10 клас. Фізика. Доцентрове (нормальне) прискорення
Summary
TLDRIn this physics class, Victor Sklyarov concludes the study of linear and curvilinear kinematics by exploring centripetal acceleration in uniform circular motion. He uses the example of a French island, Réunion, and a game show to explain the concept. The lesson covers the formula for centripetal acceleration, its direction towards the circle's center, and its dependence on speed and radius. A problem-solving example calculates the speed of a bicycle wheel given its centripetal acceleration and radius, concluding with the wheel's rotational speed.
Takeaways
- 🌐 The script is about physics lessons for 10th grade, focusing on linear and curvilinear kinematics.
- 🏝 Victor Sklyarov introduces the topic by mentioning Reunion Island and a game show that featured a rotating obstacle course.
- 🔄 The concept of uniform motion in a circle is discussed, emphasizing that it involves acceleration even though the speed remains constant.
- 📐 The formula for acceleration is explained as the change in velocity vector over time.
- 🧭 It's highlighted that the direction of acceleration aligns with the direction of the change in velocity.
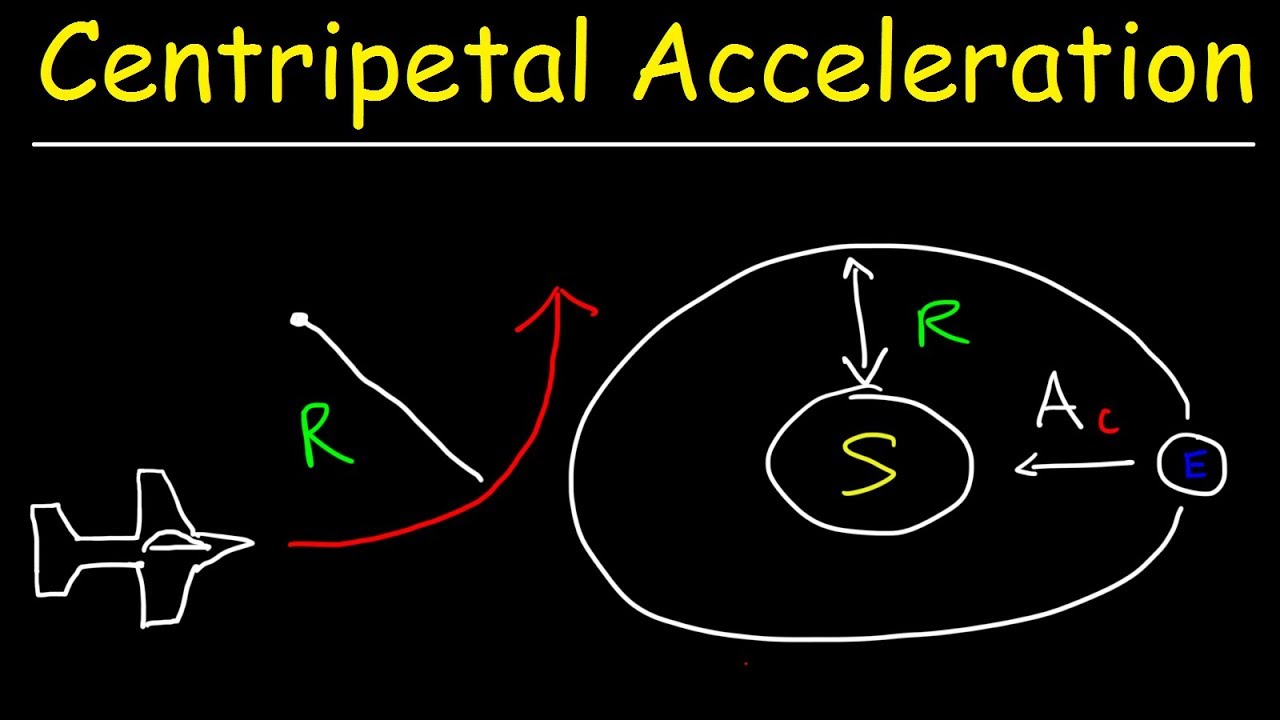
- 🔄 The script uses a diagram to illustrate that acceleration in circular motion is directed towards the center of the circle, hence called centripetal acceleration.
- 📉 A triangle is used to derive the formula for centripetal acceleration, showing the relationship between the sides of similar triangles.
- 🔢 The formula for centripetal acceleration is given as \( a_{centripetal} = \frac{v^2}{R} \), where \( v \) is the linear speed and \( R \) is the radius of the circle.
- 🚴♂️ An example problem is solved to find the speed of a bicycle given the centripetal acceleration and the radius of the wheel.
- 🔄 The relationship between linear speed, angular speed, and centripetal acceleration is discussed, leading to another formula for centripetal acceleration: \( a_{centripetal} = \omega^2 \times R \).
- 🔚 The lesson concludes with a summary of the concepts learned and a teaser for the next section on 'Dynamics'.
Q & A
What is the central concept discussed in the lesson?
-The central concept discussed in the lesson is uniform circular motion and the centripetal acceleration of an object moving along a circular path.
Why is centripetal acceleration important in circular motion?
-Centripetal acceleration is important because it is the acceleration that points towards the center of the circular path and keeps the object moving along the curve, even though its speed remains constant.
How is centripetal acceleration related to the velocity of an object?
-Centripetal acceleration is perpendicular to the velocity of the object and is directed towards the center of the circular path. It is responsible for the change in direction of the velocity vector, not its magnitude.
What is the formula for calculating centripetal acceleration?
-The formula for calculating centripetal acceleration is ac = v^2 / R, where v is the linear velocity and R is the radius of the circular path.
How can centripetal acceleration be expressed in terms of angular velocity?
-Centripetal acceleration can also be expressed as ac = ω^2 R, where ω is the angular velocity and R is the radius of the circular path.
What example from popular media is used to introduce the concept of circular motion?
-The example of the obstacle course in the sports show 'Games of the Patriots' is used, where contestants struggled to maintain balance on rotating circles moving in opposite directions.
Why do contestants on the rotating circles in 'Games of the Patriots' fall?
-Contestants fall because the circular motion causes a centripetal force that changes their direction, making it difficult to maintain balance as they run along the rotating circles.
How does the lesson derive the formula for centripetal acceleration?
-The lesson derives the formula by analyzing the change in velocity vectors at two nearby points on the circular path, showing that the change in velocity (and therefore the acceleration) points towards the center of the circle.
What real-life example is used in the problem-solving section of the lesson?
-The real-life example is a bicycle wheel where the point on the rim moves with a centripetal acceleration of 62.5 m/s², and the problem asks to find the speed of the wheel and its revolutions per minute.
What is the speed of the bicycle wheel in the example, and how many revolutions per minute does it make?
-The speed of the bicycle wheel is 5 m/s, and it makes 119 revolutions per minute.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

FISIKA KELAS X | GERAK MELINGKAR (PART 1) - Besaran-besaran dalam Gerak Melingkar

FISIKA Kelas 10 - Gerak Melingkar | GIA Academy

Quipper Video - Fisika - Gerak Melingkar Beraturan - Kelas 10

GERAK BENDA DALAM BIDANG DATAR DENGAN PERCEPATAN TETAP
Introduction to Centripetal Acceleration - Period, Frequency, & Linear Speed - Physics Problems

Gerak Melingkar • Part 1: Sudut Radian & Gerak Melingkar Beraturan (GMB)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
