RESUMÃO ANTI-HIPERTENSIVOS | Aula 39 | Farmacologia Cardiovascular rápida e fácil | Flavonoide
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth overview of antihypertensive drugs, exploring various pharmacological classes used to manage hypertension. The presenter explains the different treatment approaches, such as targeting vascular resistance, cardiac output, blood volume, and venous return. Emphasizing the importance of individualized treatment, the video outlines first- and second-line medications, including diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, and vasodilators. The script also highlights how medications can address other health conditions while managing blood pressure. This overview is ideal for students and healthcare professionals seeking a concise yet comprehensive understanding of hypertension treatment options.
Takeaways
- 😀 Treatment of hypertension involves targeting multiple physiological factors, such as increased vascular resistance, cardiac output, blood volume, and venous return.
- 😀 The goal is to find a simple pharmacological regimen that minimizes side effects, improves patient response, and ensures better adherence.
- 😀 The first step in treating hypertension is assessing the cardiovascular risk of the patient, which can be high, intermediate, or low.
- 😀 The therapeutic target for blood pressure depends on the patient's age and any existing comorbidities.
- 😀 Non-pharmacological measures should be introduced in patients with pre-hypertension, such as reducing sodium intake, increasing physical activity, and managing stress.
- 😀 For stage 1 hypertension with low or intermediate cardiovascular risk, monotherapy may be prescribed, with the possibility of adjusting the dosage or adding another drug if necessary.
- 😀 For stage 1 hypertension with high cardiovascular risk or stage 2 and 3 hypertension, a combination of two drugs from different classes is recommended.
- 😀 Diuretics are the first-line choice for hypertension treatment, working by increasing sodium and water excretion, which decreases blood volume and reduces pressure.
- 😀 Beta-blockers are not considered first-line for hypertension anymore, but may be used in patients with other health conditions such as arrhythmias or chronic heart failure.
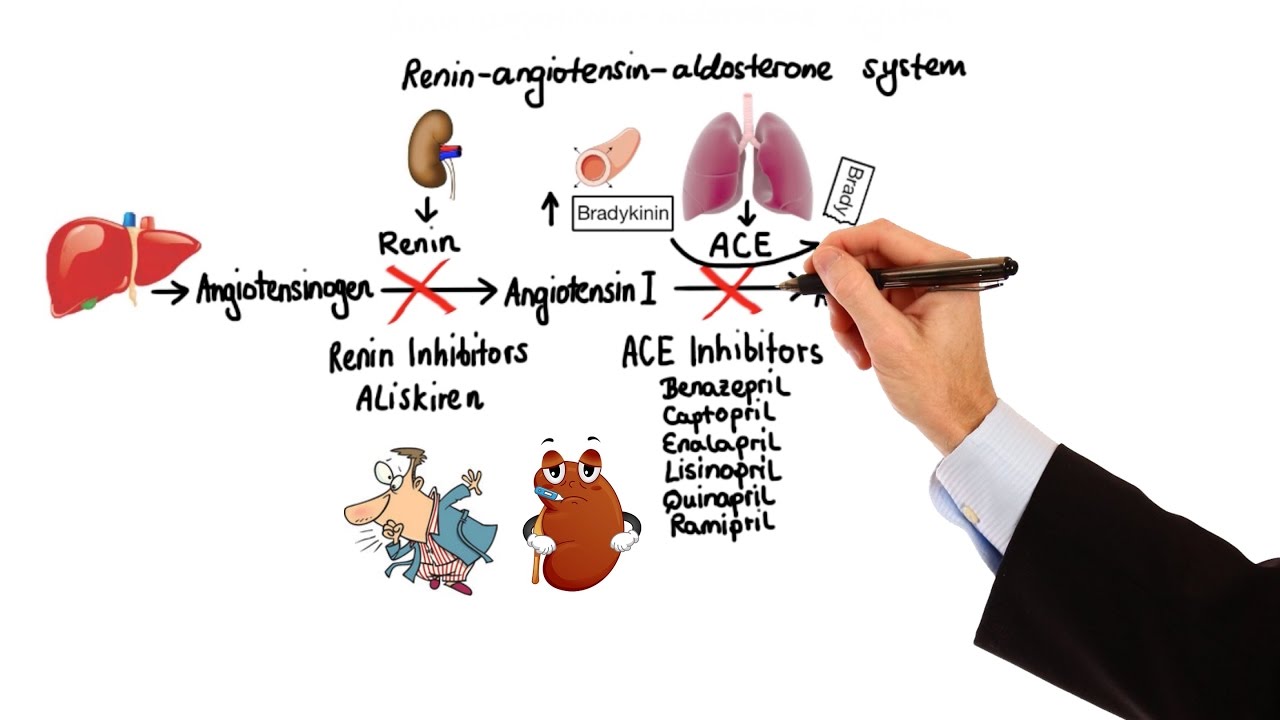
- 😀 Calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) are commonly prescribed for hypertension, with ACEIs being particularly effective for young patients or those with renal issues.
- 😀 Vasodilators, including direct vasodilators and nitrates, are used primarily in severe cases, like hypertensive emergencies or refractory hypertension, but require careful monitoring.
Q & A
What is the main goal when treating hypertension?
-The main goal is to find the simplest pharmacological regimen that is most effective, with fewer side effects and better patient adherence. This involves targeting the physiological issues that contribute to high blood pressure.
What are the physiological targets in hypertension treatment?
-The main targets include increasing systemic vascular resistance, increasing cardiac output, increasing blood volume, and increasing venous return. These factors all contribute to higher blood pressure, and treatments aim to correct these issues.
How does the risk assessment influence hypertension treatment?
-Risk assessment helps determine whether the patient is at high, intermediate, or low cardiovascular risk. This influences the choice of treatment and the desired therapeutic goal for blood pressure, based on factors like existing conditions and comorbidities.
What non-pharmacological treatments should be considered in early stages of hypertension?
-Non-pharmacological treatments include reducing sodium intake, increasing potassium and calcium intake, avoiding saturated fats, improving physical activity, controlling weight, and managing stress. These are recommended, especially in patients with pre-hypertension.
What is the importance of diuretics in hypertension treatment?
-Diuretics are important because they help reduce blood volume by promoting sodium and water excretion, which lowers the pressure on blood vessels. They are a cornerstone of hypertension management.
What are the different types of diuretics used in hypertension treatment?
-The three main types of diuretics are thiazide diuretics (used as first-line treatment), loop diuretics (used in more severe cases or when thiazides are insufficient), and potassium-sparing diuretics (used to prevent excessive potassium loss).
Why are beta-blockers not always used as a first-line treatment for hypertension?
-Beta-blockers are no longer first-line treatment for hypertension due to the risk of side effects like bradycardia and fatigue. They are instead used for patients with other conditions like arrhythmias, heart failure, or migraine.
How do ACE inhibitors (IECA) and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs) help in managing hypertension?
-Both ACE inhibitors and ARBs block the effects of angiotensin II, a hormone that causes vasoconstriction. This reduces vascular resistance and lowers blood pressure. ACE inhibitors also promote sodium and water excretion.
What are the potential risks of combining ACE inhibitors with ARBs in hypertension treatment?
-Combining ACE inhibitors with ARBs is not recommended because they have similar mechanisms of action. This can lead to excessive lowering of blood pressure and increased risks of kidney damage and hyperkalemia.
What is the role of calcium channel blockers in hypertension treatment?
-Calcium channel blockers are used as first-line treatment for hypertension, especially in elderly patients. They reduce vascular resistance by blocking calcium channels in the smooth muscle, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)