⚖️ Hukum Lavoisier: Kekekalan Massa dalam Reaksi Kimia! | Kimia Kelas 10 🧪
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Kak Stefani explains Lavoisier's Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that the total mass of substances before and after a chemical reaction remains unchanged in a closed system. Using a practical example, she demonstrates how 10 grams of sulfur and 5 grams of copper react to form copper sulfide with a mass of 15 grams. She also solves a problem involving magnesium and sulfur to show how mass is conserved. The video concludes by reinforcing the key principle of Lavoisier's law and its application in closed systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script explains Lavoisier's law of mass conservation, stating that in a closed system, the mass of substances before and after a chemical reaction remains the same.
- 😀 The law is demonstrated using a simple experiment where 10 grams of sulfur and 5 grams of copper react in a closed container, producing 15 grams of copper(II) sulfide.
- 😀 The law of mass conservation holds true as the total mass before and after the reaction is identical, confirming the principle.
- 😀 The script introduces an example where magnesium reacts with sulfur to form magnesium sulfide in a closed container, with the mass of magnesium and sulfur before the reaction totaling the mass of magnesium sulfide after the reaction.
- 😀 The mass of sulfur involved in the reaction is calculated through a simple subtraction process: total mass after reaction minus the mass of magnesium used.
- 😀 The mass of sulfur reacting in the example is determined to be 4 grams, following the formula: mass of magnesium sulfide (7 grams) minus mass of magnesium (3 grams).
- 😀 The closed system concept is emphasized, where no mass is lost or gained during the reaction, reinforcing the idea of mass conservation.
- 😀 The reaction between magnesium and sulfur results in magnesium sulfide, highlighting the principle that chemical reactions produce new substances but do not alter the total mass.
- 😀 The principle of mass conservation is applicable to all chemical reactions, whether they involve solids, liquids, or gases, as long as the system remains closed.
- 😀 The script concludes with a reminder of Lavoisier's law, encouraging further exploration of the topic in future lessons.
Q & A
What is the Law of Conservation of Mass?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass, also known as Lavoisier's Law, states that in a closed system, the mass of substances before and after a chemical reaction remains the same. The mass is conserved.
How is the Law of Conservation of Mass demonstrated in the experiment with sulfur and copper powder?
-In the experiment, 10 grams of sulfur and 5 grams of copper powder are reacted in a closed tube. After the reaction, the mass of the new substance, copper sulfide, is found to be 15 grams, which equals the total mass of the reactants, demonstrating the law.
What does the 'closed system' refer to in the context of Lavoisier's Law?
-A 'closed system' refers to a setup where no matter is allowed to escape or enter during the chemical reaction. This ensures that all the mass is accounted for before and after the reaction.
What is the mass of copper sulfide formed in the sulfur and copper powder reaction?
-The mass of copper sulfide formed after the reaction is 15 grams, which is the sum of the 10 grams of sulfur and 5 grams of copper powder.
In the example involving magnesium and sulfur, what is the mass of magnesium used?
-The mass of magnesium used in the example is 3 grams.
What is the final product in the magnesium and sulfur reaction?
-The final product of the reaction between magnesium and sulfur is magnesium sulfide.
What is the mass of the magnesium sulfide formed in the magnesium and sulfur reaction?
-The mass of the magnesium sulfide formed in the reaction is 7 grams.
How do we calculate the mass of sulfur used in the reaction with magnesium?
-To calculate the mass of sulfur, we subtract the mass of magnesium (3 grams) from the total mass of the product (7 grams). Therefore, the mass of sulfur used is 4 grams.
What type of system is described in the magnesium and sulfur reaction?
-The magnesium and sulfur reaction is described as occurring in a closed system, meaning no mass is lost or gained during the reaction.
Why is the Law of Conservation of Mass important in chemical reactions?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass is crucial because it ensures that matter is neither created nor destroyed during chemical reactions. This principle helps predict the outcomes of reactions and ensures the mass balance in chemical equations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

tugas kimia praktik hukum kekekalan massa/hukum lavoisier

KIMIA | Praktikum Hukum Lavoisier
Law of Conservation of Mass - Fundamental Chemical Laws, Chemistry
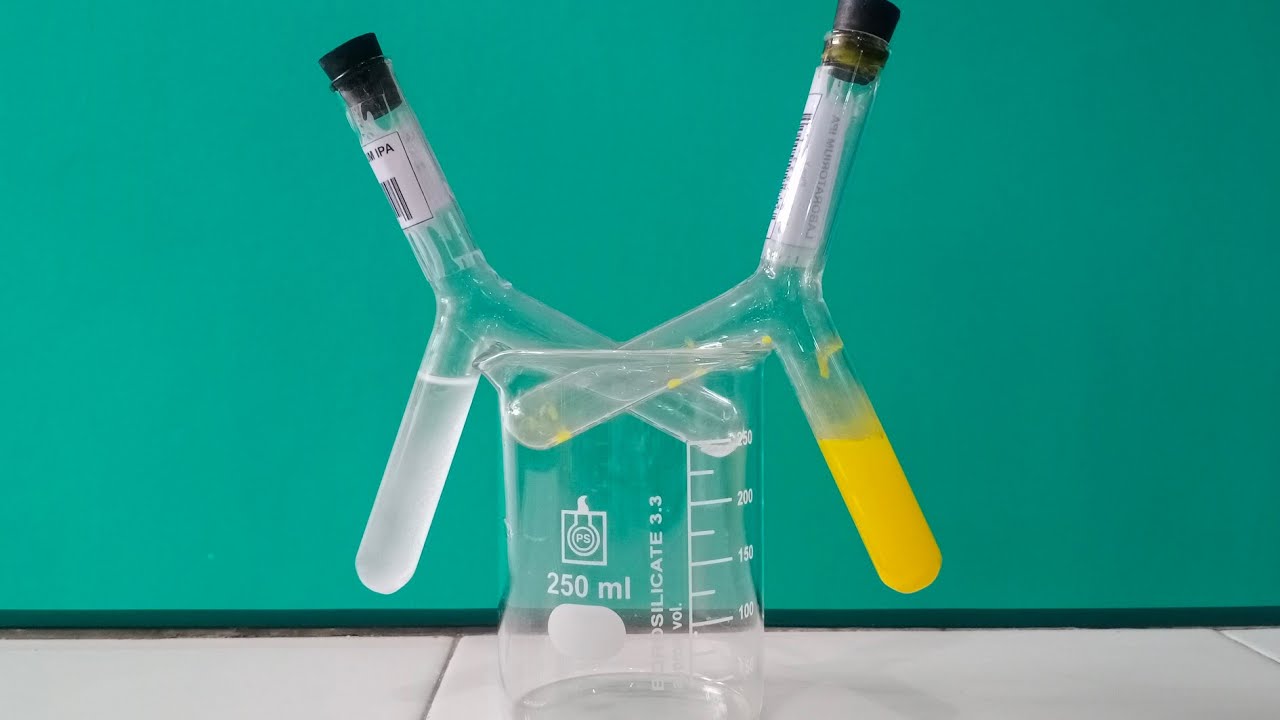

Praktikum Hukum Lavoisier ( Kekekalan Massa ) Hukum Dasar Kimia Kelas X

Praktikum Hukum Kekekalan Massa_Pembakaran Pita Magnesium @dewikimia9013

Hukum Lavoisier (Hukum Kekekalan Massa) | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)