O que é a energia cinética e a energia potencial? | 10F1.1 | Aula 1
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the principles of kinetic and potential energy, emphasizing the law of conservation of energy. It explains that energy can be transferred between objects but not created or destroyed. The script uses the example of a washing machine to illustrate energy transformation and dissipation. It further breaks down the fundamental types of energy, including gravitational potential energy, and introduces the concept of internal energy as the sum of kinetic and potential energy at a microscopic level, which is related to temperature and particle motion. The script concludes with a practical exercise to calculate the kinetic energy of a car and the effects of changing its velocity and mass.
Takeaways
- 🔄 The law of conservation of energy states that energy can be transferred between objects but cannot be created or destroyed.
- 🛠 In the context of a washing machine, energy is provided, transformed into different forms, and some is always dissipated as noise, vibration, or heat, but it is not lost.
- 🏋️ Energy exists in two fundamental forms: kinetic energy, associated with motion, and potential energy, associated with the potential to change motion through interactions.
- ⚡ Kinetic energy is calculated as one-half the mass times the velocity squared, with mass in kilograms and velocity in meters per second.
- 🌐 Potential energy is stored energy and depends on the interactions between systems, such as gravitational, electrical, magnetic, elastic, chemical, and nuclear potential energy.
- 📚 The formula for gravitational potential energy is mass times gravitational acceleration times height.
- 🌡 Internal energy of a system is the sum of kinetic and potential energy at the microscopic level, related to the motion and interactions of particles within the system.
- 🌡️ The internal kinetic energy is associated with temperature, where higher temperatures result in greater particle motion.
- 🔗 The internal potential energy depends on the number of particles and the chemical bonds between them, with more particles leading to higher potential energy.
- 🚗 An exercise in the script calculates the kinetic energy of a 1000 kg car moving at 90 km/h, converting the speed to meters per second and applying the kinetic energy formula.
- 🔢 If the velocity of an object doubles, the kinetic energy increases by a factor of four, not two, highlighting the importance of understanding the relationship between velocity and kinetic energy in safety contexts.
Q & A
What is the principle of energy conservation discussed in the script?
-The principle of energy conservation states that energy can be transferred between objects but cannot be created or destroyed. In any process, the total amount of energy remains constant.
What happens to the energy that is not utilized in the washing machine example provided in the script?
-The energy that is not utilized in the washing machine is not destroyed but transformed into other forms such as noise, vibration, or heat, which is not useful for the machine's operation.
What are the two fundamental types of energy mentioned in the script?
-The two fundamental types of energy mentioned are kinetic energy, which is associated with motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy that has the potential to be used.
How is kinetic energy defined and calculated?
-Kinetic energy is defined as the energy associated with the motion of an object. It is calculated using the formula \( \frac{1}{2} \times \text{mass} \times \text{velocity}^2 \), where mass is in kilograms and velocity is in meters per second.
What is gravitational potential energy and how is it calculated?
-Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored due to an object's position in a gravitational field. It is calculated using the formula \( \text{mass} \times \text{gravitational acceleration} \times \text{height} \) above a reference point.
What is internal energy and how is it related to the microscopic motion of particles?
-Internal energy is the total energy contained within a system, which includes both the kinetic and potential energy of the particles at the microscopic level. It is associated with the random motion (agitation) of particles, which is a reflection of the system's temperature.
How does the temperature of a system affect its internal kinetic energy?
-The temperature of a system is directly related to the internal kinetic energy. As the temperature increases, the particles move more vigorously, resulting in greater internal kinetic energy.
What is the relationship between the velocity of an object and its kinetic energy?
-The kinetic energy of an object is directly proportional to the square of its velocity. If the velocity doubles, the kinetic energy increases by a factor of four, not just two.
What is the challenge presented in the script regarding the car's kinetic energy?
-The challenge is to determine the effect on the car's kinetic energy if the car's mass is reduced to one-third of its original mass, and to understand how the kinetic energy changes with different mass and velocity conditions.
How does the script suggest using the concept of kinetic energy to understand the potential dangers of a car's speed?
-The script illustrates that if a car's speed doubles, its kinetic energy quadruples, which can be much more dangerous for the occupants due to the increased energy involved in a collision.
What additional resources does the script mention for further study and discussion?
-The script mentions a Discord server as an additional resource for further study and discussion, where students can ask questions and engage with the community for better understanding.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Energi dan Perubahannya - X OTKP SMKS Hang Tuah I Jakarta
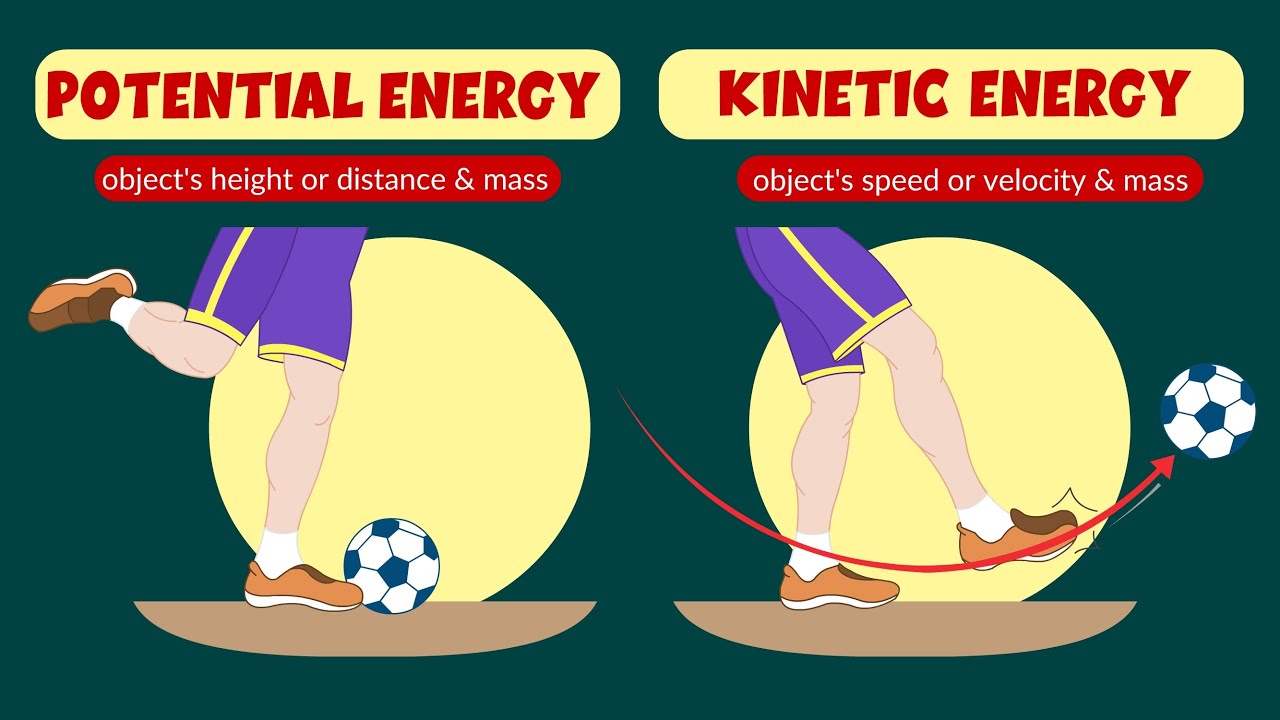
Potential and kinetic energy - Law of conservation of energy - Video for kids

Work Power and Energy by Science Matters for Grade 8 Science
Types of Energy | Energy Forms | Energy Sources and Uses

ENG 201 Lecture 4.1.1

De onde vem a Lei da Conservação da Energia na FÍSICA?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
