Ohm’s Law Tutorial with easy practice problems | Basic Circuits
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial delves into Ohm's Law, a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that links voltage, current, and resistance. The presenter explains that Ohm's Law is expressed as V=IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance. They clarify the linear relationship between these variables and how changes in one affect the others. The video includes practical examples to demonstrate how to calculate current using Ohm's Law in simple circuits. It also touches on the concepts of resistivity, conductivity, and the significance of Ohm's Law in various electrical applications. The presenter emphasizes the importance of understanding Ohm's Law for future studies in circuit analysis and electrical engineering.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that relates voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
- 🌊 The script uses the analogy of water flow to explain the concept of resistance, which is a force that opposes the flow of current in a circuit.
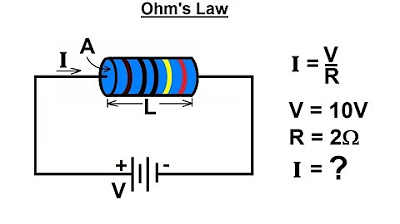
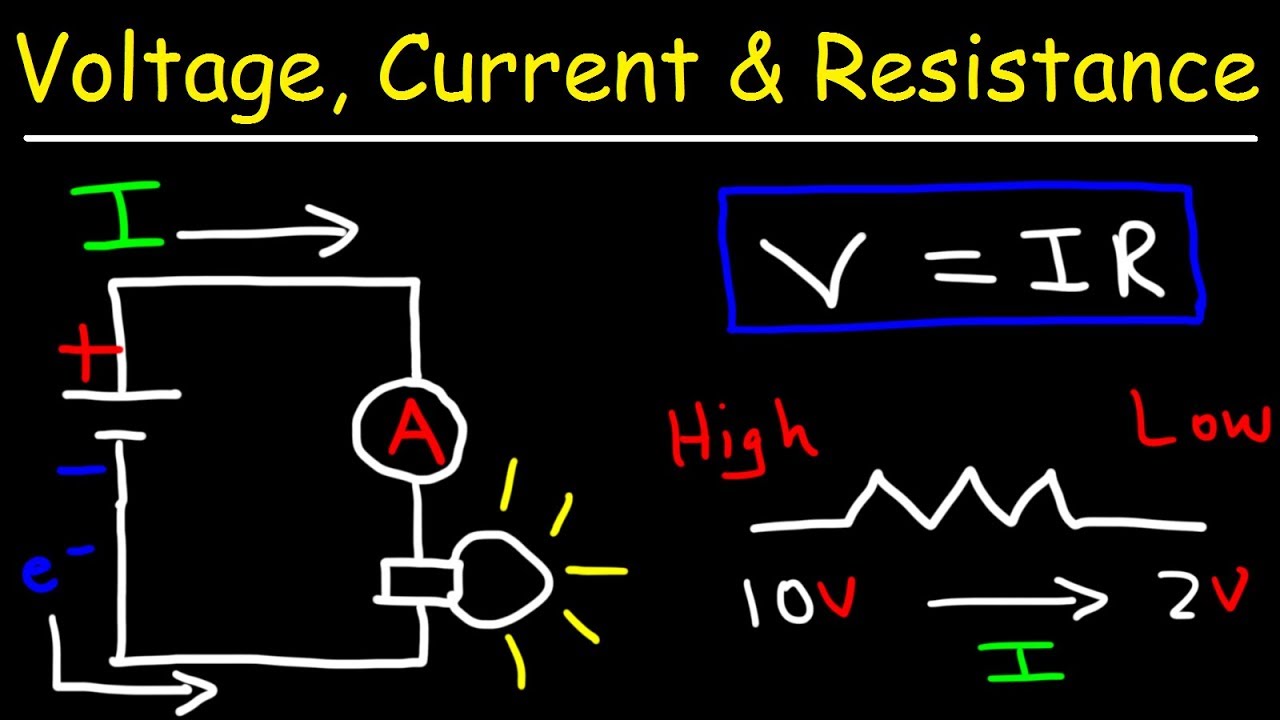
- ⚡ Ohm's Law is mathematically expressed as V = I * R, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance. This formula can be rearranged to solve for any of the variables.
- 🔄 The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is linear, meaning changes in one variable will proportionally affect the others.
- 🔍 Resistivity is mentioned as a different concept from resistance, but it is not the focus of the script.
- 📐 Ohm's Law is applicable to resistors, which are considered linear components in most cases for simplification in calculations.
- 🔄 The script emphasizes the importance of understanding the direction of current flow and keeping consistent with the chosen perspective throughout calculations.
- 🌐 The concept of 'ohms' as a unit of measurement for resistance is introduced, along with the concept of conductivity, measured in siemens or mhos.
- ⚠️ Two extreme cases of Ohm's Law are explained: a short circuit (R = 0, resulting in infinite current) and an open circuit (R = ∞, resulting in zero current).
- 📝 Practical examples are provided to demonstrate how Ohm's Law can be applied to simple circuits to calculate current, emphasizing the importance of understanding relative voltage differences rather than absolute values.
- 📚 The script concludes by highlighting the importance of Ohm's Law in further studies of circuits and electrical engineering.
Q & A
What is Ohm's Law and how does it relate to voltage, current, and resistance?
-Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering that states the relationship between voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R). It is expressed as V = I * R, meaning the voltage across a resistor is equal to the current flowing through it times the resistance of the resistor.
What is the significance of Ohm's Law in circuit analysis?
-Ohm's Law is significant because it provides a linear relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, which is a foundational concept used in all levels of electrical engineering and circuit analysis. It allows for the calculation of unknown quantities in a circuit when two of the three are known.
Can Ohm's Law be rearranged to solve for different variables?
-Yes, Ohm's Law can be rearranged to solve for any of the three variables (voltage, current, or resistance). For example, it can be rearranged to I = V/R to find the current, or R = V/I to find the resistance.
What is the difference between resistivity and resistance mentioned in the script?
-Resistivity is a material property that quantifies how strongly a given material opposes the flow of electric current. Resistance, on the other hand, is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a specific component or part of a circuit, which depends on the resistivity of the material, its dimensions, and shape.
What are the two extreme cases of Ohm's Law mentioned in the script?
-The two extreme cases of Ohm's Law mentioned are when resistance is zero (short circuit) and when resistance is infinite (open circuit). In the short circuit case, the current would be infinite if the voltage is not zero. In the open circuit case, the current would be zero regardless of the voltage.
What is the term used for the reciprocal of resistance, and what are its units?
-The reciprocal of resistance is called 'conductivity'. Its units can be expressed in mhos or siemens (symbolized by 'S'). For example, if a resistor has 100 ohms of resistance, its conductivity would be 1/100 siemens.
How does the script illustrate the concept of voltage being relative?
-The script illustrates the concept of voltage being relative by explaining that the voltage across a resistor is the difference in potential between two points, regardless of the absolute values of those points. This means that the voltage is comparative and depends on the potential difference, not the actual values.
What does the script suggest about the direction of current in a circuit?
-The script suggests that the direction of current in a circuit is a matter of perspective and should be consistently maintained once established for the purpose of calculations. It emphasizes that the direction should not be changed midway through calculations to avoid confusion.
How does the script handle negative voltage values in circuit analysis?
-The script handles negative voltage values by treating them as relative to an arbitrarily decided zero potential point. It emphasizes that the key is the potential difference between two points, and the actual sign (positive or negative) does not change the analysis as long as the relationship is consistent.
What advice does the script give for solving problems using Ohm's Law?
-The script advises to write down the chosen direction of current and the setup of the problem once decided, and to stick with it throughout the calculations. It warns against changing the direction or setup midway, as this can lead to confusion and errors.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)