CCNA 200-301 en Français - Leçon 11 : Revue des notions Ethernet LAN
Summary
TLDRThis video covers the fundamentals of local area networks (LAN), focusing on equipment like switches and hubs, their roles in data transmission, and differences between full-duplex and half-duplex communication. It explains how data is transmitted through various types of cables at different speeds, with a focus on the role of switches in full-duplex transmission and how hubs operate on half-duplex. The video also discusses collision detection, the significance of MAC addresses, and the difference in data transmission logic between modern switches and older hubs. A key takeaway is the importance of understanding these foundational network concepts.
Takeaways
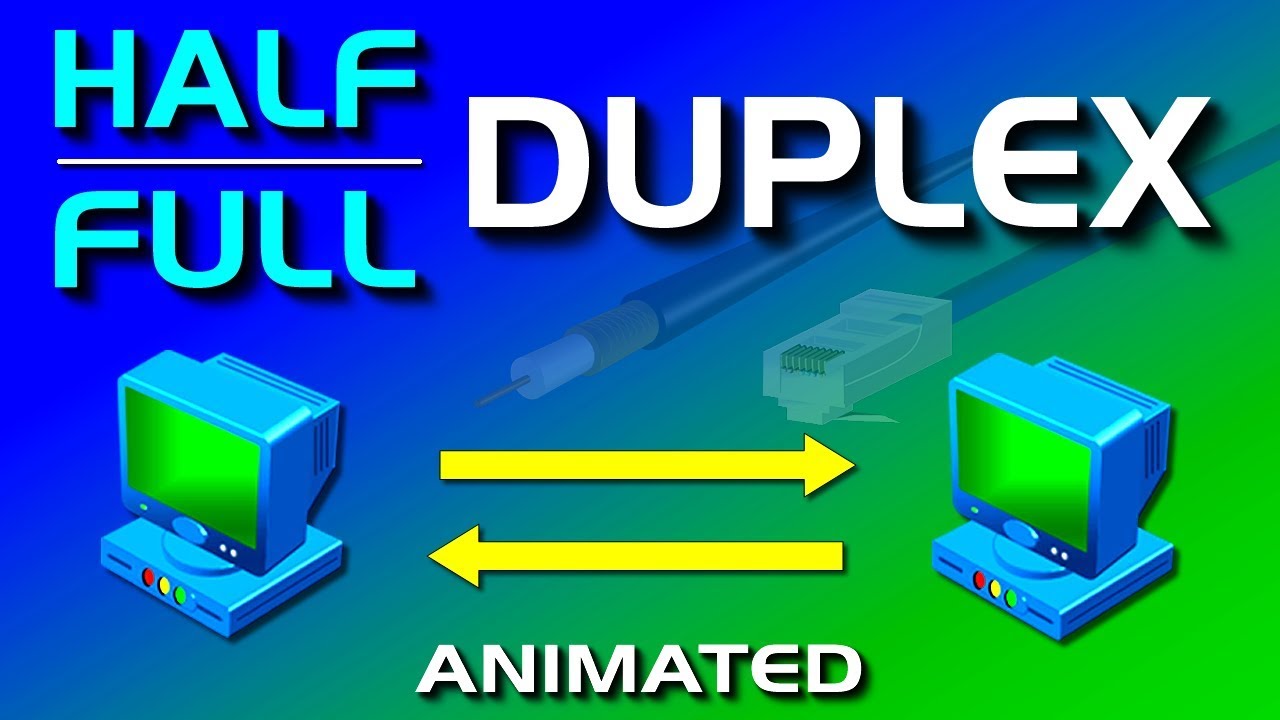
- 😀 A switch operates in full-duplex mode, allowing data to be transmitted and received simultaneously, which makes it more efficient than a hub.
- 😀 A hub operates in half-duplex mode, meaning it can either transmit or receive data at a time, which can lead to delays and collisions.
- 😀 Full-duplex transmission is faster and more reliable, with switches supporting this mode for various connection speeds (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps).
- 😀 Cables used in full-duplex transmission include different types like Cat5e (10 Mbps), Cat6 (100 Mbps), and Cat6a (1 Gbps), each with different data rate capabilities.
- 😀 A hub simply repeats the electrical signal across all ports and does not manage traffic intelligently based on MAC addresses, making it more prone to collisions.
- 😀 A switch, on the other hand, uses MAC addresses to intelligently forward data to the correct port, reducing the likelihood of collisions.
- 😀 The key difference between hubs and switches is that hubs work at the physical layer (Layer 1), while switches operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
- 😀 The process of data transmission in a LAN typically involves a PC generating a frame, which is sent with its MAC address to a switch, which then forwards it to the correct destination PC.
- 😀 Collision detection mechanisms such as CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) are important in half-duplex networks to handle situations where multiple devices try to transmit at the same time.
- 😀 Full-duplex networks, like those using switches, eliminate collisions by allowing each device to transmit and receive independently, avoiding the need for collision handling mechanisms.
Q & A
What are the two types of equipment used to transmit data in a local area network (LAN)?
-The two types of equipment used to transmit data in a LAN are switches (commutateurs) and PBXs (Private Branch Exchanges).
How does a switch function in a LAN?
-A switch functions in a LAN by transmitting data in full duplex mode, meaning it can send and receive data simultaneously, making the process faster and more efficient.
What is the difference between full duplex and half duplex transmission?
-Full duplex transmission allows data to be sent and received simultaneously, while half duplex transmission only allows data to be sent in one direction at a time, requiring the equipment to wait before transmitting.
What is the significance of MAC addresses in network equipment?
-MAC addresses are used to identify devices within a network. Switches use MAC addresses to decide how to forward data packets, whereas basic network hubs do not have this capability, leading to shared media and potential collisions.
Why is full duplex transmission faster than half duplex?
-Full duplex transmission is faster because data can be transmitted and received simultaneously, reducing the need for waiting periods as seen in half duplex systems where one device must wait for the other to stop transmitting before it can send its data.
What role do cables play in LAN data transmission?
-Cables in a LAN, such as Cat 5, Cat 5e, and Cat 6 cables, transmit data at specific speeds (e.g., 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1 Gbps). Each cable type supports full duplex transmission, ensuring that data can flow in both directions at once.
How does a hub function differently from a switch in a LAN?
-A hub operates at the physical layer (Layer 1) and transmits data to all connected devices without using MAC addresses, leading to a shared medium and potential collisions. A switch, on the other hand, operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) and forwards data to specific devices based on their MAC addresses, reducing collisions and improving network efficiency.
What is the concept of a 'shared media' network, and how does it affect data transmission?
-In a shared media network, like one using a hub, all devices share the same bandwidth. This can lead to collisions if multiple devices try to transmit data simultaneously. In contrast, networks using switches have point-to-point connections, allowing independent data transmission without collisions.
How does the CSMA/CD protocol help prevent collisions in a half duplex network?
-The CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) protocol helps prevent collisions by having devices listen to the network before transmitting. If the network is busy, the device waits and then retransmits after a random backoff period if a collision is detected.
What happens when a collision occurs in a half duplex network, and how is it handled?
-When a collision occurs in a half duplex network, the transmitting device stops, sends a jamming signal to inform all devices of the collision, and waits for a random backoff period before retransmitting the data.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Half Duplex vs Full Duplex

Introduction to Ethernet - CompTIA Network+ N10-007 - 1.3
CCNA 200-301 en Français - Leçon 11 : Revue des notions Ethernet LAN Switch / Hub

18. CAMBRIDGE IGCSE (0478-0984) 2.1 Data transmission methods

CCNA 200-301 en Français - Leçon 12 : LAB - Transmission des DATA dans un réseau local

Broadcast Domains and Collision Domains - CompTIA Network+ N10-007 - 1.3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
