Money’s Mostly Digital, So Why Is Moving It So Hard?
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the evolution of money through a fruit trade analogy, explaining how trade led to the creation of credits and the fractional-reserve banking system. It delves into the complexities of money creation, the role of central banks, and the abstraction and standardization that have allowed money to move more freely. The narrative also touches on the history of banking, the development of checks and the Federal Reserve, the rise of electronic payments, and the international financial system with SWIFT. It concludes with the emergence of fintech startups like Wise, which offer simpler and cheaper alternatives to traditional money transfers, emphasizing the importance of trust and accuracy in the digital financial system.
Takeaways
- 🍎 The concept of trade can lead to mutual benefits, as seen in the initial example of trading an apple for an orange.
- 🌳 The introduction of trade with a time delay, like trading apples now for oranges later, requires trust and promises.
- 🔄 The complexity of trade can increase with more participants and different goods, necessitating a more sophisticated system.
- 🏺 The idea of fruit credits or clay balls symbolizes an early form of currency, representing value without being a physical good.
- 🥬 The expansion of the trading system to include vegetables and other goods shows the adaptability and inclusivity of trade systems.
- 📈 The recognition of theoretical value turning into real value through representation, like clay balls, is a precursor to modern financial instruments.
- 🏦 The creation of financial institutions to safeguard and even pay interest on fruit credits is analogous to modern banking practices.
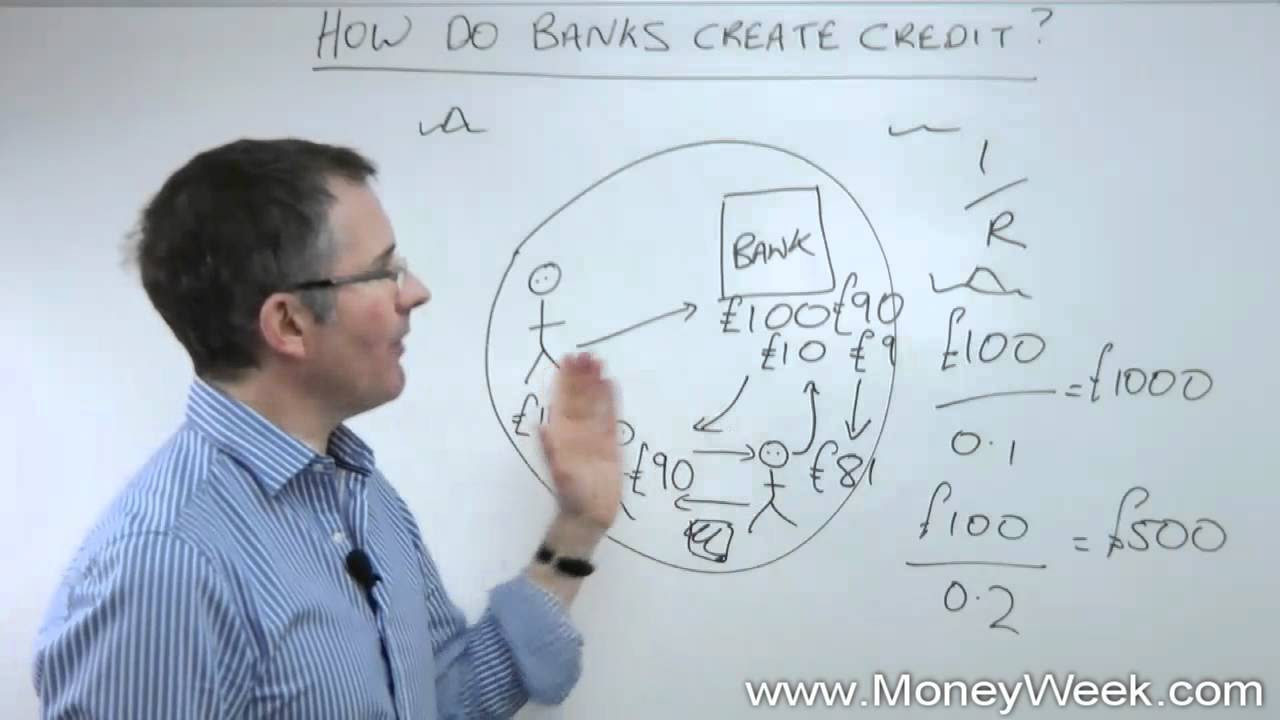
- 💹 The fractional-reserve banking system is explained through the example of loans creating new money, illustrating the concept of money multiplication.
- 🔄 The movement of money is shown to create value, with the example of a watermelon farmer using credits to expand her business.
- 🌐 The evolution of money from physical currency to abstract forms like checks and digital transfers has made it easier to move and trade.
- 🔐 The importance of security and trust in financial systems is highlighted, as without them, the entire monetary system could collapse.
Q & A
How does the concept of trading apples and oranges illustrate the basic principle of trade?
-The script uses the example of trading apples and oranges to demonstrate that trade can lead to mutual benefits, where each party ends up happier by exchanging goods they have for goods they want.
What is the significance of introducing a third person in the trade scenario involving apples, oranges, and pears?
-Introducing a third person with pears adds complexity to the trade, showing how indirect exchange can facilitate trades that might not be possible in a direct two-party exchange, ultimately leading to a more efficient distribution of goods.
How does the introduction of fruit credits simplify the trading system described in the script?
-Fruit credits, represented by clay balls with a generic fruit symbol, simplify the trading system by providing a standardized medium of exchange that eliminates the need to match specific goods for trade, thus reducing the complexity of direct barter.
What role do fruit credits play in the evolution of the trading system described in the script?
-Fruit credits act as a form of currency within the trading system, representing a theoretical value that can be exchanged for physical goods. They evolve from a simple representation of goods to a form of value that can be stored, lent, and used to facilitate trade.
How does the script explain the concept of money creation through the lending process of banks?
-The script explains that money is created when banks lend out deposits, as the original depositors still have access to their funds while the borrower also has new money to use, effectively increasing the total money supply within the system.
What is the fractional-reserve banking system mentioned in the script, and how does it relate to money creation?
-The fractional-reserve banking system is a practice where banks only keep a fraction of their deposits as reserves and lend out the rest. This system allows banks to create new money through lending, as the loans become new deposits that can be used within the economy.
How does the script use the example of a watermelon farmer to explain the role of banks in money creation?
-The script uses the watermelon farmer's need for additional credits to purchase an irrigation system as an example of how banks can create money by lending credits to borrowers, which then circulate within the economy and contribute to the overall money supply.
What is the significance of abstraction and standardization in the evolution of money and financial systems as described in the script?
-Abstraction allows for the representation of value without the need for physical goods, while standardization enables the easy transfer and acceptance of different forms of money across various regions and institutions. Both are crucial for the development of efficient financial systems.
How does the script describe the evolution of money transfer methods from paper checks to electronic systems?
-The script outlines the progression from paper checks, which were manually processed and prone to errors, to electronic systems like the ACH Network and SWIFT, which provide standardized, secure, and efficient methods for moving money both domestically and internationally.
What is the role of SWIFT in international money transfers as explained in the script?
-SWIFT provides a standardized messaging format and secure network for banks to communicate payment orders, facilitating international money transfers without the need to physically move funds between countries.
How does the script address the challenges and costs associated with international money transfers?
-The script discusses the high fees and complexities of international money transfers, citing the example of Wise, a fintech startup that offers a simpler and less costly alternative by bypassing traditional intermediaries.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)