The Fall of Rome Explained In 13 Minutes
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fall of the Western Roman Empire, highlighting its vastness at peak and the relentless barbarian invasions that contributed to its decline. It delves into key events such as the Gothic War, military defeats, and ineffective leadership that plagued the Empire. Economic struggles, reliance on slave labor, and the rise of Christianity further weakened its foundation. The deposition of Romulus Augustus in 476 marked the Empire's end, yet Rome's cultural and political legacy continued to shape Europe for centuries. The video also promotes 'The Great Courses Plus,' emphasizing educational opportunities on Roman history.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ The Western Roman Empire fell on September 4th, 476 AD, when Romulus Augustulus was deposed by the barbarian Odoacer.
- 🌍 At its height, the Roman Empire spanned 1.9 million square miles and maintained the largest professional army of its time.
- ⚔️ The Empire faced continuous barbarian invasions that eroded its territorial integrity, especially in the West.
- 📉 The Gothic War began in 376 when mistreated Goths revolted, leading to the catastrophic Battle of Adrianople in 378.
- 👑 Alaric, king of the Visigoths, initially served in the Roman army but later sacked Rome in 410 due to mistreatment by the Romans.
- 💰 Economic decline in the Western Empire was exacerbated by the loss of wealthy provinces and reliance on military spending.
- 🛡️ Diocletian's division of the Empire into Eastern and Western halves initially helped governance but ultimately contributed to the West's fall.
- ✝️ The rise of Christianity diminished the authority of Roman emperors and complicated the integration of conquered peoples.
- 📅 The Western Roman Empire saw its final days when Orestes deposed Emperor Julius Nepos, leading to Romulus Augustulus' brief reign.
- 🕊️ Despite its fall, Rome's influence persisted through the Byzantine Empire and shaped the cultural landscape of medieval Europe.
Q & A
Who was the last Roman Emperor and when was he deposed?
-The last Roman Emperor was Romulus Augustus, who was deposed on September 4, 476 AD.
What were some major factors that contributed to the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
-Major factors included relentless barbarian invasions, economic decline, ineffective leadership, and internal strife.
What was the significance of the Battle of Adrianople in 378?
-The Battle of Adrianople was a disastrous defeat for Rome, resulting in the death of Emperor Valens and the loss of two-thirds of the Roman army.
How did the treatment of the Goths lead to conflict with Rome?
-The Goths faced maltreatment and famine after seeking refuge in Roman territory, which led to the Gothic War and their rebellion against the Romans.
What event marked the sack of Rome in 410 AD?
-Alaric, king of the Visigoths, successfully besieged Rome in 410 AD, leading to the city being sacked for three days.
How did the division of the Roman Empire affect its stability?
-The division allowed for more effective governance of the Eastern and Western Empires initially, but it eventually led to the Western Empire's decline as it became financially weaker than the Eastern Empire.
What role did slave labor play in the Roman economy?
-The Roman economy heavily relied on slave labor, and the lack of new conquests meant a decline in the availability of slaves, contributing to economic collapse.
In what ways did ineffective leadership contribute to the Empire's decline?
-Many later emperors were out of touch with the populace and lacked military or administrative competence, leading to a loss of faith in their leadership.
How did Christianity's rise impact the Roman Empire?
-Christianity, as a monotheistic faith, challenged the Roman religious framework and authority, undermining the emperors' legitimacy and complicating the integration of new peoples.
What was the legacy of the Roman Empire after its fall in 476 AD?
-Despite its fall, Rome's legacy continued through the Byzantine Empire, which lasted until 1453, and through cultural influences in languages, religion, and infrastructure in Europe.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
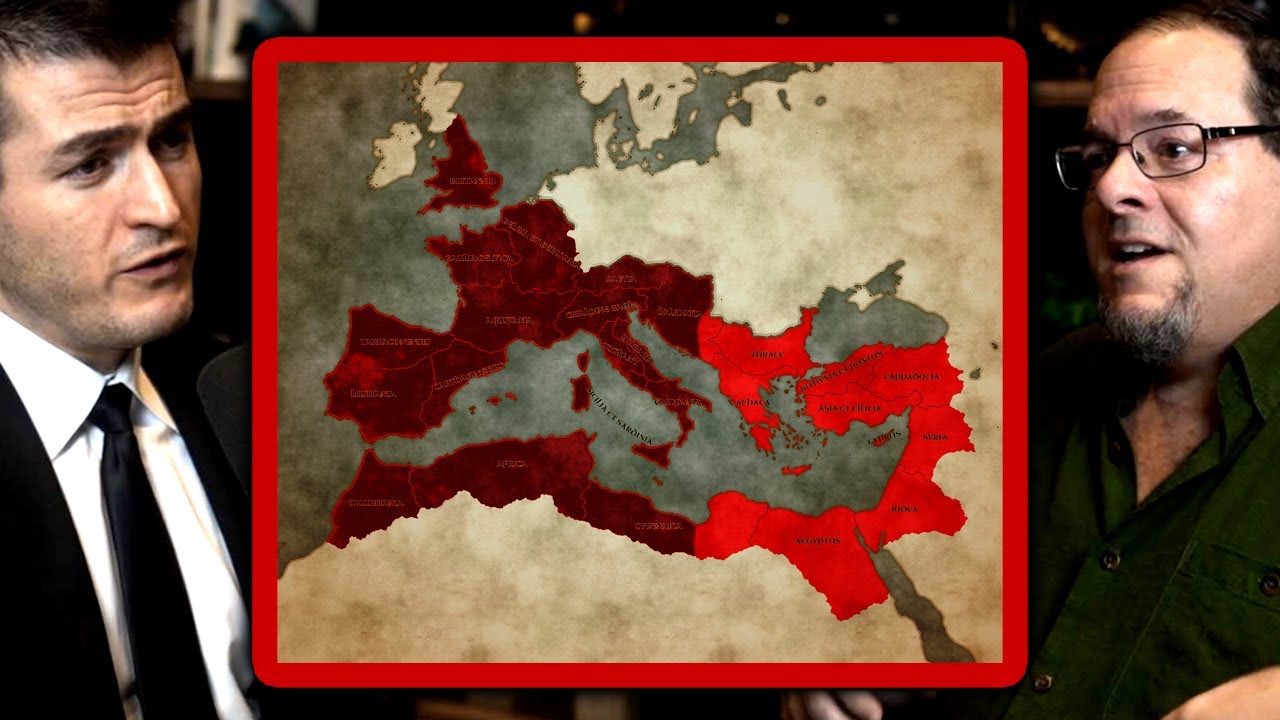
How the Roman Empire split into Western and Eastern empires | Gregory Aldrete and Lex Fridman

Capitolo 1 L'impero romano cristiano e la crisi del III secolo parte prima

History Behind Kingdom Come Deliverance 2 - Medieval History

HISTÓRIA GERAL #7 ROMA ANTIGA (MONARQUIA, REPÚBLICA E IMPÉRIO).

✅ La CAÍDA del IMPERIO ROMANO | ¿Por qué cayó el IMPERIO ROMANO? Resumen en 12 minutos

¿Cómo fue la caída del Imperio romano de occidente?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
