Episode 15: Price Floors and Price Ceilings
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the economic concepts of **price floors** and **price ceilings**. It discusses how price floors, set above market equilibrium, can lead to surpluses, particularly in industries like agriculture. Conversely, price ceilings, set below equilibrium, can create shortages, as seen with housing and gasoline markets. The script highlights the unintended consequences of these interventions, such as surplus goods that need to be managed or black markets that emerge from shortages. The video concludes by suggesting that rather than imposing artificial prices, the government can manage demand and supply to achieve market equilibrium naturally.
Takeaways
- 😀 Price and quantity in a free market are determined by supply and demand without outside interference.
- 😀 The government can intervene in markets to protect society or specific sectors, such as by setting price floors or ceilings.
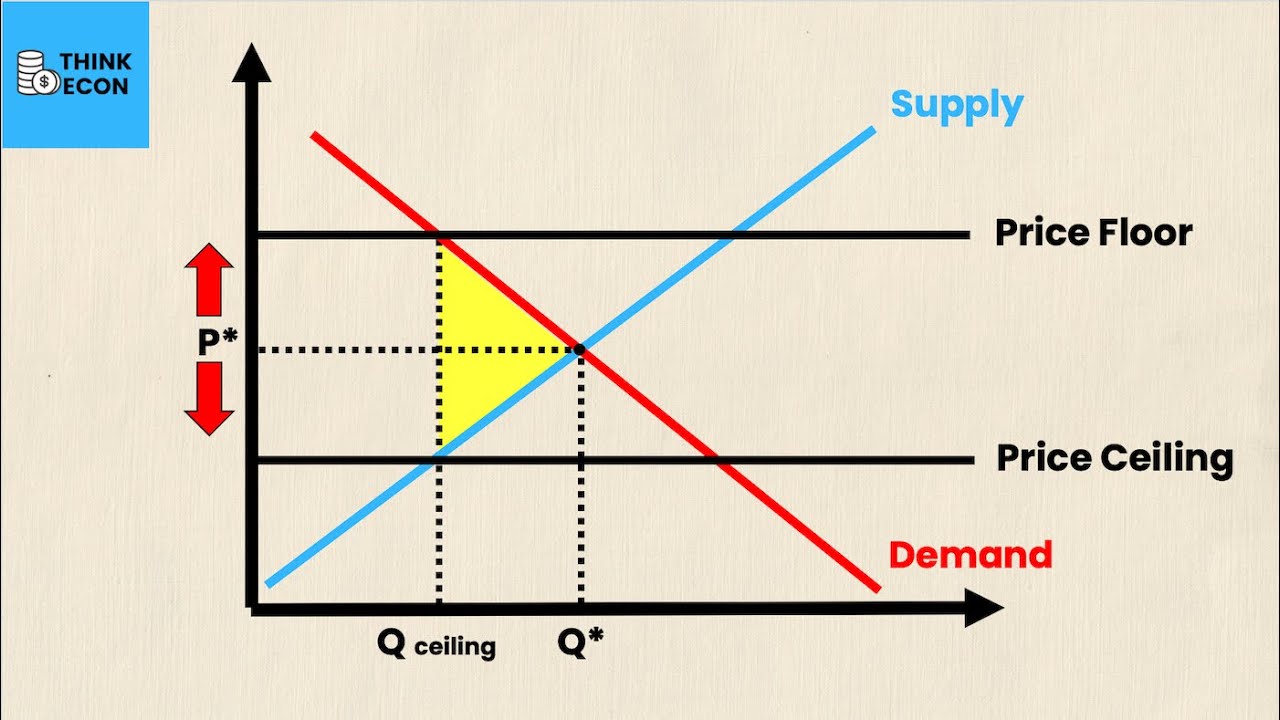
- 😀 A price floor is a minimum legal price set above the market equilibrium to protect sellers from prices too low to cover costs.
- 😀 The price floor can create a surplus, where producers are willing to supply more than consumers are willing to buy at the set price.
- 😀 Surplus problems caused by price floors can be costly to manage, as governments may need to buy up excess goods or distribute them in other ways.
- 😀 If the government refuses to manage the surplus, the market may experience waste, as seen with dairy farmers dumping milk.
- 😀 Rather than imposing price floors, the government can influence demand or supply to push the price towards the desired equilibrium.
- 😀 Price ceilings are used when the government wants to protect consumers from excessively high prices, often for essential goods like housing or energy.
- 😀 When a price ceiling is set below the equilibrium price, it creates a shortage, where demand exceeds supply.
- 😀 Shortages from price ceilings can lead to problems like rationing, black markets, and long lines, as prices cannot adjust to clear the market.
- 😀 To avoid market distortions, the government can manage demand (e.g., public transit) or increase supply (e.g., tapping into reserves) to bring prices closer to the desired ceiling without causing shortages.
Q & A
What is a price floor, and how does it affect the market?
-A price floor is a legal minimum price set by the government above the market equilibrium to ensure that sellers receive a fair price for their goods. It can create a surplus if the price is set too high, as consumers may not be willing to buy at that price, leading to excess supply.
Why might the government impose a price floor in the market?
-The government may impose a price floor to protect sellers, particularly in industries like agriculture, where prices might fall below a level that allows producers to cover their costs. The goal is to ensure the survival of certain industries, like farming, that are essential for the economy.
What happens when a price floor is set above the market equilibrium?
-When a price floor is set above the market equilibrium, a surplus occurs because the higher price leads to increased supply from sellers, but reduced demand from consumers. This results in excess goods that may not be sold.
How can the government address a surplus caused by a price floor?
-The government might purchase the surplus to prevent it from being wasted, but this creates additional costs for taxpayers. Alternatively, the government might allow the market to adjust or encourage demand-side measures to reduce the surplus.
What are some potential outcomes when the government refuses to buy the surplus created by a price floor?
-If the government refuses to purchase the surplus, farmers may have no way to sell their excess goods, leading to waste. For example, in the case of milk, farmers might dump the surplus into rivers or dispose of it in other ways.
What are price ceilings, and why are they implemented?
-Price ceilings are government-imposed limits on how high prices can go, typically used to protect consumers from prices that are perceived as too high, such as in housing or essential goods like gasoline. The goal is to ensure affordability for consumers.
What happens when a price ceiling is set below the market equilibrium?
-When a price ceiling is set below the market equilibrium, a shortage occurs because the lower price increases demand, but suppliers are unwilling to provide enough goods at that price. This results in scarcity and can lead to issues like rationing or black markets.
Why do price ceilings lead to problems like long lines or black markets?
-Price ceilings create a shortage by artificially lowering prices below the market equilibrium, leading to excess demand. Since suppliers can't raise prices, they may limit supply or consumers may turn to black markets where prices are not controlled.
How can the government manage a market to achieve a desired price without using price controls?
-Instead of using price controls, the government can influence market conditions by either increasing demand or reducing supply. For example, they could promote demand through advertising campaigns, or reduce supply through subsidies or restrictions on production.
What role do price controls play in the economy, and why can they be problematic?
-Price controls like price floors and ceilings are intended to correct perceived market failures, but they can often create imbalances. Price floors can lead to surpluses, while price ceilings can lead to shortages. Both types of controls interfere with the natural market equilibrium and can lead to inefficiencies.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Consumer and Producer Surplus- Micro Topic 2.6 (Holiday Edition)

Price Ceilings and Floors- Micro Topic 2.8

Government Intervention- Micro Topic 2.8
Price Ceiling and Price Floor | Think Econ

Penawaran, Permintaan, dan Efisiensi Pasar: Surplus Konsumen, Produsen, Deadweight Loss (Part 30)

Quarter 3 - Module 10: Government Intervention in Market Prices: Price Ceiling
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
