Jenis-jenis Perairan Darat #kumer
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video on Earth science, the presenter discusses various types of terrestrial waters, including rivers, lakes, swamps, and groundwater. The video explores how these water bodies form, their characteristics, and classifications, such as rivers sourced by rain, glaciers, or a mix of both. The video also touches on different lake types, like volcanic, tectonic, and artificial lakes, as well as swamp classifications based on location and water quality. The video concludes with a detailed look at groundwater, its distribution in Indonesia, and its importance to life, emphasizing the need to protect this valuable resource.
Takeaways
- 😀 Water bodies on land include rivers, lakes, swamps, and groundwater, all of which are primarily sourced from rainwater.
- 😀 Rivers are freshwater bodies that flow from higher altitudes to lower areas, forming different profiles in the upstream, midstream, and downstream.
- 😀 Rivers can be classified based on their water source: rainwater, glacier melt, or a combination of both.
- 😀 Rivers are also categorized by their flow patterns, such as perennial (year-round), intermittent (seasonal), episodic (only during the rainy season), and ephemeral (present only during the rainy season).
- 😀 River flow patterns can vary and include parallel, dendritic, trellis, rectangular, and radial patterns depending on the terrain and geological features.
- 😀 Rivers are classified based on their genetic origin as well, such as consequent, consequent branch, obsequent, and re-sequent rivers, which follow different structural or geological influences.
- 😀 Lakes are large depressions filled with water and can be classified based on their formation, such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, or man-made lakes.
- 😀 Swamps are shallow water bodies often surrounded by wetlands, and their classification depends on their location (inland, near rivers, or coastal) and the type of water (fresh, salty, or brackish).
- 😀 Groundwater is water stored in the soil or rock layers beneath the earth's surface and is categorized into shallow and deep groundwater based on their position and accessibility.
- 😀 The preservation of groundwater and other water bodies is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and human use, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
Q & A
What are the types of inland waters discussed in the video?
-The types of inland waters discussed include rivers, lakes, swamps, and groundwater.
What defines inland water?
-Inland water refers to all forms of water found on land, including liquid, ice, or snow, and it encompasses rivers, lakes, swamps, and groundwater.
What is the primary source of most inland water?
-The majority of inland water comes from rainfall.
How are rivers classified based on their water source?
-Rivers can be classified into four types based on their water source: rain-fed, glacier-fed, mixed (from springs, rain, and melting snow), and ephemeral (which only flows during the rainy season).
What are the different stages of a river's profile?
-A river's profile is divided into three stages: the upper course (with a V-shaped valley and steep cliffs), the middle course (U-shaped valley with horizontal and vertical erosion), and the lower course (wide U-shaped valley, often leading to the formation of deltas or oxbow lakes).
What are the types of lakes mentioned in the video?
-Lakes are classified into volcanic, tectonic, tectonic-volcanic, dammed, glacial, and karst lakes.
What are swamp types based on their location?
-Swamps can be classified based on location into three types: inland swamps, river-side swamps, and coastal swamps.
What factors classify swamps based on water characteristics?
-Swamps can be classified by the salinity of their water into freshwater, brackish, and saltwater swamps.
What are the different types of groundwater?
-Groundwater is categorized into shallow or phreatic groundwater (which is found above impermeable layers) and deep or artesian groundwater (which is found between two impermeable layers).
What is the significance of groundwater conservation?
-Groundwater is a vital resource for many forms of life, and it is important to manage and preserve it for sustainable use.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Geografi Kelas X (29) Perairan Darat | Jenis Perairan Darat (Air Tanah, sungai, danau, rawa)

Dinamika Perairan Darat

Sources of Freshwater

TEKTONISME DAN PENGARUHNYA TERHADAP KEHIDUPAN (TUGAS GEOGRAFI SMA NEGERI 1 TABANAN)
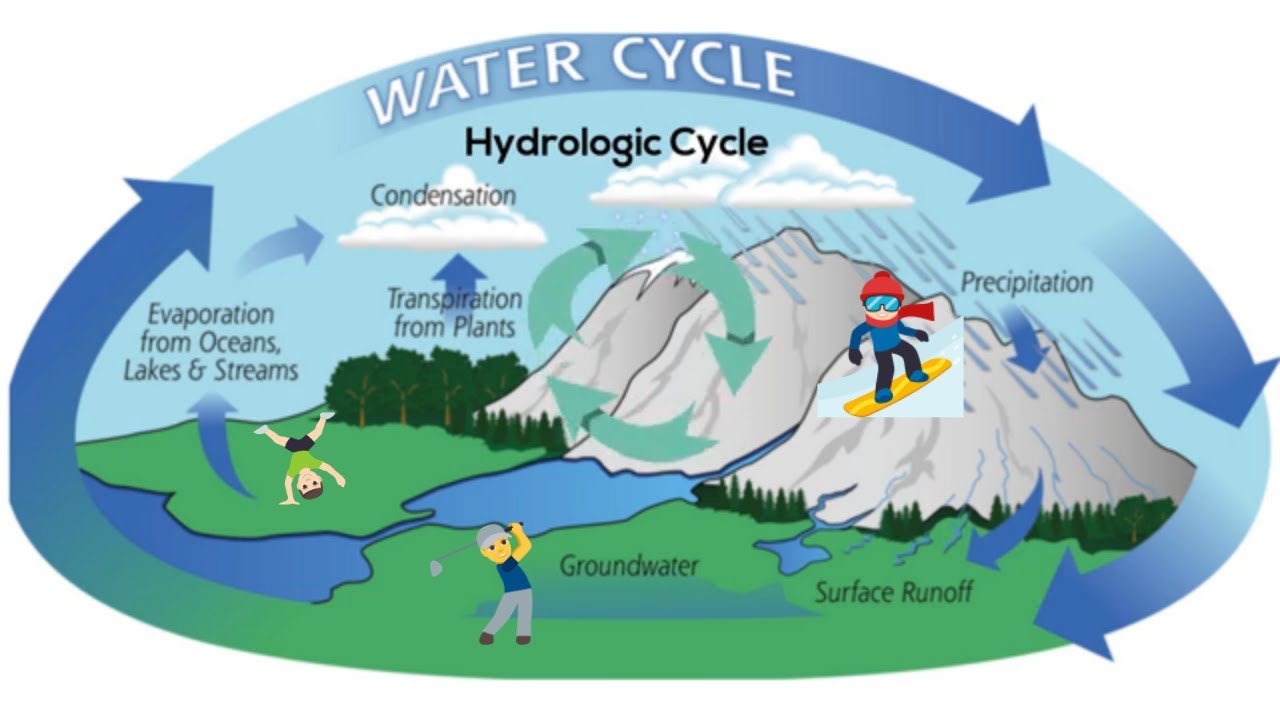
The water (hydrologic) cycle

SIKLUS HIDROLOGI DAN PERAIRAN DARAT #geography #air #danau #rawa #sungai #kurikulummerdeka
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
