Representación de vectores en el plano cartesiano.
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host introduces vector representation in the Cartesian plane. The example provided includes points A, B, C, and D. The process of plotting these points on the Cartesian plane is explained, followed by the construction of vectors AB and CD. Emphasis is placed on understanding vectors as directed segments with length, direction, and sense. The host also details the importance of origins and endpoints in vectors. The tutorial concludes with practical steps to plot vectors and measure their lengths. Follow Mate Más TV on social media for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 📌 The video discusses the representation of vectors in the Cartesian plane.
- 📌 Vectors are defined as directed segments with length, direction, and sense.
- 📌 When working with vectors, it's important to identify the origin and the endpoint.
- 📌 The first example involves locating points A and B on the Cartesian plane.
- 📌 The point A is located at coordinates (x, y) and the point B is located at coordinates (7, 5).
- 📌 The vector AB is drawn by connecting points A and B with a directed line segment.
- 📌 The next example involves locating points C and D on the Cartesian plane.
- 📌 The point C is located at coordinates (6, 22) and the point D is located at coordinates (1, 6).
- 📌 The vector CD is drawn by connecting points C and D with a directed line segment.
- 📌 The video emphasizes placing an arrow at the endpoint to indicate the direction of the vector.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is the representation of vectors in the Cartesian plane.
How are vectors described in the video?
-Vectors are described as directed segments with length, direction, and sense. They have an origin and an end point.
What points are used to represent vector AB?
-The points used to represent vector AB are point A and point B.
What are the coordinates of point A?
-Point A is at coordinates (2, 3).
What are the coordinates of point B?
-Point B is at coordinates (7, 5).
How do you represent vector AB on the Cartesian plane?
-To represent vector AB, plot points A and B on the Cartesian plane, and then draw a directed line segment from A to B with an arrow indicating the direction from A to B.
What are the coordinates of point C for vector CD?
-Point C is at coordinates (6, -2).
What are the coordinates of point D for vector CD?
-Point D is at coordinates (1, 6).
How is vector CD represented on the Cartesian plane?
-To represent vector CD, plot points C and D on the Cartesian plane, and then draw a directed line segment from C to D with an arrow indicating the direction from C to D.
What is a key aspect to remember when working with vectors?
-A key aspect to remember is that vectors are directed segments with a specific origin and end point.
What does the arrow on a vector indicate?
-The arrow on a vector indicates the direction of the vector, pointing from the origin to the end point.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Vektor di Bidang Datar Part 1 (Konsep dan Ruang Lingkup) - Matematika Kelas 12

Vektor.

Scalars and Vectors | Vector Addition | General Physics 1

Statika Partikel 3D (3/5): Vektor Posisi dalam Tiga Dimensi
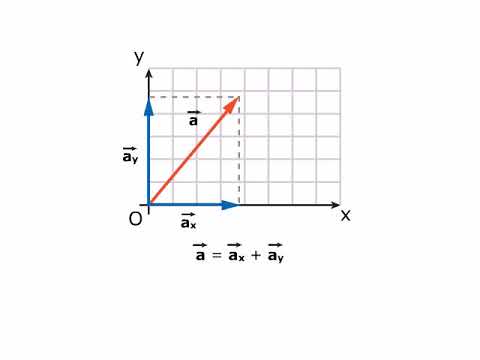
TEORIA Versori e componenti cartesiane di un vettore AMALDI ZANICHELLI
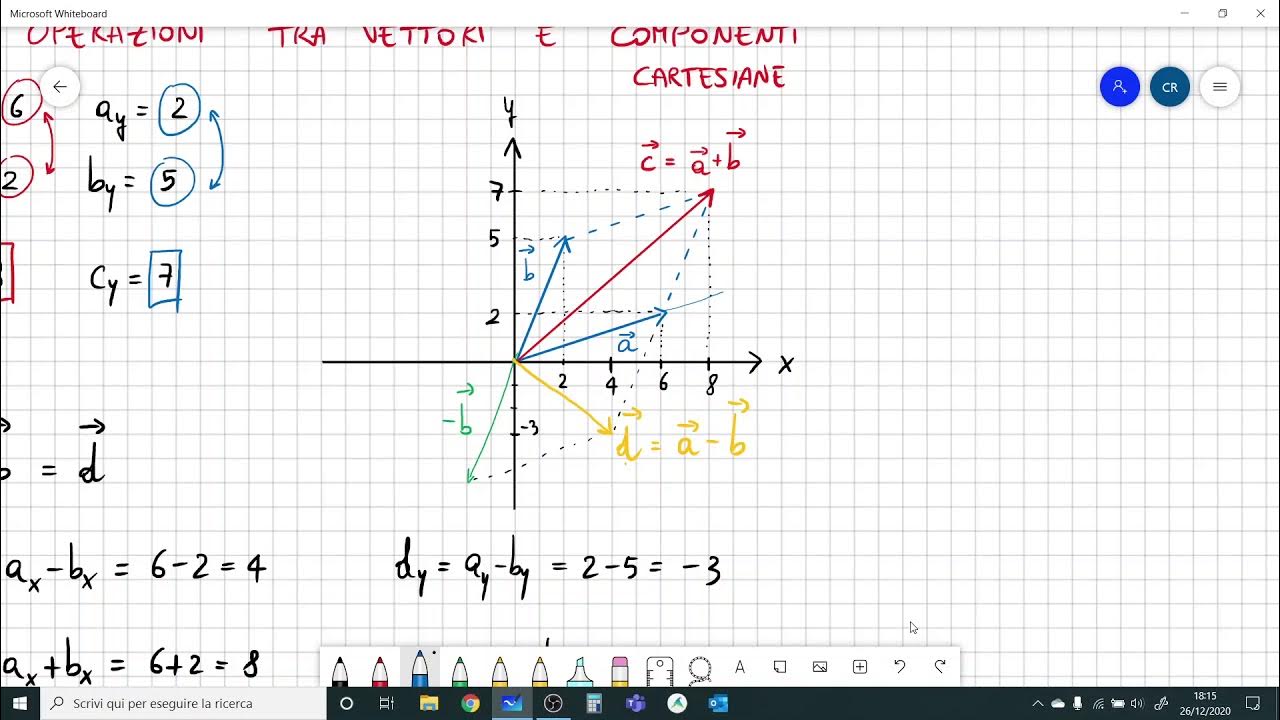
Operazioni tra vettori in componenti cartesiane
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)