VEKTOR: PENGERTIAN DAN PENJUMLAHAN - MATERI FISIKA KELAS 10 | Edcent.id
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the fundamental concepts of vectors in physics, explaining the difference between scalar and vector quantities. It covers how vectors have both magnitude and direction, and how they can be represented visually with arrows. The video demonstrates vector addition using graphical methods like the tail-to-tip and parallelogram methods. It also explains how to break vectors into components along the x and y axes using trigonometry. Finally, the video shows how to express vectors with unit vectors and calculate their magnitude using the Pythagorean theorem.
Takeaways
- 😀 Physics quantities are divided into two categories: scalar quantities (no direction) and vector quantities (with direction).
- 😀 Scalar quantities, like mass and speed, only have magnitude and no direction.
- 😀 Vector quantities, such as weight and velocity, have both magnitude and direction.
- 😀 Scalars can be represented by just their numerical value, e.g., mass of 2 kg, but vectors need to be described with both magnitude and direction, e.g., velocity of 20 m/s towards the north.
- 😀 Vectors can be represented visually using arrows, where the length indicates magnitude and the direction of the arrow indicates the vector's direction.
- 😀 When two vectors have opposite directions, the vector is considered negative, and its magnitude is represented by a shorter or reversed arrow.
- 😀 Vectors can be added using graphical methods, such as the tip-to-tail method or the parallelogram method.
- 😀 The tip-to-tail method involves placing the tail of one vector at the tip of another, and the resulting vector (sum) is drawn from the origin of the first vector to the tip of the second.
- 😀 The parallelogram method involves drawing vectors from a common point, then creating a parallelogram to find the resultant vector using its diagonal.
- 😀 Vector components can be broken down into x and y components, with trigonometry used to calculate them, e.g., Fx = F * cos(θ) and Fy = F * sin(θ).
Q & A
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
-Scalar quantities only have magnitude (e.g., mass, time), while vector quantities have both magnitude and direction (e.g., velocity, force).
Can you provide examples of scalar quantities?
-Examples of scalar quantities include time, speed, mass, and temperature.
What are some examples of vector quantities?
-Examples of vector quantities include force, velocity, displacement, and acceleration.
How is a vector represented in physics?
-A vector is typically represented as an arrow, where the length of the arrow denotes its magnitude and the direction of the arrow represents its direction.
What is the significance of the negative sign when dealing with vectors?
-A negative sign in a vector indicates that the direction of the vector is opposite to the direction of the positive reference axis.
How are vectors added using the graphical method?
-In the graphical method, vectors are added by placing the tail of one vector at the head of the other, maintaining their direction and magnitude, and then drawing the resultant vector from the tail of the first vector to the head of the second vector.
Can you explain the parallelogram method of vector addition?
-In the parallelogram method, vectors are placed with their tails at the same point. The resultant vector is then represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram formed by the two vectors.
How is the magnitude of the resultant vector calculated in the parallelogram method?
-The magnitude of the resultant vector in the parallelogram method is calculated using the formula: R = √(A² + B² + 2ABcosθ), where A and B are the magnitudes of the two vectors and θ is the angle between them.
What are the components of a vector?
-The components of a vector are the projections of the vector along the x-axis and y-axis (in 2D). These components are typically expressed as Fx = Fcosθ for the x-component and Fy = Fsinθ for the y-component.
How can you calculate the magnitude of a vector given its components?
-The magnitude of a vector can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem: |F| = √(Fx² + Fy²), where Fx and Fy are the components of the vector along the x and y axes, respectively.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Besaran vektor dan besaran skalar (Fisika SMA/MA Sagufindo kls X smt 1 : Vektor)

Vektor.

Definições de Grandezas Físicas: Escalares e Vetoriais - Principais diferenças
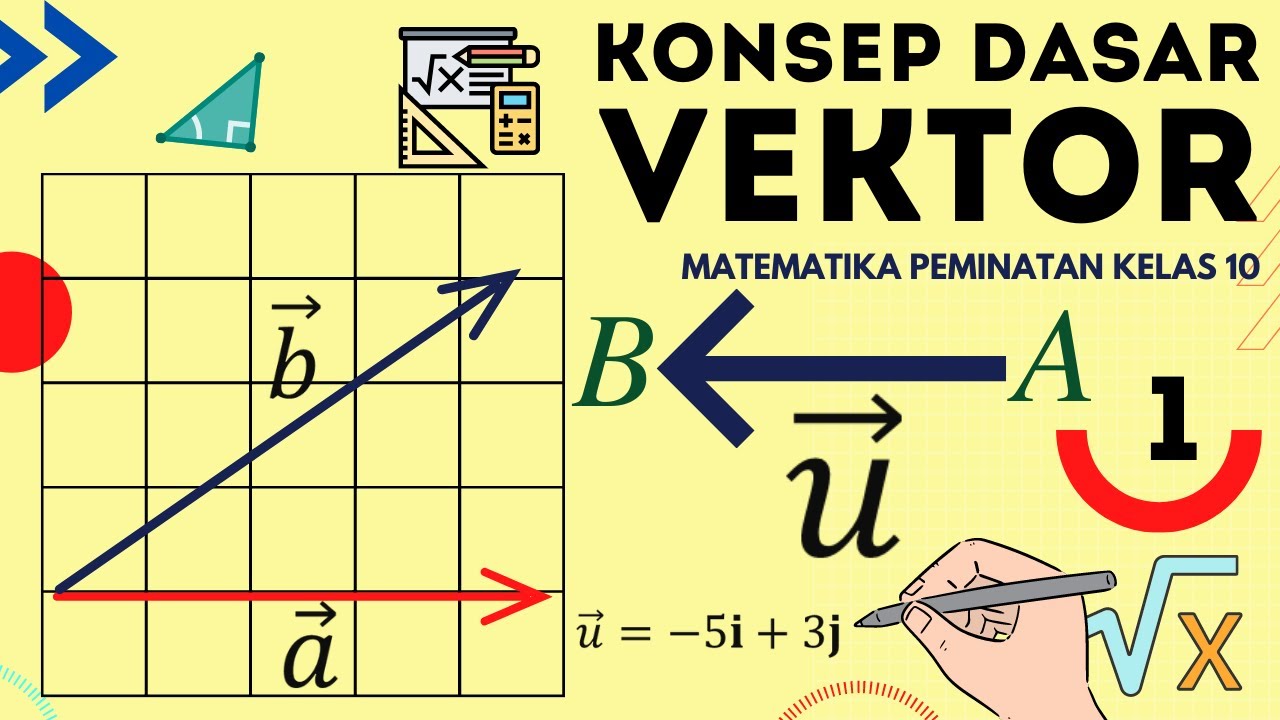
Vektor Matematika Kelas 10 : Konsep Dasar Vektor Matematika Peminatan Kelas 10 - Part 1

Scalars, Vectors, and Vector Operations
Scalars and Vectors
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
