Structure of the Cell Membrane
Summary
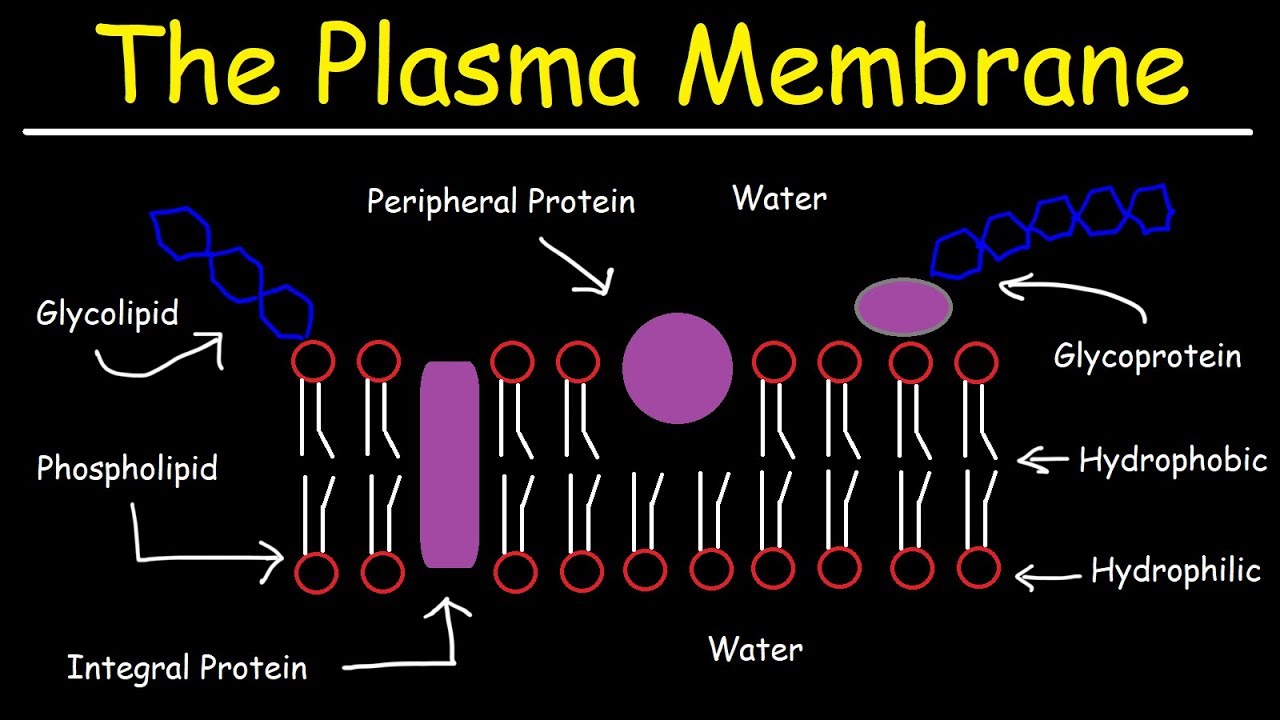
TLDRThis video delves into the structure of the cell membrane, highlighting its fluid mosaic nature. It explains the lipid bilayer, composed of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads facing watery environments and hydrophobic tails avoiding water. Proteins embedded within the bilayer facilitate the movement of larger molecules, which cannot pass through the phospholipids, into and out of the cell. The video promises a deeper exploration of substance transport across the cell membrane.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The cell membrane is selectively permeable, allowing certain substances to pass through while blocking others.
- 🔬 The structure of the cell membrane is described as a fluid mosaic, similar to a picture made up of small tiles.
- 💧 The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, which is two layers of phospholipids that are not rigid and allow for flexible movement.
- 🌊 Phospholipids have hydrophilic heads that are attracted to water and hydrophobic tails that repel water, leading to their specific orientation within the membrane.
- 🌐 The hydrophilic heads face the extracellular fluid and cytoplasm, while the hydrophobic tails face each other, away from the watery environments.
- 🔍 Proteins are embedded within the phospholipid layers of the cell membrane, some of which have carbohydrates attached.
- 🚪 The fluid mosaic model illustrates that the cell membrane is composed of various components, creating a flexible boundary around the cell.
- 🌀 Small molecules can pass through the cell membrane via the spaces between phospholipids, but larger molecules require a different mechanism.
- 🛤️ Larger molecules move through the cell membrane by passing through proteins embedded within it, which form tunnels for transport.
- 🔄 The movement of substances through the cell membrane will be explored in more detail in separate discussions.
Q & A
What is the structure of the cell membrane described as?
-The structure of the cell membrane is described as a fluid mosaic.
Why is the cell membrane referred to as a mosaic?
-The cell membrane is referred to as a mosaic because it is made up of different parts, similar to how a mosaic is a picture made up of little tiles.
What are the two layers of the cell membrane called?
-The two layers of the cell membrane are called a lipid bilayer.
How do phospholipids in the lipid bilayer behave?
-Phospholipids in the lipid bilayer have the ability to move in a flexible wave-like motion, indicating that the bilayer is not rigid.
What are the hydrophilic parts of phospholipids and where are they oriented?
-The round head portions of phospholipids are hydrophilic, meaning they are attracted to water, and they are oriented toward the extracellular fluid and cytoplasm.
What are the hydrophobic parts of phospholipids and how do they orient themselves?
-The phospholipid tails are hydrophobic, meaning they repel watery areas, and they orient themselves away from the watery content, towards each other.
What role do proteins play in the cell membrane?
-Proteins embedded in the phospholipid layers of the cell membrane help larger molecules pass through by forming tunnels, allowing substances to move from the extracellular area into the cell or from the intracellular area out of the cell.
Are there any carbohydrates attached to the proteins in the cell membrane?
-Yes, some proteins in the cell membrane have carbohydrates attached to them.
How does the fluid mosaic model contribute to the cell membrane's flexibility?
-The fluid mosaic model contributes to the cell membrane's flexibility by allowing different parts, including phospholipids and proteins, to move and interact with each other.
How do substances move through the cell membrane?
-Substances move through the cell membrane by seeping through the spaces between phospholipids or by moving through proteins embedded in the membrane.
What is the significance of the cell membrane being selectively permeable?
-The cell membrane being selectively permeable allows it to control which substances can enter or exit the cell, maintaining a stable internal environment.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)