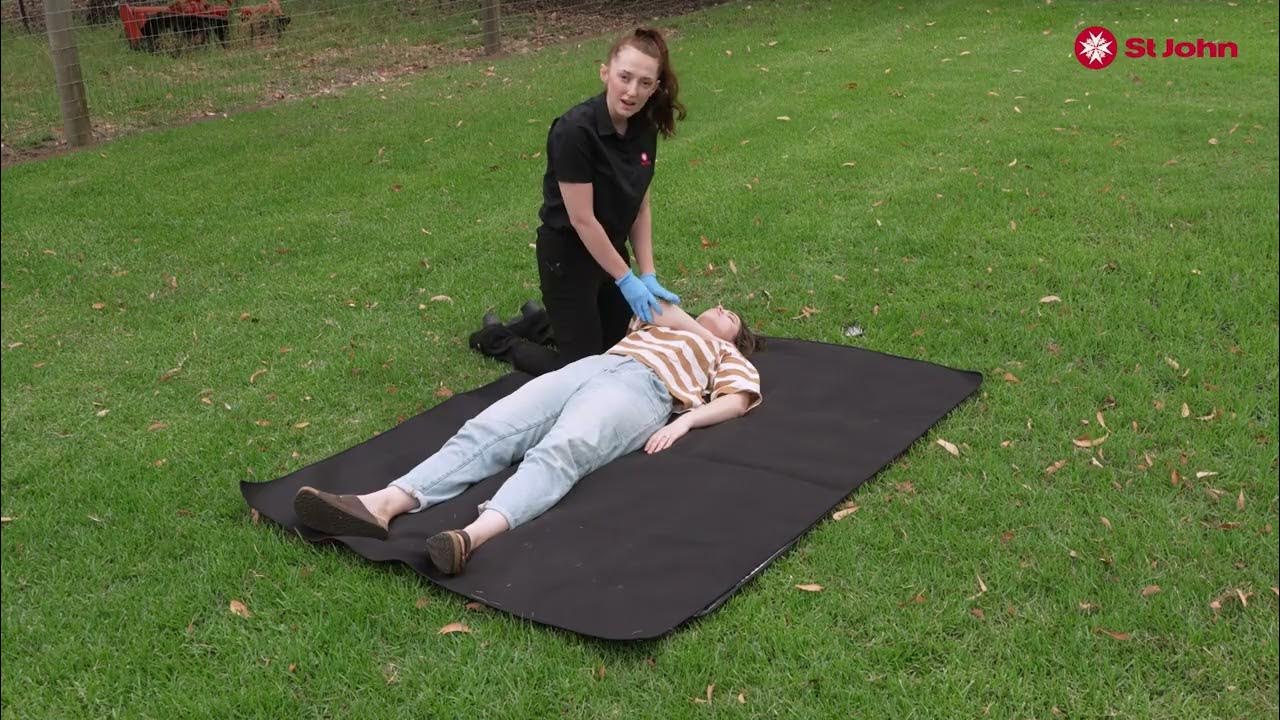
XABCDE no trauma: APRENDA NA PRÁTICA!
Summary
TLDRThis script outlines a step-by-step emergency response process for trauma care, detailing the assessment and management of patients with potential hemorrhages, fractures, and neurological injuries. It covers the key stages of patient evaluation, from securing the cervical spine and airway management to checking vital signs, including circulation, breathing, and neurological responses. The script emphasizes the importance of using tools like tourniquets and oxygen administration, ensuring appropriate trauma care until the patient is stabilized and safely transported. This is a comprehensive guide for first responders in critical situations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Start by visually assessing for hemorrhage, checking for severe bleeding, and applying pressure with bandages, a pressure dressing, or a tourniquet if necessary.
- 😀 Always communicate with the victim, assessing their responsiveness, consciousness, and if they recall the event. Inform them about the help they’re receiving.
- 😀 For cervical spine control, ensure proper alignment of the neck, checking for airway obstructions, and use a cervical collar for stabilization.
- 😀 Apply oxygen to trauma victims: 10 liters for light trauma and 15 liters for severe trauma, using a reservoir mask.
- 😀 Conduct a thorough search of the victim’s breathing and respiratory system (chest expansion, symmetry, and lung filling) by dividing the chest into quadrants for a visual and tactile check.
- 😀 Assess the circulatory system (C): Check skin condition, pulse, perfusion, and abdominal rigidity or tenderness. A lack of perfusion or abdominal pain signals shock.
- 😀 For the neurological state (D), evaluate consciousness, pupil response, and motor responses. Ensure they can move their limbs and respond to verbal commands.
- 😀 For exposure (E), be cautious about exposing intimate areas, only doing so if necessary for proper assessment. Fractures should be immobilized immediately.
- 😀 Always stabilize the cervical spine until the victim is safely secured on a stretcher or other immobilizing equipment.
- 😀 In the vehicle, re-assess the victim frequently, ensuring all necessary treatments and adjustments are made, including fluid infusions and further monitoring of vital signs.
Q & A
What is the first step when approaching a victim in a trauma situation?
-The first step is to perform a visual search for any major bleeding, particularly focusing on arterial bleeding. This is part of the 'X' in the ABCDE protocol.
What methods can be used to control hemorrhaging in a victim's leg?
-Several methods can be used, including filling the wound with a dressing, applying pressure with a Zobeg, using a compressive dressing, or applying a tourniquet with a triangular bandage or a tactical tourniquet.
When should a cervical collar be applied to the victim?
-A cervical collar should be applied after confirming that the victim is responsive and after ensuring no obvious airway obstruction. It helps stabilize the cervical spine during transport.
How much oxygen should be administered to a trauma victim?
-For a mild trauma victim, oxygen should be administered at 10 liters per minute. For a severe trauma victim, it should be administered at 15 liters per minute using a reservoir mask.
What is the purpose of the 'B' step in the trauma assessment?
-The 'B' step involves evaluating the victim's breathing by performing a visual and tactile search for proper lung expansion and symmetry, and checking for signs of distress, such as noisy or labored breathing.
What does the 'C' step in the trauma assessment focus on?
-The 'C' step focuses on assessing circulation by checking the victim's pulse, skin color, perfusion, and inspecting the abdomen and pelvic region for signs of injury, such as tenderness or rigidity.
How is neurological status evaluated during the 'D' step?
-Neurological status is assessed using the Glasgow Coma Scale, checking for responsiveness in terms of verbal, motor, and eye responses. Motor responses are tested by asking the victim to move limbs and press hands.
What is the purpose of the 'E' step in trauma care?
-The 'E' step involves exposing the injured areas while maintaining the victim's dignity, checking for fractures, and immobilizing any injured limbs. The goal is to stabilize the victim for transport while avoiding further injury.
What should be done if the victim shows signs of shock?
-If the victim shows signs of shock, such as pale, cool, and clammy skin, or has a pulse rate above 120, it is crucial to quickly address the issue by controlling bleeding, providing oxygen, and preparing for immediate transport to a medical facility.
What is the secondary survey, and when should it be done?
-The secondary survey is a more detailed assessment performed once the victim is stabilized and transported to the ambulance. It includes reevaluating all systems to check for any missed injuries or complications, and it is repeated regularly during transport.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)