¿Cuáles son los fluidos NEWTONIANOS y NO NEWTONIANOS?
Summary
TLDRThis video from the INTEC channel explores the world of fluids, distinguishing between Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. Newtonian fluids, like water and oil, maintain a constant viscosity and exhibit a linear relationship between shear stress and rate of deformation. Non-Newtonian fluids, however, show a complex behavior where viscosity varies with stress and temperature, exemplified by substances like shampoos and toothpaste. The video promises a deeper dive into the fascinating behavior of these fluids in upcoming episodes, encouraging viewers to stay tuned for more.
Takeaways
- 🔬 A fluid is defined as a substance that continuously deforms when a shear stress is applied to it.
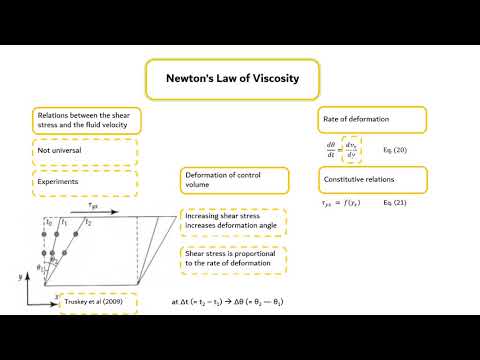
- 🌡️ Newtonian fluids maintain a constant viscosity over time, with a linear relationship between shear stress and velocity gradient.
- 🔑 The viscosity of Newtonian fluids is dependent on temperature, decreasing as temperature increases.
- 💧 Examples of Newtonian fluids include water, oils, glycerin, and air.
- 🚫 Non-Newtonian fluids do not have a linear relationship between shear stress and velocity of formation.
- 🌀 Non-Newtonian fluids can exhibit varying viscosity that changes with temperature and applied shear stress.
- 🧴 Pseudoplastic fluids, like shampoos and paints, are an example of non-Newtonian fluids where viscosity decreases with increased shear rate.
- 🌾 Dilatant fluids, such as cornstarch mixed with water, increase in viscosity with increased shear rate.
- 🍫 Plastic fluids, like clay, toothpaste, and chocolate, do not flow until a certain shear stress is applied.
- 📺 The next video will delve deeper into the behavior of both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.
Q & A
What is a fluid?
-A fluid is a substance that continuously deforms when a shearing force is applied to it, regardless of the magnitude of the force.
What are the two main classifications of fluids?
-The two main classifications of fluids are Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.
How is the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid related to time?
-The viscosity of a Newtonian fluid remains constant over time, and its relationship between shear stress and velocity remains linear.
What happens to the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid when temperature increases?
-As the temperature increases, the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid decreases, meaning it is inversely proportional to the rise in temperature.
Give some examples of Newtonian fluids.
-Examples of Newtonian fluids include water, oils, kerosene, and even air.
What is a non-Newtonian fluid?
-A non-Newtonian fluid is one where the relationship between shear stress and velocity is not linear, meaning its viscosity is not constant and varies with temperature and applied shear stress.
What are some behaviors exhibited by non-Newtonian fluids?
-Non-Newtonian fluids can exhibit behaviors such as pseudoplastic (shear thinning), dilatant (shear thickening), and plastic (yield stress).
Which common items are examples of pseudoplastic non-Newtonian fluids?
-Examples of pseudoplastic non-Newtonian fluids include shampoos and paints.
What is an example of a dilatant non-Newtonian fluid?
-An example of a dilatant non-Newtonian fluid is a mixture of cornstarch and water.
What is meant by the term 'plastic' in the context of non-Newtonian fluids?
-Plastic non-Newtonian fluids are those that exhibit a yield stress, meaning they do not flow until a certain stress is applied, such as toothpaste and chocolate.
What will be discussed in the next video of the series?
-The next video will delve deeper into the behavior of both Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

DIFFERENCE BETWEEN NEWTONIAN AND NON-NEWTONIAN FLUIDS

Mekanika Fluida FM01 (Lecture1: 2/4). Newtonian/Non-Newtonian Fluid
BE3002 Transport Phenomena in Biosystem Module 2_Segment 4

3. Rheological Behavior of Fluids

Rheology Part 3 - Flow Profiles - A Video Tutorial by samMorell.com

Praktikum Farmasi Fisika:Viskositas dan Rheologi Sediaan Farmasi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
