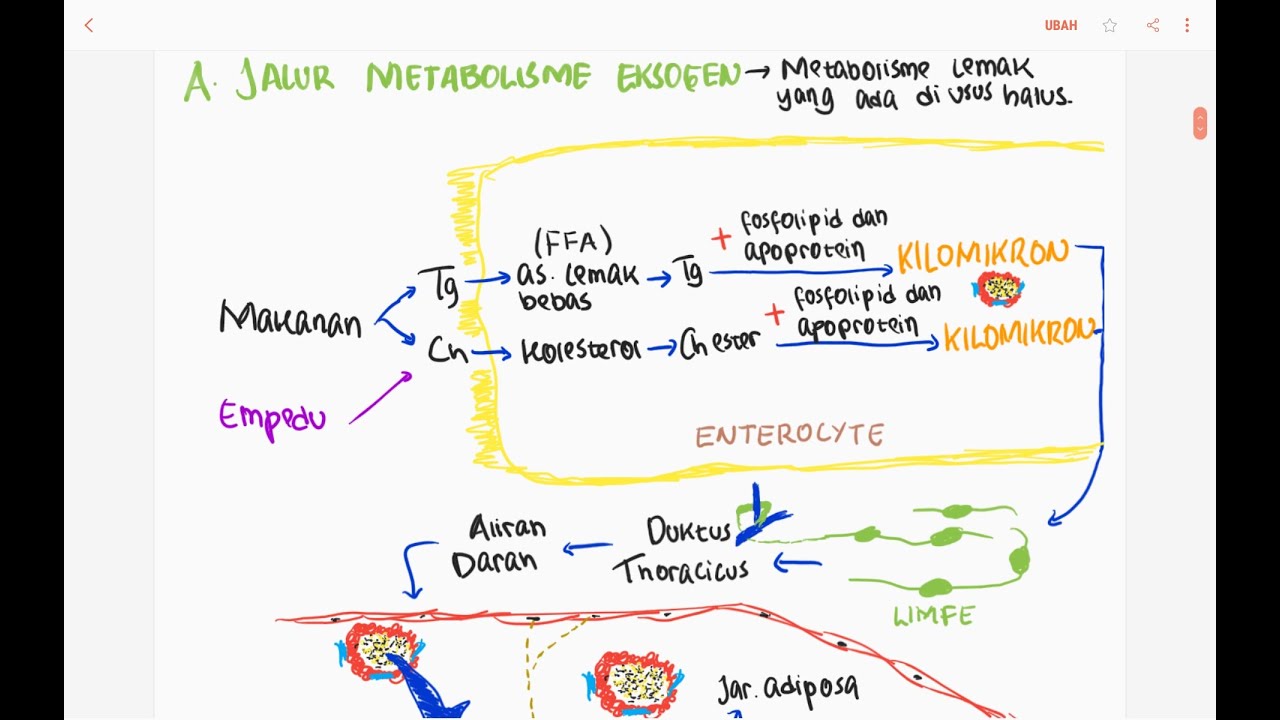
Metbolisme Lipid 1 : Jalur Eksogen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
