Me Salva! CIN25 - Lançamento Oblíquo
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of the oblique throw is explored, focusing on the trajectory and velocity components. The object follows a parabolic path due to gravity, and the movement is divided into horizontal and vertical components. The horizontal motion remains constant, while the vertical motion is influenced by gravity. Key takeaways include the importance of the launch angle in determining the range and height, with the optimal angle being 45º. The video also explains how to calculate the horizontal and vertical components of velocity using basic trigonometry, setting the stage for further examples in later lessons.
Takeaways
- 😀 The oblique throw is a movement where an object is thrown diagonally, creating a parabolic trajectory due to gravity.
- 😀 The key concept in understanding the oblique throw is separating the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity.
- 😀 The horizontal component of velocity (X-velocity) remains constant, while the vertical component (Y-velocity) changes due to gravity.
- 😀 In an oblique throw, the object moves both upwards and horizontally at the same time, with gravity affecting the vertical speed.
- 😀 The time taken for the object to go up and down is the same as the time it spends moving horizontally.
- 😀 The horizontal motion follows a Uniform Rectilinear Motion (MRU), with constant velocity, while the vertical motion follows a Uniformly Accelerated Motion (MRV), with acceleration due to gravity.
- 😀 The influence of the angle of projection (θ) is crucial in determining the object's range and height.
- 😀 A steeper launch angle (e.g., 60º) results in more vertical speed and a slower horizontal speed, causing the object to travel higher and stay in the air longer.
- 😀 A launch angle of 45º gives the maximum range, as it balances both the horizontal distance and time in the air.
- 😀 To calculate the components of the velocity (horizontal and vertical), multiply the diagonal speed by the cosine (for horizontal) and sine (for vertical) of the launch angle.
Q & A
What is the basic concept of an oblique throw?
-An oblique throw refers to throwing an object diagonally, where gravity pulls the object down, resulting in a parabolic trajectory.
Why does the object follow a parabolic trajectory in an oblique throw?
-The object follows a parabolic trajectory because, in addition to its horizontal motion, gravity continuously pulls it down, causing the vertical speed to change over time.
What is the key to understanding projectile motion in an oblique throw?
-The key is to separate the horizontal and vertical components of the object's velocity and analyze each one independently.
What are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity in an oblique throw?
-The horizontal component (X-velocity) represents the forward motion, which remains constant, while the vertical component (Y-velocity) is influenced by gravity, changing as the object moves upward and downward.
How does gravity affect the vertical component of the object's motion?
-Gravity slows down the object as it rises, causing the vertical speed to decrease until it reaches zero at the highest point, then accelerates the object downward, increasing its vertical speed.
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical motion in an oblique throw?
-Horizontal motion (MRU - Uniform Rectilinear Motion) remains constant since no external force affects it, while vertical motion (MRV - Uniformly Varied Motion) is subject to constant acceleration due to gravity.
What does the time spent in the air for an oblique throw depend on?
-The time spent in the air depends on the vertical motion, as the time it takes to go up and come down is the same time it takes for the object to move horizontally.
How does the angle of projection affect the distance an object travels in an oblique throw?
-The angle of projection influences both the vertical and horizontal components of velocity. A steeper angle increases the vertical component but reduces the horizontal distance traveled, while a smaller angle results in a greater horizontal distance. The optimal range occurs at a 45-degree angle.
Why does an object thrown at a 45-degree angle achieve the maximum range?
-At 45 degrees, the vertical and horizontal components of velocity are balanced, maximizing both the time the object spends in the air and its forward motion, leading to the maximum horizontal distance.
How can you calculate the horizontal and vertical components of the velocity in an oblique throw?
-The horizontal component is found by multiplying the initial velocity by the cosine of the angle of projection, while the vertical component is found by multiplying the initial velocity by the sine of the angle.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
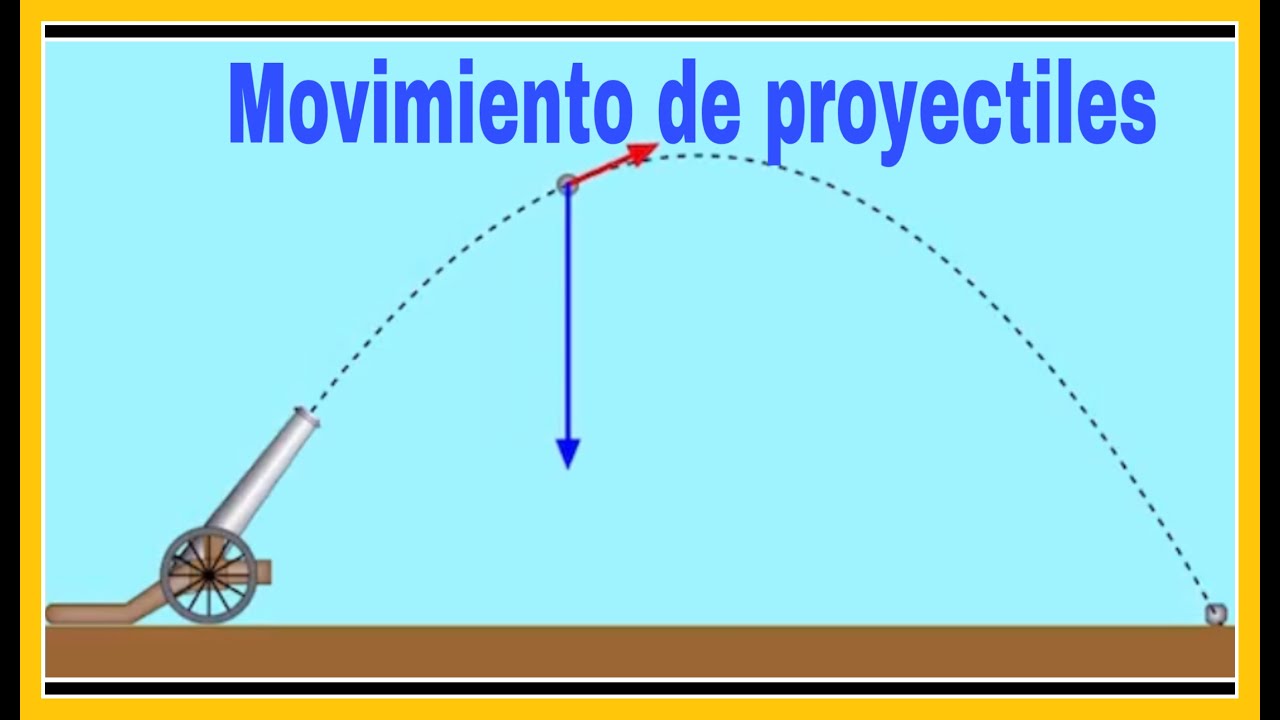
FISICA (CLASE 46) - MOVIMIENTO parabólico O MOVIMIENTO de proyectiles - MOVIMIENTO EN EL PLANO
The Maths of General Relativity (2/8) - Spacetime velocity

Waagerechter Wurf | Wurfzeit und Wurfweite

Hukum bernoulli pada tangki bocor
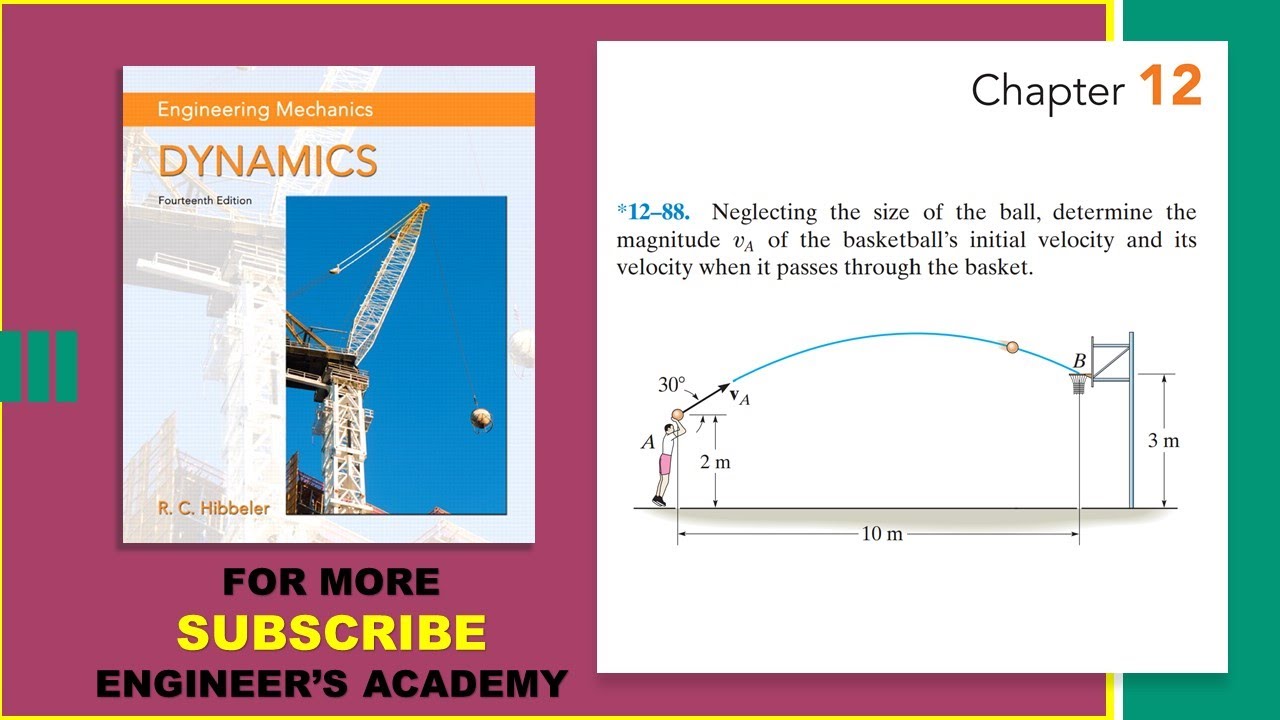
12-88 | Engineering Dynamics Hibbeler 14th Edition | Engineers Academy

Hewitt-Drew-it! PHYSICS 14.Ball Toss
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
