Lecture 2 — The Power of Prototyping | HCI | Stanford University
Summary
TLDRThis video emphasizes the crucial role of prototyping in effective design, highlighting it as a strategy for quickly obtaining feedback and refining ideas. Prototypes act as tangible representations of design concepts, facilitating communication among stakeholders and allowing for exploration and learning. By experimenting with incomplete prototypes, designers can uncover insights, adjust their approach, and enhance user experiences. The video illustrates this with examples from the design of digital cameras and personal digital assistants, demonstrating how prototyping fosters innovation by enabling teams to explore a wide range of possibilities early in the design process.
Takeaways
- 😀 Prototyping is a crucial strategy for effective design, allowing for quick feedback and learning.
- 💡 Prototypes serve as a communication tool, helping designers articulate their ideas and hypotheses to stakeholders.
- 🔍 The goal of prototyping is to gain insights and feedback rather than to produce a polished final product.
- 📏 Prototypes are often incomplete and should be easy to modify as the design process evolves.
- 🖥️ The Kodak DC210 example illustrates how prototypes can focus on user interface design rather than the final product's functionality.
- 🔨 Jeff Hawkins' wooden block prototype for the Palm Pilot highlights the importance of testing form factors in early design stages.
- ✈️ Large-scale prototyping, like the Boeing cross-country airplane mock-up, can provide valuable insights into user experience before actual implementation.
- 🔄 An effective design process involves alternating between broad exploration of ideas and focused refinement.
- 📊 The cost of making design changes increases over time, emphasizing the need to address significant issues early in the process.
- ❓ Prototypes should be viewed as questions that lead to exploration and creativity in design, encouraging designers to ask many questions.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of prototyping in design?
-The primary purpose of prototyping is to rapidly create approximations of design ideas to gather feedback and learn, facilitating effective design through exploration and iteration.
How does prototyping facilitate communication among stakeholders?
-Prototypes serve as common ground for stakeholders, including clients, design team members, and users, helping them understand design concepts more concretely and enabling reflective conversations about the design.
What does the term 'incomplete' mean in the context of prototypes?
-In the context of prototypes, 'incomplete' refers to the idea that prototypes are not final products but rather tools that are intentionally designed to explore ideas and gather feedback, allowing for easier adjustments and refinements.
What are known unknowns and unknown unknowns in design, and how does prototyping help with them?
-Known unknowns are uncertainties that designers are aware of but need to explore further, while unknown unknowns are uncertainties that designers haven't even considered. Prototyping helps uncover both types of uncertainties by allowing for experimentation and feedback.
Can you give an example of a successful prototyping process from the video?
-The video discusses the Kodak DC210 digital camera as an example, where early prototypes helped refine the user interface and functionality, leading to a more effective final product.
What is the significance of the oscillation between broad exploration and focused refinement in design?
-This oscillation is significant because it allows designers to initially explore a wide range of possibilities before narrowing down to specific solutions, ensuring that the final design is well-informed and user-centered.
How does the cost of change vary throughout the design process?
-The cost of making changes rises significantly over time in the design process, especially as a product approaches finalization and release, making early prototyping critical for effective design.
What is the relationship between prototyping and user experience?
-Prototyping directly influences user experience by allowing designers to test and refine interactions, ensuring that the final product meets user needs and expectations based on real feedback.
Why is it important to ask questions during the prototyping process?
-Asking questions during the prototyping process is important because it helps designers explore different ideas and options, leading to better insights and ultimately a more effective design solution.
What lessons can be learned from the prototyping strategies used by Apple in their retail store design?
-The lesson learned from Apple's prototyping strategy is that testing different store configurations and customer interactions before opening helped refine the layout, resulting in a retail experience centered around activities rather than individual products.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
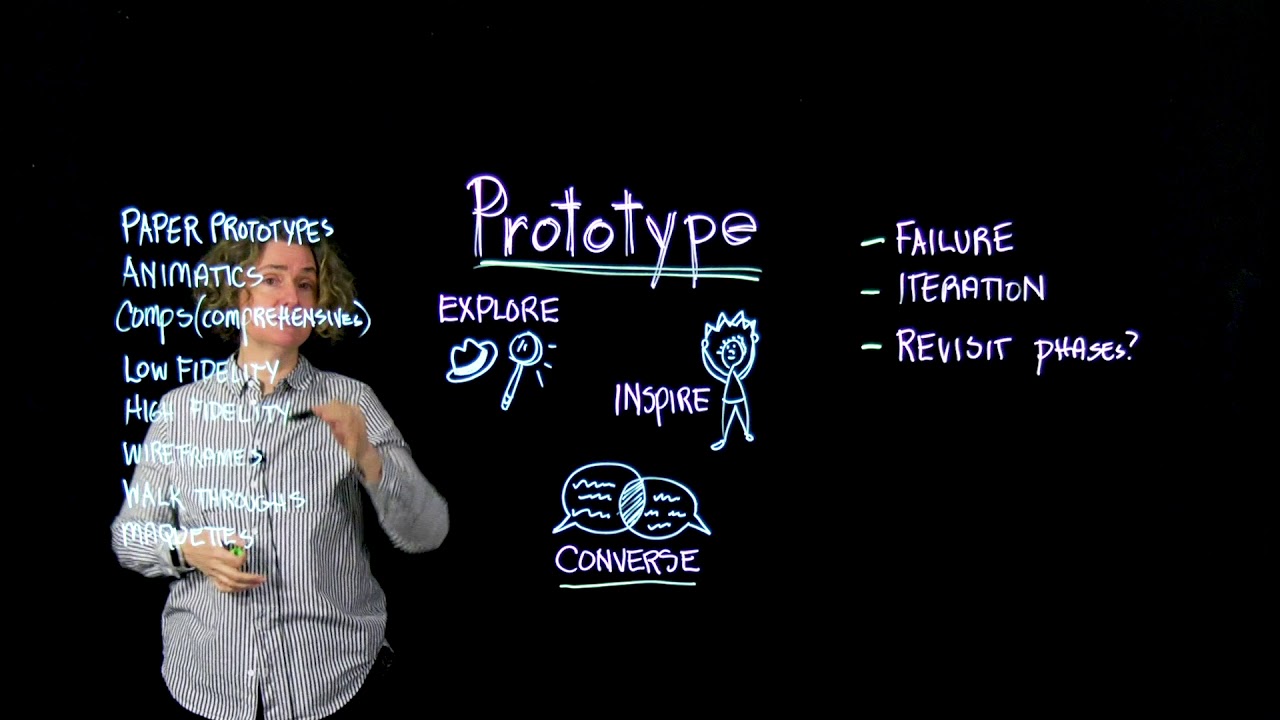
4. Design Thinking: Prototype

PKK SMK Kelas XI Bab Pembuatan Prototype - Materi Prototype

Design Thinking - Paper Prototypes
Lecture 08 Part 1 Low Fidelity Prototyping

Bahan Ajar | Kewirausahaan XI | Konsep Desain Prototype Produk Barang dan Jasa

Lima Tahapan Design Thinking | CIAS QuickFix with Dr. Indrawan Nugroho
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
