Tipos de Memória - Memória e Neuropsicologia - Aula 2 #memória #neuropsicologia
Summary
TLDRThis transcript delves into the cognitive models and types of memory, highlighting the functional structure of memory and learning. It differentiates between short-term sensory memory, short-term working memory, and long-term memory, further breaking down long-term memory into declarative (episodic and semantic) and non-declarative (procedural, priming, classical conditioning, and non-associative learning). The lecture emphasizes the importance of working memory in manipulation and integration of information, crucial for academic performance and learning. It also discusses the brain areas associated with each memory type, providing insights from the famous HM case study, which underscores the distinction between episodic and procedural memory. The content is engaging, informative, and encourages further exploration into the fascinating world of memory and neuroscience.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Memory is divided into multiple types, each serving different cognitive functions.
- 🔍 Sensory memory is a brief type that deals with immediate sensory inputs.
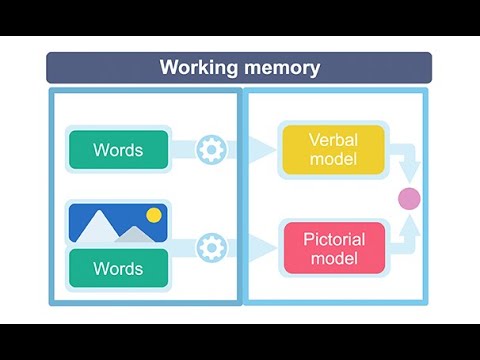
- 📈 Short-term memory, or working memory, has a limited capacity of about 7±2 items and lasts for seconds to a minute.
- 🔄 Working memory actively manipulates information and is crucial for learning and cognitive tasks.
- 📚 Long-term memory has a longer duration and is divided into declarative (explicit) and non-declarative (implicit) memories.
- 🎓 Episodic memory involves the recollection of personal experiences with contextual details like time and place.
- 🎯 Semantic memory consists of factual knowledge about the world without the context of when or how it was learned.
- 🏎️ Procedural memory, a type of non-declarative memory, involves skills and habits like riding a bike or playing an instrument.
- 🔍 Priming is a non-declarative memory phenomenon where exposure to a stimulus influences the response to a subsequent stimulus.
- 🔧 Classical conditioning is a form of non-associative learning where two stimuli are paired to produce a new response.
- 🧬 The study of memory, including famous cases like HM, has revealed the complexity and diversity of memory functions and associated brain areas.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the script?
-The main topic of the script is the types of memory and cognitive models of memory, including their structures and functions.
What are the two broad categories of memory mentioned in the script?
-The two broad categories of memory mentioned in the script are long-term memory and short-term memory.
What is sensory memory in the context of the script?
-Sensory memory is a brief type of memory that holds information from sensory inputs, such as sight and hearing, before it is either processed further or lost.
How is working memory different from short-term memory?
-Working memory is different from short-term memory in that it involves active manipulation of information, whereas short-term memory is more passive, involving the brief retention of information.
What is the capacity limit of short-term memory?
-The capacity limit of short-term memory is roughly seven items, plus or minus two, which is often referred to as the 'magic number seven' in cognitive psychology.
What are declarative memories according to the script?
-Declarative memories are conscious memories that can be accessed verbally. They include episodic memory, which relates to personal experiences, and semantic memory, which involves factual knowledge about the world.
What is non-declarative memory and how is it expressed?
-Non-declarative memory, also known as implicit memory, is memory that cannot be expressed verbally but can be demonstrated through performance. It includes procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning.
What is the significance of the case of HM in the study of memory?
-The case of HM is significant because it demonstrated the distinction between different types of memory, particularly the ability to learn new motor skills (procedural memory) without the formation of new declarative memories, after the removal of his hippocampi.
How does priming work in non-declarative memory?
-Priming in non-declarative memory works by activating a network of associated knowledge based on a given stimulus. For example, hearing a song lyric can trigger the recall of the entire song due to the association between the lyrics and the stored memory of the song.
What is an example of classical conditioning in non-declarative memory?
-An example of classical conditioning in non-declarative memory is the salivation of a dog in response to the sound of a bell, after the sound has been paired with food over time.
What are the main points to remember from the script about the types of memory?
-The main points to remember are that memory can be divided into long-term and short-term memory, with long-term memory further divided into declarative (episodic and semantic) and non-declarative (procedural, priming, and classical conditioning). Each type has distinct characteristics and is associated with different cognitive processes and brain areas.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)